- 622. 设计循环队列">题目1:622. 设计循环队列
- 题目2:数据流的移动平均计算
- 二叉树的最小深度">题目0-1:二叉树的最小深度
- 打开转盘锁">题目0-2:打开转盘锁
- 题目1:墙与门
- 题目 2: 岛屿的数量
- 题目3:完全平方数
- Stack: 栈
- 1. min stack : 最小栈
- 2. Valid Parentheses: 有效括号
- 3. Daily Temperatures: 每日温度
- 4. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation: 评估逆波兰表示法
- Stack and DFS: 用栈求解DFS题目
- 1. Number of Islands: 岛屿数量 — 见BFS
- 2. Clone Graph: 克隆图
- 3.Target sum: 目标和
- 总结用法:
- 1. 用栈实现队列
- 2.用队列实现栈的功能
- 3.解码字符串: Decode String
- 4.图像渲染:Flood Fill
- 5. 01矩阵 01 Matrix
- 6.钥匙和房间:Keys and Rooms
题目1:622. 设计循环队列
题目描述:
实现循环队列
直观思路:
就是一个数据结构题目,队列大小固定,
主要就是设计首尾指针,控制队列的移动
解法1
原思路:
设置一个head指针,一个tail指针
- 构造就是初始化一个大小为k的队列 Q
- Front 就是
return Q[head] - Rear 就是
return Q[tail] - enQueue 就是
Q.append(value), tail +=1 - deQueue 就是
Q.pop(0), head +=1 - isEmpty() 可以判断 head tail的关系,或者设置一个count 判断count
- if head == tail — 可能空了 也可能满了 还是多个count吧
- isFull() 同上
code:
class MyCircularQueue:def __init__(self, k: int):self.k = kself.Q = [0]*kself.head = 0self.tail = 0self.count = 0def enQueue(self, value: int) -> bool:if self.count == self.k :return Falseself.tail = (self.tail +1) % self.kself.Q[self.tail -1] = valueself.count +=1return Truedef deQueue(self) -> bool:if self.count == 0:return Falseself.head = (self.head + 1)% self.kself.count -=1return Truedef Front(self) -> int:if self.isEmpty():return -1return self.Q[self.head]def Rear(self) -> int:if self.isEmpty():return -1return self.Q[self.tail-1]def isEmpty(self) -> bool:# print(self.count)return self.count == 0def isFull(self) -> bool:return self.count == self.k
矫正思路:
- 首先append是不对的,循环做不到,还是要用tail指针添加
- 弹出时也不能是pop() ,应该头指针后移,count -1就行
- head 和 tail 不是一味的+1 要注意循环
- tail指针的使用要注意细节,索引时都要 -1 ,绕了我半天
- 索引时注意要判断非空情况
题目2:数据流的移动平均计算
Moving Average from Data Stream
这题leetcode中竟然是会员专享
题目描述:
Given a stream of integers and a window size, calculate the moving average of all integers in the sliding window.
Implement the MovingAverage class:
- MovingAverage(int size) Initializes the object with the size of the window size.
- double next(int val) Returns the moving average of the last size values of the stream.
eg:
Input["MovingAverage", "next", "next", "next", "next"][[3], [1], [10], [3], [5]]Output[null, 1.0, 5.5, 4.66667, 6.0]ExplanationMovingAverage movingAverage = new MovingAverage(3);movingAverage.next(1); // return 1.0 = 1 / 1movingAverage.next(10); // return 5.5 = (1 + 10) / 2movingAverage.next(3); // return 4.66667 = (1 + 10 + 3) / 3movingAverage.next(5); // return 6.0 = (10 + 3 + 5) / 3
直观思路:
这题难在读题上,看了好几遍没有理解,看例子,就是滑动窗口求平均数,
code:
class MovingAverage:def __init__(self, size: int):self.Q = []self.size = sizedef next(self, val: int) -> float:if len(self.Q) == self.size:self.Q.pop(0)self.Q.append(val)return mean(self.Q)
这题没啥可以说的 时间空间复杂度主要由 list 的pop 影响
用其他的语言可能会稍微有点值得分析的东西
题目0-1:二叉树的最小深度
class Solution:def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:if not root:return 0else:stack= [(1, root),]min_depth = float('inf')while stack:depth, root = stack.pop()children = [root.left, root.right]# if not root.left and root.right:if not any(children):min_depth = min(depth, min_depth)for c in children:if c:stack.append((depth + 1, c))return min_depth
题目0-2:打开转盘锁
题目1:墙与门
Walls and Gates
题目描述:
You are given an m x n grid rooms initialized with these three possible values.
- -1 A wall or an obstacle.
