Making economic decisions(财务报表的目的) ⭐️
谁会用到财务报表?
- 投资者
- 政府部门
- 债权人
- 管理层
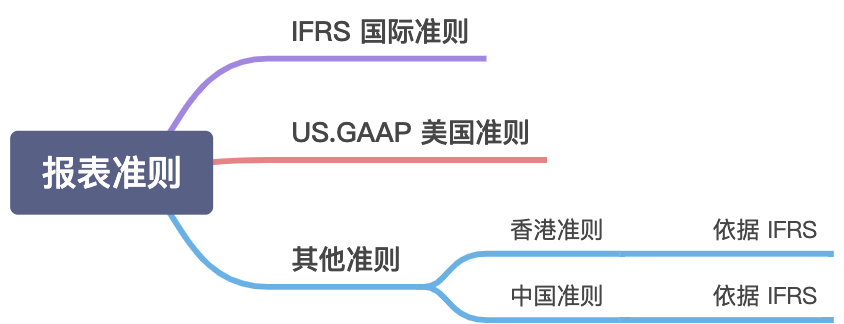
财务报表的准则 ⭐️
+ IFRS (国际准则)
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) 制定
国际会计准则委员会(International Accounting Standards Board ,简称IASB)。 IASB的前身是国际会计准则委员会(International Accounting Standards committee,简称IASC),在2000年进行全面重组并于2001年初改为国际会计准则理事会。
+ US.GAAP (美国通用会计准则)
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) 制定
Financial Accounting Standards Board 财务会计准则委员会(美国)
百度百科:https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E8%B4%A2%E5%8A%A1%E4%BC%9A%E8%AE%A1%E5%87%86%E5%88%99%E5%A7%94%E5%91%98%E4%BC%9A
IFRS VS US.GAAP 的区别?
三大报表的钩稽关系
- 利润表里的Net income 是对 B/S表里的 R/E 留存收益的解释说明;
- 现金流量表里的 Net cash 是对 B/S表里的 Cash的补充说明;
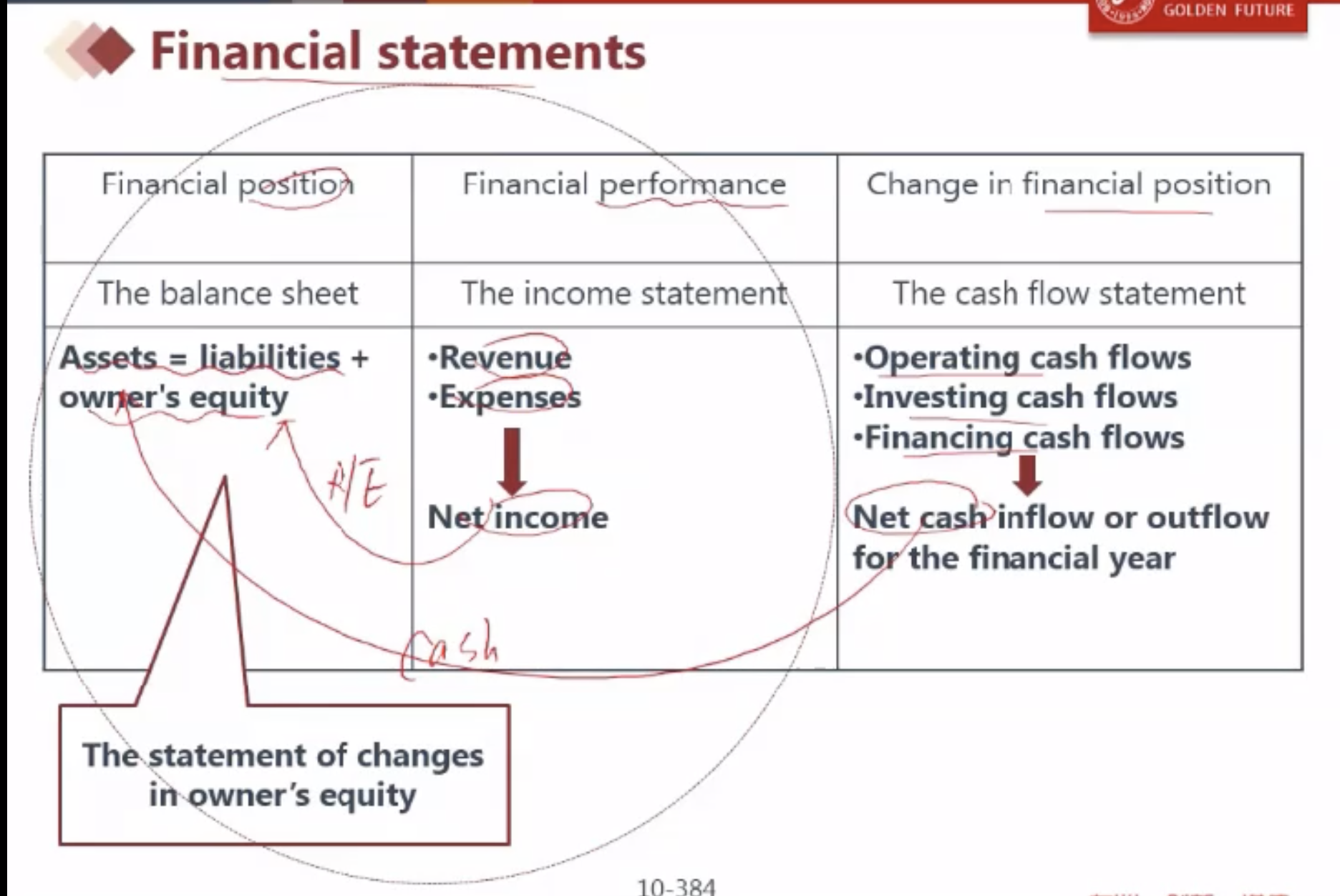
1) Balance sheet 资产负债表
reports the firm’s financial position at a point in time**?**
+ Assets 资产
+ Liabilities 负债
+ Owner’s equity 所有者权益(有2个别称)
也可叫做: residual interest 剩余价值 / net assets 净资产
为什么可以叫做 Net assets 净资产?⭐️
为什么可以叫做 residual interest 剩余价值? ⭐️
公司的收入,先给员工,给供应商,给债权人,给政府交税,最后才给股东,所以叫剩余价值。
2) Income statement 利润表
Revenues 主营业务收入
Expenses 费用
Other income 其他业务收入
3) Cash flow statement 现金流量表
Operating cash flows / CFO ⭐️⭐️
经营活动现金流
- 从customer 收到的cash (流入)
-
Investing cash flows
投资活动现金流
are those resulting from the acquistion or sale of property,plant,and equipment;of a subsidiary or segement;of securities; and of investments in other firms.
