Region(区域)
JavaFX Region 类是所有 JavaFX 布局窗格的父类,如 Pane(窗格)等。JavaFX Region 类具有一组属性和特征,它们被扩展 Region 的所有 JavaFX 布局类共享。
The JavaFX Region class is the base class for all JavaFX layout panes, like Pane etc. The JavaFX Region class has a set of properties and characteristics which are shared by all the JavaFX layout classes which extend Region.
Region 类继承结构
JavaFX Region 类相关的类继承结构如下所示:
The class hierarchy around the JavaFX Region class looks like this:
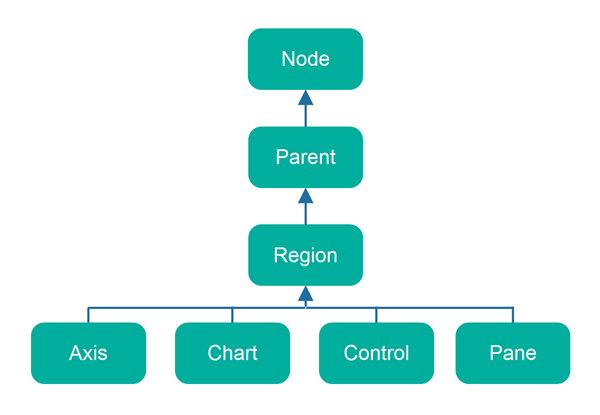
请记住,JavaFX 有许多类是 Axis、Chart、Control 和 Pane 的子类。所有这些也是 Region 的间接子类,并且也将具有与 Region 相同的属性。
Remember, that JavaFX has many classes which are subclasses of Axis, Chart, Control and Pane. All of these are also indirect subclasses of Region, and will also have the same properties as Region.
Region 属性
JavaFX Region 类的子类共享的属性是:
The properties of the JavaFX Region class which are shared by its subclasses are:
- Background(背景)
- Content Area(内容区域)
- Padding(内边距)
- Borders(边框)
- Margin(边距)
- Region Insets
这些概念在此处进行了说明:
These concepts are illustrated here:
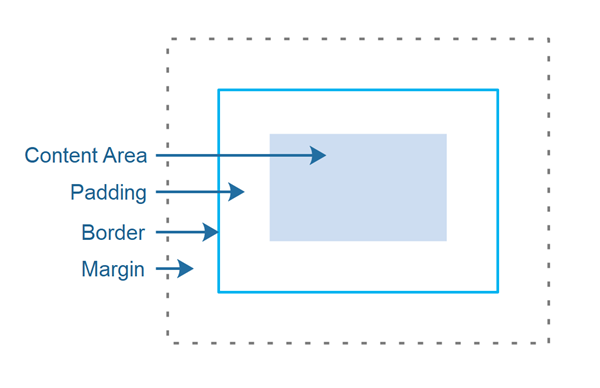
内容区域是布局容器将在其中绘制其子项的位置。
The content area is where the layout container will draw its children within.
内边距是内容区域和边框之间的空间。
The padding is the space between the content area and the border.
边框是一条线(或类似线),可以显示在内容区域和 Region 的内边距周围。
The border is a line (or similar) which can be displayed around the content area + padding of a Region.
边距是 Region 与其父布局容器内的其它组件之间的空间。
The margin is the space between a Region and other components within its own parent layout container.
设置内边距
您可以使用其 setPadding() 方法设置 JavaFX Region 或 Region 子类的内边距。在此示例中,我使用 HBox 来演示,它也是 Region 的子类,因为并非所有 Region 的子类都遵循它们上设置的填充(窗格不遵循,据我所知)。以下是设置 HBox 的内边距的实例:
You can set the padding of a JavaFX Region, or subclass of Region, using its setPadding() method. In this example I use a HBox which is also a subclass of Region, because not all Region subclasses respect the padding set on them (Pane doesn’t, as far as I can see). Here is how to set the padding of an HBox:
HBox hBox=new HBox(new Label("Hello Pane"));hBox.setPadding(new Insets(10));
设置边框
可以在 JavaFX Region 上设置边框。您可以将标准描边(一条线)或边框图像用作边框。边框图像可用于在 Region 周围绘制画框 —— 就像画作周围的框架一样。不过,边框描边更为常见。
It is possible to set a border on a JavaFX Region. You can use both an standard stroke as border (a line) or a border image. Border images could be used to draw a picture frame around a Region - just like the frame around a painting. Border strokes are more common though.