- 0 A gate.
- INF Infinity means an empty room. We use the value 231 - 1 = 2147483647 to represent INF as you may assume that the distance to a gate is less than 2147483647.
Fill each empty room with the distance to its nearest gate. If it is impossible to reach a gate, it should be filled with INF.
向每个空屋子填上距离门最近的距离值,如果没有就填inf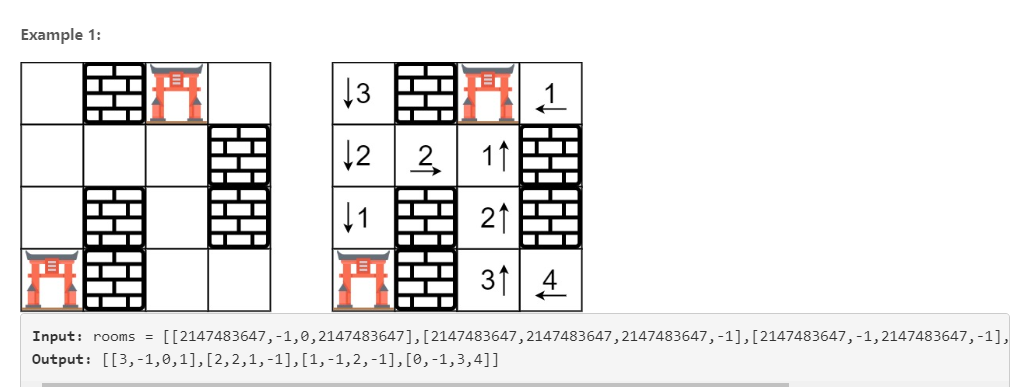
解法1:暴力解法
要是非要做,就是暴力解法,要对每个空屋子都要去搜索一遍,
这样就是
- 遍历每个格子,如果格子为空,则开始BFS找最近的门,
- 如果找到最近的门,填入数字,如果没有就是inf
但是时间复杂度和空间复杂度想想都很大 — 不好计算具体多大,所以看官方的分析了就
就是说,在mn个格子上,最坏的情况要在每个格子上都做 mn次搜索,这个时间复杂度显然不满足要求了就
解法2:从门反找

根据提示的意思,就是从所有的门同时出发,去找空屋子 ,那离得近的肯定先找到空屋子,这样如果空屋子里有数据,那就是最短的,没有,当前这个就是最短的。
问题:假如有g 个门,那这样每个屋子都要被访问g遍
emmm 不对,不依赖门的个数
抄了两份答案 一份不是题解的思路,一份
def wallsAndGates(rooms):# 得到高宽n, m = len(rooms), len(rooms[0])# 找到所有门q = [(i,j) for i in range(n) for j in range(m) if not rooms[i][j]]for i, j in q:for x, y in [(i-1,j), (i+1,j),(i,j-1),(i,j+1)]:if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < m and rooms[x][y] == 2**31-1: # "-inf"rooms[x][y] = rooms[i][j] + 1q.append((x, y))
我是这样写的
class Solution:
def wallsAndGates(self, rooms: List[List[int]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify rooms in-place instead.
"""
m = len(rooms)
n = len(rooms[0])
q = []
direction = [(1,0),(-1,0),(0,1),(0,-1)]
# 先找到所有的门
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if rooms[i][j] == 0:
# 将gate的坐标加入队列
q.append((i,j))
while len(q) == 0:
point = q.pop(0)
row = point[0]
col = point[1]
for (x,y) in direction:
r = row + x
c = col + y
if ( 0<= r < m and 0<= c <n and room[r][c] ==2147483647):
rooms[r][c] = rooms[row][col] +1
q.append((x, y)) #
但是没有运行起来,不知是为何 — 逻辑看着不像是有问题
题目 2: 岛屿的数量
Number of Islands
首先题目的含义: 岛屿就是陆地连成一片,整个陆地全方位又被水环绕
eg:

方法1:BFS
从左上角开始遍历,遇到1 则做BFS,将遇到的1(同岛屿)的坐标全部记录到hash_map,直到全部遇到水,岛屿数量+1
继续遍历找1,且不在hash_map的,重复上述过程
官方描述:
线性扫描二维网格图,如果一个节点包含一个’1’,那么它是一个触发广度优先搜索的根节点。将其放入队列并将其值设置为“0”以标记为已访问节点。迭代搜索排队节点的邻居,直到队列变空。
空间复杂度:就是hash_map - n
时间复杂度:mnBFS_times
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
self.grid = grid
N = len(grid)
M = len(grid[0])
# 用递归实现
def bfs(self, row, col):
N = len(self.grid)
M = len(self.grid[0])
directions = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)]
queue = deque()
queue.append((row, col))
while queue:
x, y = queue.popleft()
self.grid[x][y] = "0"
for dx, dy in directions:
nx = dx + x
ny = dy + y
if 0 <= nx < N and 0 <= ny < M and self.grid[nx][ny] == "1":
queue.append((nx, ny))
self.grid[nx][ny] = "0"
count = 0
for row in range(N):
for col in range(M):
if self.grid[row][col] == "1":
count += 1
bfs(row, col)
return count
方法2:DFS
线性扫描二维网格图,如果一个节点包含一个’1’,那么它是一个触发深度优先搜索的根节点。
在 DFS 期间,每个访问节点都应设置为“0”以标记为已访问节点。计算触发 DFS 的根节点的数量,这个数字将是岛的数量,因为从某个根开始的每个 DFS 都标识一个岛。
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
#create variable to store result