买了一个股票/机器/厂房/设备 (流出)站在钱的角度(因为是现金流量表)
-
Finacing cash flows
融资活动现金流
发型5年期债券 (流入)
- 5年到期后,还债券 (流出)
The statement of comprehensive income 综合收益表(接在 NI 表后面)⭐️
CI = NI 净利润在利润表 + OCI 其他综合收益表(在B/S的所有者权益里)
The statement of changes in equity 股东权益变动表 ⭐️
reports the amounts and sources of changes in equity investor’s investment in the firm over a period of time.
如:2018.12.31 -2019.12.31 ,前10大股东,股份变动情况。
公司的股东数(在这张报表里出显示出来)
- 股东数 2018 43281人 (说明:股票更集中)
- 股东数 2019 64381人 (说明:股权分散)
Measurement of finacial elements
- Historical cost 历史成本 ⭐️⭐️
- Amortized cost 摊余成本 (衡量的Financial Asset 是金融资产/无形资产)比如:专利
- Current cost 现在买的价格
- Realizable value 现在卖的价格
- Present value 现值
- Fair value 公允价值 ⭐️⭐️
Net Book Value NBV / Carrying Value CV (针对:实物资产)
账面净值(历史成本 减去 折旧费用)
如:公司花了100W买了一个设备,设备可以用10 years(在B/S 表里面体现)
第一年:历史成本 100 W ,累计折旧A/D 费用10W ,账面净值:90W (会计如何记账呢?)
第二年:历史成本 100 W ,累计折旧A/D 费用20W,账面净值:80W
:::tips 难点,需要认真理解:35min,(视频2.mp4) :::
公允价值(FV) VS 历史成本(HC)
公允价值:当前市场的真实价值。(问题:公允价值的衡量?)
如:5年前买的一个设备是100万,但是现在说是200W(这个公允价值是如何衡量的?不好衡量e)
满足公允价值的条件:
- 买卖双方不能是利益相关方。( Unrelated Party)
- 买卖双方自愿。( Willing)
- 买卖双方知道真实价格(Well informed)(如:一个小孩拿着妈妈的一个钻戒去换别人的一个儿童玩具。)
:::tips Tips:
- 历史成本法占优势!目前正在向公允价值方法转移。
- 历史成本法相对靠谱; :::
Other relevant information ⭐️
Financial statement notes(footnotes) 附注(需要审计的)
disclosed 披露
- Issues disclosed in footnotes
Provide information about accounting methods(会计方法), assumption(会计假设), and estimates used by management(会计估计)
公开账户计算方法。(财报里面的数据是怎么计算出来的。) 固定资产折旧是怎么算的? 会计方法:比如使用的历史成本法还是公允价值法?/ 先进先出法 会计估计/会计假设:比如买了个100万设备,估计了用5年还是10年 公司的法律诉讼/员工养老金
Management’s discussion and analysis (unaudited) MD&A 管理层的评论与分析
disclosed 披露
站在管理层的角度,不需要审计,也没法审计。
Under IFRS
- 对公司过去的表现
Under US GAAP
- sinificant events and uncertainties.(重大不确定性)
- Forward-looking expenditures and divestiures.
考试点
Q:比如在那张表里看公司的重大不确定性?
A: MD&A
Proxy statements 代理投票权说明书 ⭐️
disclosed 披露
- 管理层薪酬 Management compensation;
- 潜在的利益冲突 conflict of interests;
考试点:比如在哪里看管理员薪酬?
A: proxy statements
:::info
Tips:
1、半年报semiannually/季度报 quarterly 是不需要审计的!!!
2、年报需要审计!
:::
Interim reports 中期报告/临时报告(不需要审计)
Earnings announcements 盈利公告
External sources 外部分析
考试题举例 ⭐️