设置描边边框
这是在 Region 上设置描边边框的示例。在此示例中,使用的是 Region 的子类 Pane。 要了解“stroke line joine”、“stroke line cap”等术语的含义,请查看 SVG 相关教程。这些概念(很可能)在 SVG 和 JavaFX 中的含义相同,尽管实现的细节可能会有所不同。
Here is an example of setting a stroke border on a Region. In this example it is the Region subclass Pane that is used. To understand what terms like “stroke line joine”, “stroke line cap” etc. mean, check out SVG Stroke tutorial. The concepts (most likely) mean the same both in SVG and JavaFX, although the details of the implementation may vary.
Pane pane = new Pane();StrokeType strokeType = StrokeType.INSIDE;StrokeLineJoin strokeLineJoin = StrokeLineJoin.MITER;StrokeLineCap strokeLineCap = StrokeLineCap.BUTT;double miterLimit = 10;double dashOffset = 0;List<Double> dashArray = null;BorderStrokeStyle borderStrokeStyle =new BorderStrokeStyle(strokeType,strokeLineJoin,strokeLineCap,miterLimit,dashOffset,dashArray);BorderStroke borderStroke =new BorderStroke(Color.valueOf("08ff80"),borderStrokeStyle,new CornerRadii(0),new BorderWidths(8));Border border = new Border(borderStroke);pane.setBorder(border);
设置背景
您可以使用 JavaFX Background 类设置 JavaFX Region 的背景。在正确初始化它之前,您可能需要对它进行一些设置。您可以设置填充颜色作为背景,或使用图像作为背景。
You can set the background of a JavaFX Region using the JavaFX Background class. It may take you a bit of meddling with it before you have it initialized correctly. You can set both a color filled background, or use an image as background.
设置背景颜色
您可以像这样为 JavaFX 区域设置背景颜色:
You can set a background color for a JavaFX Region like this:
Pane pane = new Pane();BackgroundFill backgroundFill =new BackgroundFill(Color.valueOf("#ff00ff"),new CornerRadii(10),new Insets(10));Background background =new Background(backgroundFill);pane.setBackground(background);
传递给 BackgroundFill 构造器的 CornerRadii 实例设置背景填充角的半径 —— 如果需要圆角。如果不需要,请将圆角半径设置为 0。
The CornerRadii instance passed to the BackgroundFill constructor sets the radius of the corners of the background fill - if round corners are wanted. If not, set corner radius to 0.
传递给 BackgroundFill 构造器的 Insets 实例设置 Region 边缘之间的内部填充和背景填充。
The Insets instance passed to the BackgroundFill constructor sets the internal padding between the edge of the Region and the background fill.
可以将多个 BackgroundFill 实例应用在彼此之上。这是一个展示如何做到这一点的例子:
It is possible to have several BackgroundFill instances applied on top of each other. Here is an example of how to do that:
Pane pane = new Pane();BackgroundFill backgroundFill1 =new BackgroundFill(Color.valueOf("#ff00ff"),new CornerRadii(0),new Insets(0));BackgroundFill backgroundFill2 =new BackgroundFill(Color.valueOf("#00ff00"),new CornerRadii(10),new Insets(10));Background background =new Background(backgroundFill1, backgroundFill2);pane.setBackground(background);
在本例中,backgroundFill2 将绘制在 backgroundFill1 之上。由于 backgroundFill2 具有圆角半径和填充集,因此 backgroundFill1 将在 backgroundFill2 的边缘周围可见。
In this example, backgroundFill2 will be drawn on top of backgroundFill1. Since backgroundFill2 has corner radius and a padding set, backgroundFill1 will be visible around the edges of backgroundFill2.
设置背景图片
也可以使用图像作为 JavaFX Region 的背景。以下是使用图像作为 Region(以 Pane 为例)背景的示例:
It is also possible to use an image as background for a JavaFX Region. Here is an example of using an image as background for a Region (a Pane):
Pane pane = new Pane();String filePath = "data/background.jpg";Image image = null;try {image = new Image(new FileInputStream(filePath));} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}BackgroundImage backgroundImage =new BackgroundImage(image,BackgroundRepeat.NO_REPEAT, // repeat XBackgroundRepeat.NO_REPEAT, // repeat YBackgroundPosition.CENTER, // positionnew BackgroundSize(100, // width = 100%100, // height = 100%true, // width is percentagetrue, // height is percentagetrue, // contain image within boundstrue // cover all of Region content area));pane.setBackground(new Background(backgroundImage));