res = 0
#get number of columns and rows
m = len(grid)
n = len(grid[0])
#create dfs function
# 循环实现
def dfs(grid, i, j):
#if current position out of boundary,return
if i < 0 or j < 0 or i >= m or j >= n:
return
#if current position is water,return
if grid[i][j] == "0":
return
#set current location as water to avoid repetition
grid[i][j] = "0"
#check surrounding
dfs(grid, i + 1, j)
dfs(grid, i - 1, j)
dfs(grid, i, j + 1)
dfs(grid, i, j - 1)
# traverse through every postition
for i in range(0, m):
for j in range(0, n):
#when current grid is land, add to result
if grid[i][j] == "1":
res += 1
#traverse through surrounding
dfs(grid, i, j)
return res

对比:
其实这题的主要解法思路都一样, 都是线性扫描二维网格图,如果一个节点包含一个’1’,那么它是一个触发广度优先搜索的根节点,然后围绕这个根节点,将附近连接的陆地都标志为0
差异在标记附近陆地的方式上,
- BFS 是将每个节点的4个方向都标记完,然后再标记下一层的4个方向: 漫盖式
- DFS 是将每个节点的从4个方向,先挑着一个方向找到底,然后回溯回来,再找下一个方向 — 串线式
题目3:完全平方数
给一个整数,计算使用完全平方数求和得到这个整数的最少个数
就是 用最少的完全平方数求和得到这个整数
这tm 也能用到BFS吗?
感觉用递归可以解呢? 求出数字x的最大完全平方数,然后累计,剩余部分继续递归。直到剩余部分为0
这种方法是暴力解法:
方法1:暴力解法
we enumerate all possible combinations and find the minimal one of them.
枚举所有的可能性,选一组数量最少的
不太聪明 复杂度太高 — 组合的时候不能处理一下吗?
方法2:动态规划
就是将x之前数的最小组合数都计算出来,保存成表,表的最后一个数就是结果
看懂这张图就差不多了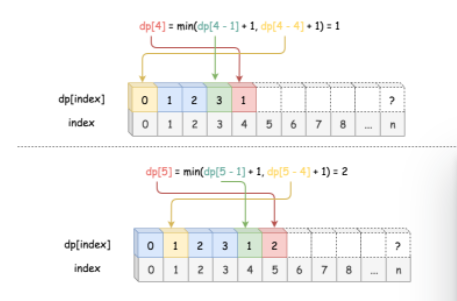
步骤:
As for almost all DP solutions, we first create an array dp of one or multiple dimensions to hold the values of intermediate sub-solutions, as well as the final solution which is usually the last element in the array.
> Note that, we create a fictional element dp[0]=0 to simplify the logic, which helps in the case that the remainder (n-k) happens to be a square number.As an additional preparation step, we pre-calculate a list of square numbers (i.e. square_nums) that is less than the given number n.
As the main step, we then loop from the number 1 to n, to calculate the solution for each number i (i.e. numSquares(i)). At each iteration, we keep the result of numSquares(i) in dp[i], while resuing the previous results stored in the array.
At the end of the loop, we then return the last element in the array as the result of the solution.
方案3:贪心枚举
对方案1 的暴力解法做优化:
- Starting from the combination of one single number to multiple numbers, once we find a combination that can sum up to the given number n,
- then we can say that we must have found the smallest combination, since we enumerate the combinations greedily from small to large.
算法流程:
First of all, we prepare a list of square numbers (named square_nums) that are less than the given number n.
In the main loop, iterating the size of combination (named count) from one to n, we check if the number n can be divided by the sum of the combination, i.e. is_divided_by(n, count).
The function is_divided_by(n, count) can be implemented in the form of recursion as we defined in the intuition section.
In the bottom case, we have count==1, we just need to check if the number n is a square number itself. We could use the inclusion test with the list squarenums that we prepared before, _i.e.
- $$ n =\intext{square_nums}$$ n∈square_nums. And if we use the set data structure for square_nums, we could obtain a faster running time than the approach of n == int(sqrt(n)) ^ 2.
案例: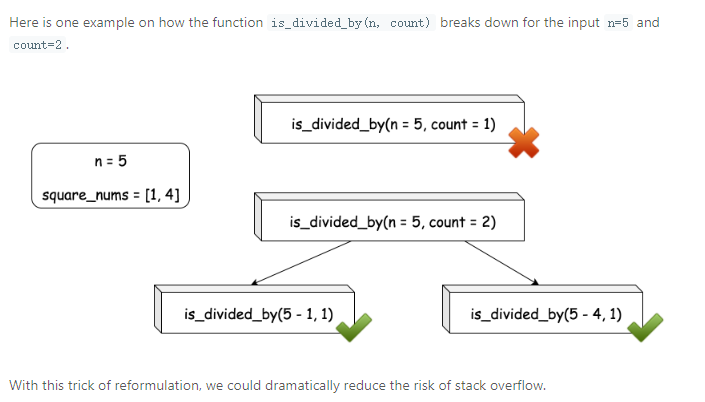
该说不说,简化了很多
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
def is_divided_by(n, count):
"""
return: true if "n" can be decomposed into "count" number of perfect square numbers.
e.g. n=12, count=3: true.
n=12, count=2: false
"""
if count == 1:
return n in square_nums
for k in square_nums:
if is_divided_by(n - k, count - 1):
return True
return False
square_nums = set([i * i for i in range(1, int(n**0.5)+1)]) # 查询速度更快
for count in range(1, n+1):
if is_divided_by(n, count):
return count
就是从少向多查,最差的情况 我n个1可以解决问题
- 能被1个数组合成吗?
- 能被2个数组合成吗?
- 剩余的部分(n-k_1), 能被(n-1)个数组合成吗?
- 剩余的部分(n-k_2), 能被(n-1)个数组合成吗?
- 再分!
- 能被3个数组合成吗?
复杂度分析:
方法4:Greedy + BFS
其实该题,可以看作是一个n叉树的结构,如下: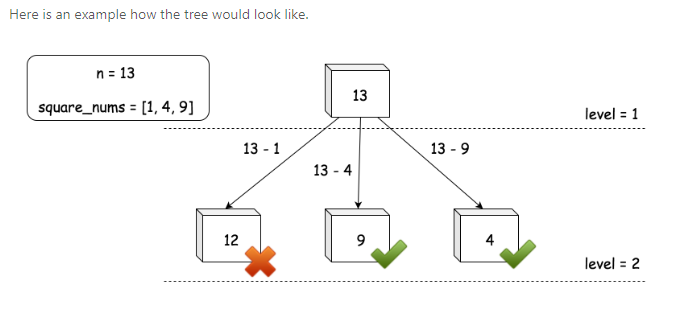
我们要做的就是找到合适节点的最小深度:
合适(目标)节点是哪个呢?需要满足两个条件
1). the value of the node (i.e. the remainder) should be a square number (节点值要是square number )
2). the distance between the node and the root should be minimal among all nodes that meet the condition (1).(深度最小)
那这道题是不是变成了,层序遍历找square number 的问题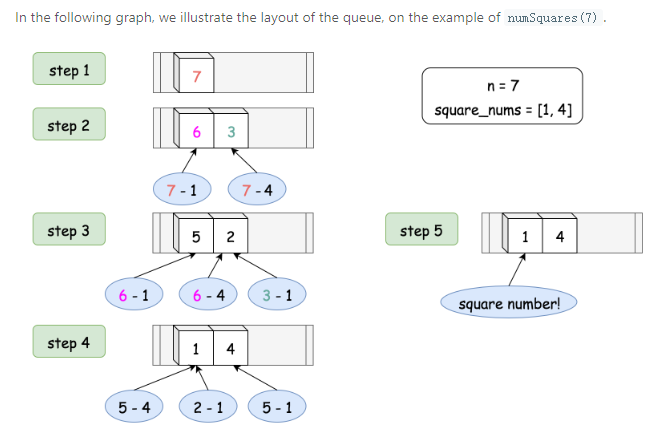
class Solution:
def numSquares(self, n):
# list of square numbers that are less than `n`
square_nums = [i * i for i in range(1, int(n**0.5)+1)]
level = 0
queue = {n} # 只要不是square numbers就要放入队列
while queue:
level += 1
#! Important: use set() instead of list() to eliminate the redundancy,
# which would even provide a 5-times speedup, 200ms vs. 1000ms.
next_queue = set()
# construct the queue for the next level
for remainder in queue:
for square_num in square_nums:
if remainder == square_num:
return level # find the node!
elif remainder < square_num:
break
else:
next_queue.add(remainder - square_num)
queue = next_queue
return level
复杂度:
方案5: 数学法:
根据拉格朗日四平方定理:
每个 自然数 都可以表示为4个整数的均方和
where the four numbers _a_1,_a_2,_a_3 are 整数

就是检查是不是4个数的组成稍微复杂一些
需要按照一个公式来检查,但是这个公式的实现我有些没看懂
class Solution:
def isSquare(self, n: int) -> bool:
sq = int(math.sqrt(n))
return sq*sq == n
def numSquares(self, n: int) -> int:
# four-square and three-square theorems
while (n & 3) == 0:
n >>= 2 # reducing the 4^k factor from number
if (n & 7) == 7: # mod 8
return 4
if self.isSquare(n):
return 1
# check if the number can be decomposed into sum of two squares
for i in range(1, int(n**(0.5)) + 1):
if self.isSquare(n - i*i):
return 2
# bottom case from the three-square theorem
return 3
Stack: 栈
1. min stack : 最小栈
设计一个支持 push、pop、top 和在恒定时间内检索最小元素的堆栈。
实现以下功能:
Implement the MinStack class:
- MinStack() initializes the stack object.
- void push(int val) pushes the element val onto the stack.
- void pop() removes the element on the top of the stack.
- int top() gets the top element of the stack.
- int getMin() retrieves the minimum element in the stack.
思路:
就是设计一个栈,拥有栈的功能,然后维护一个min值即可
但是这样存在一个问题就是 最小值出栈 了怎么办? — 维护一个最小值的有序栈 — 空间复杂度上来 ,当弹出最小值的时候就把最小值的栈也弹出
plan 1:维护一个最小数栈
如下: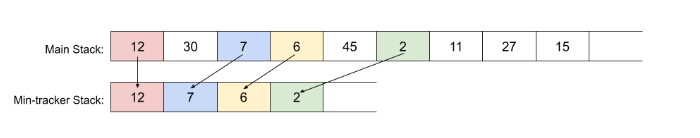
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
self.min_stack = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.stack.append(x)
if not self.min_stack or x <= self.min_stack[-1]:
self.min_stack.append(x)
def pop(self) -> None:
if self.min_stack[-1] == self.stack[-1]:
self.min_stack.pop()
self.stack.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return self.min_stack[-1]
空间时间复杂度:
问题: 当有两个最小数相同时咋办 — 弹出就无了 — 所以要小于等于
Plan 2: 维护[num,min_num] 元组
在每个元素上维护两个值,一个当前值,一个当前最小值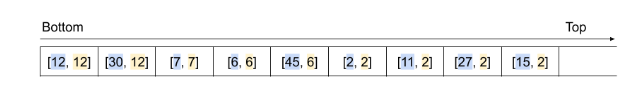
class MinStack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
# If the stack is empty, then the min value
# must just be the first value we add
if not self.stack:
self.stack.append((x, x))
return
current_min = self.stack[-1][1]
self.stack.append((x, min(x, current_min)))
def pop(self) -> None:
self.stack.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1][0]
def getMin(self) -> int:
return self.stack[-1][1]
缺点:当数据太多时 内存消耗比较大
2. Valid Parentheses: 有效括号
给定一个仅包含字符 ‘(‘, ‘)’, ‘{‘, ‘}’, ‘[‘ 和 ‘]’ 的字符串 s,确定输入字符串是否有效。
输入字符串在以下情况下有效:
- 开括号必须用相同类型的括号闭合。
- 开括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
eg :
思路: 这是一个经典的用栈的题目了
遇到一个左括号就入队,遇到一个右括号就出队 ,类型不同的阔号出序不对就报错
def isValid(self, s):
bracket_map = {"(": ")", "[": "]", "{": "}"}
open_par = set(["(", "[", "{"])
stack = []
for i in s:
if i in open_par:
stack.append(i)
elif stack and i == bracket_map[stack[-1]]:
stack.pop()
else:
return False
return stack == []
时间复杂度:n
空间复杂度:n (最差的情况,只有左半边)
3. Daily Temperatures: 每日温度
给定一个代表每日温度的整数数组,返回一个数组 answer,
其中 answer[i] 是您在第 i 天之后必须等待的天数才能获得更高的温度。
如果没有可能的未来日期,请保留 answer[i] == 0 。
eg: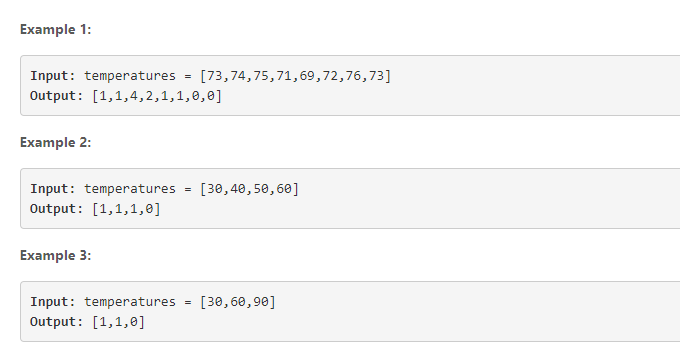
就是后面的数比当前数大的最近距离
思路:
暴力方法,一个个找,两层for循环,这样最坏的情况就是,每个数都是n ,时间复杂度为, n^2
所以不行
plan 1: 单调栈

https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/solution/mei-ri-wen-du-by-leetcode-solution/
from: leetcode
class Solution:
def dailyTemperatures(self, temperatures: List[int]) -> List[int]:
length = len(temperatures)
ans = [0] * length
stack = []
for i in range(length):
temperature = temperatures[i]
while stack and temperature > temperatures[stack[-1]]:
prev_index = stack.pop()
ans[prev_index] = i - prev_index
stack.append(i)
return ans
4. Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation: 评估逆波兰表示法
根据 逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。
有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
注意 两个整数之间的除法只保留整数部分。
可以保证给定的逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。

思路: 遇到数则进栈,否则将计算栈顶的两个元素,将结果重新入栈
class Solution:
def evalRPN(self, tokens: List[str]) -> int:
stack = []
ope = set("+", "-", "*", "/")
def handler(operator, a, b):
if operator == "+":
return a+b
elif operator == "-":
return a-b
elif operator == "*":
return a*b
else:
return int(a/b)
for num in tokens:
if num in ope:
b = int(stack.pop())
a = int(stack.pop())
temp = handler(num, a, b)
stack.append(int(temp))
else:
stack.append(int(num))
return stack[0]
疑问:没有三个数的同时运算好像,
Stack and DFS: 用栈求解DFS题目
1. Number of Islands: 岛屿数量 — 见BFS
2. Clone Graph: 克隆图

深度copy,案例: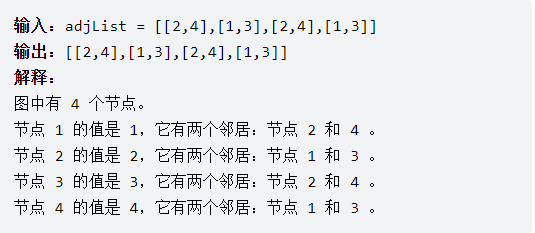
就是遍历,复制图,遍历可以使用DFS or BFS
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0, neighbors = None):
self.val = val
self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else []
"""
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.visited = {} # set(value),dict{key:value}
def cloneGraph(self, node):
"""
:type node: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if not node:
return node
# 如果该节点已经被访问过了,则直接从哈希表中取出对应的克隆节点返回
if node in self.visited:
return self.visited[node]
# 克隆节点,注意到为了深拷贝我们不会克隆它的邻居的列表
clone_node = Node(node.val, [])
# 哈希表存储
self.visited[node] = clone_node
# 遍历该节点的邻居并更新克隆节点的邻居列表
if node.neighbors:
for n in node.neighbors:
clone_node.neighbors.append(self.cloneGraph(n))
return clone_node
from collections import deque
class Solution(object):
def cloneGraph(self, node):
"""
:type node: Node
:rtype: Node
"""
if not node:
return node
visited = {}
# 将题目给定的节点添加到队列
queue = deque([node])
# 克隆第一个节点并存储到哈希表中
visited[node] = Node(node.val, [])
# 广度优先搜索
while queue:
# 取出队列的头节点
n = queue.popleft()
# 遍历该节点的邻居
for neighbor in n.neighbors:
if neighbor not in visited:
# 如果没有被访问过,就克隆并存储在哈希表中
visited[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val, [])
# 将邻居节点加入队列中
queue.append(neighbor)
# 更新当前节点的邻居列表
visited[n].neighbors.append(visited[neighbor])
return visited[node]
3.Target sum: 目标和
给一个整数数组,一个target
求出,使用整数数组加减组合成 target 的组合方式数目
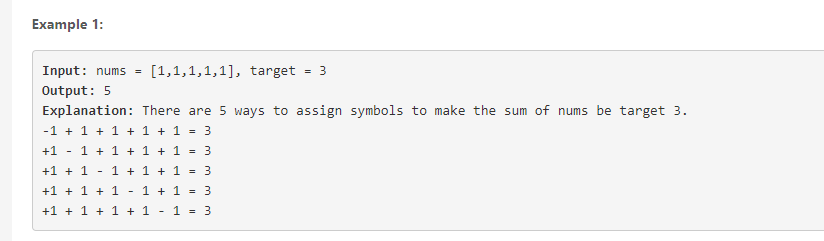
直观上用排列组合,这就复杂了 — 怎么用DFS 栈求解呢。。
plan1: DFS递归
plan2: 1维度动态规划
plan3: 2维度动态规划
上面这俩题没有很好的搞明白
总结用法:
1. 用栈实现队列

思路:用两个栈实现队列的功能
方法1:push O(1), pop amortized O(1)
class MyQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.s1 = []
self.s2 = []
def push(self, x):
self.s1.append(x)
def pop(self):
self.peek()
return self.s2.pop()
def peek(self):
if not self.s2:
while self.s1:
self.s2.append(self.s1.pop())
return self.s2[-1]
def empty(self):
return not self.s1 and not self.s2
方法2: push O(n), pop O(1)
class MyQueue:
def __init__(self):
self.s1 = []
self.s2 = []
def push(self, x):
while self.s1:
self.s2.append(self.s1.pop())
self.s1.append(x)
while self.s2:
self.s1.append(self.s2.pop())
def pop(self):
return self.s1.pop() # 0
def peek(self):
return self.s1[-1] #
def empty(self):
return not self.s1
2.用队列实现栈的功能

解法1:直接抄袭1.的解法2
更改以下两点
def pop(self):
return self.s1.pop(0) # 0
def peek(self):
return self.s1[0] #
时间:push(n),pop(1)
解法2:push O(1), pop amortized O(1)
暂时没有找到
解法3:One Queue, push - O(n)O(n), pop O(1)O(1)
class MyStack:
def __init__(self):
self.q1 = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.q1.append(x)
q1_size = len(self.q1)
for _ in range(q1_size-1):
self.q1.append(self.q1.pop(0))
def pop(self) -> int:
self.q1.pop(0)
def top(self) -> int:
return self.q1[0]
def empty(self) -> bool:
return len(self.q1) == 0
3.解码字符串: Decode String
看案例就清楚了 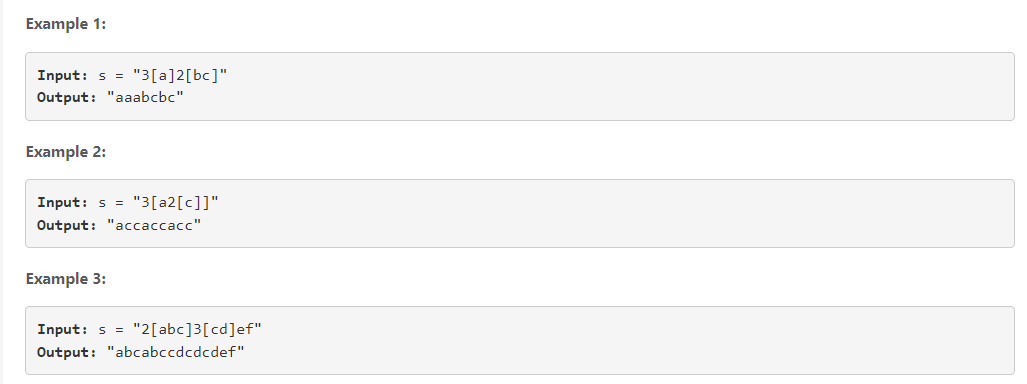
思路:建立目标list [], 使用队列 遇到数字k则开始for循环将数字后的list串,向目标list []中添加k次即可
想简单了 — 当有括号逃套括号的时候(例子2),就会出现问题了 — 需要向下递归
解法1:栈
参考:https://leetcode.cn/problems/decode-string/solution/decode-string-fu-zhu-zhan-fa-di-gui-fa-by-jyd/

应该是先入栈 遇到左括号进栈,右括号出栈 — 和逆波兰计算很像 — 这样来说 用递归解就非常简单
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
stack, res, multi = [], "", 0
for c in s:
if c == '[':
stack.append([multi, res])
res, multi = "", 0
elif c == ']':
cur_multi, last_res = stack.pop()
res = last_res + cur_multi * res
elif '0' <= c <= '9':
multi = multi * 10 + int(c)
else:
res += c
return res
时间复杂度:遍历s的时间 + 组合串的时间
空间复杂度:最差的情况直到最后才遇到右括号 ,n
解法2:递归法

class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
def dfs(s, i):
res, multi = "", 0
while i < len(s):
if '0' <= s[i] <= '9':
multi = multi * 10 + int(s[i])
elif s[i] == '[':
i, tmp = dfs(s, i + 1)
res += multi * tmp
multi = 0
elif s[i] == ']':
return i, res
else:
res += s[i]
i += 1
return res
return dfs(s,0)
4.图像渲染:Flood Fill
给一个二维数组,起始位置,以及要重新更改的颜色
将起始位置所在的「色块」染成指定更改的颜色。 — 就是岛屿的个数那题 的一种最简单的情况 — 题目说了个麻烦,直接用DFS,BFS即可 时间复杂度应该一致
解法1:BFS
class Solution:
def floodFill(self, image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, newColor: int) -> List[List[int]]:
currColor = image[sr][sc]
if currColor == newColor:
return image
n, m = len(image), len(image[0])
que = collections.deque([(sr, sc)])
image[sr][sc] = newColor
while que:
x, y = que.popleft()
for mx, my in [(x - 1, y), (x + 1, y), (x, y - 1), (x, y + 1)]:
if 0 <= mx < n and 0 <= my < m and image[mx][my] == currColor:
que.append((mx, my))
image[mx][my] = newColor
return image
解法2: DFS
class Solution:
def floodFill(self, image: List[List[int]], sr: int, sc: int, newColor: int) -> List[List[int]]:
n, m = len(image), len(image[0])
currColor = image[sr][sc]
def dfs(x: int, y: int):
if image[x][y] == currColor:
image[x][y] = newColor
for mx, my in [(x - 1, y), (x + 1, y), (x, y - 1), (x, y + 1)]:
if 0 <= mx < n and 0 <= my < m and image[mx][my] == currColor:
dfs(mx, my)
if currColor != newColor:
dfs(sr, sc)
return image
时间,空间复杂度:O(n*m)
5. 01矩阵 01 Matrix
给一个01矩阵 ,计算每个位置离0的最短距离
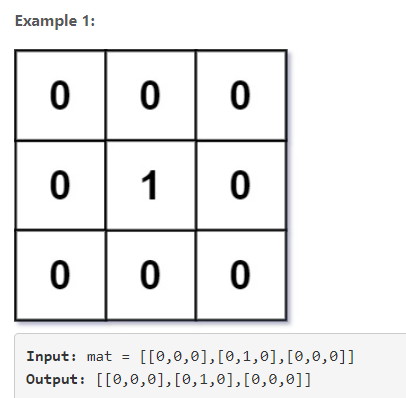

直接就是墙与门的最简情况 —- 最短距离,无脑直接对每个位置遍历做BFS
class Solution:
def updateMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dist = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
zeroes_pos = [(i, j) for i in range(m) for j in range(n) if matrix[i][j] == 0]
# 将所有的 0 添加进初始队列中
q = collections.deque(zeroes_pos)
seen = set(zeroes_pos)
# 广度优先搜索
while q:
i, j = q.popleft()
for ni, nj in [(i - 1, j), (i + 1, j), (i, j - 1), (i, j + 1)]:
if 0 <= ni < m and 0 <= nj < n and (ni, nj) not in seen:
dist[ni][nj] = dist[i][j] + 1
q.append((ni, nj))
seen.add((ni, nj))
return dist
这个写法有俩问题:
- 空间复杂度高: 完全可以原地修改 + 层序遍历 因为0始终是0
- 将所有0加入初始队列感觉没有必要
需要知道层数的BFS

我自己写了一版本 超时了 ,下面这版本比我的简洁,但是思路一样 但是现在也超时了 看来是必须要用空间换时间了
class Solution:
def updateMatrix(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
nrow, ncol = len(mat), len(mat[0])
queue = []
for r, row in enumerate(mat):
for c, val in enumerate(row):
if val != 0: queue.append((r, c))
distance = 1
while queue:
q = []
for r, c in queue:
if ((r == 0 or mat[r - 1][c] >= distance) and (c == 0 or mat[r][c - 1] >= distance) and (r == nrow - 1 or mat[r + 1][c] >= distance) and (c == ncol - 1 or mat[r][c + 1] >= distance)):
mat[r][c] = distance + 1
q.append((r, c))
distance += 1
queue = q
return mat
好吧 放弃 就用第一版吧
解法2:动态规划
https://leetcode.cn/problems/01-matrix/solution/01ju-zhen-by-leetcode-solution/
矩阵里的动态规划 for 太多 不喜欢用 但是可以看看思路
6.钥匙和房间:Keys and Rooms
做的快的话一起看看


