BIO
当用户进程发起请求时,一直阻塞直到数据拷贝到用户空间为止才返回。
import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.net.ServerSocket;import java.net.Socket;public class BIOEchoServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);while (true) {Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();System.out.println("new client conn: " + socket);new Thread(() -> {try {BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));String msg;while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println("receive client msg: " + msg);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();}}}
每来一个客户端连接都要分配一个线程,如果客户端一直增加,服务端线程会无限增加,直到服务器资源耗尽。
NIO
Java 中的 NIO 使用的是 IO 多路复用技术实现的,多个 IO 操作共同使用一个 selector(选择器)去询问哪些 IO 准备好了,selector 负责通知那些数据准备好了的 IO,它们再自己去请求内核数据。
public class NIOEchoServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 创建一个SelectorSelector selector = Selector.open();// 创建ServerSocketChannelServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();// 绑定8080端口serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8002));// 设置为非阻塞模式serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 将Channel注册到selector上,并注册Accept事件serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);System.out.println("server start");while (true) {// 阻塞在select上(第一阶段阻塞)selector.select();// 如果使用的是select(timeout)或selectNow()需要判断返回值是否大于0// 有就绪的ChannelSet<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();// 遍历selectKeysIterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();// 如果是accept事件if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {// 强制转换为ServerSocketChannelServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();System.out.println("accept new conn: " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 将SocketChannel注册到Selector上,并注册读事件socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {// 如果是读取事件// 强制转换为SocketChannelSocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();// 创建Buffer用于读取数据ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);// 将数据读入到buffer中(第二阶段阻塞)int length = socketChannel.read(buffer);if (length > 0) {buffer.flip();byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];// 将数据读入到byte数组中buffer.get(bytes);// 换行符会跟着消息一起传过来String content = new String(bytes, "UTF-8").replace("\r\n", "");System.out.println("receive msg: " + content);}}iterator.remove();}}}}
AIO
public class AIOEchoServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 启动服务端AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8003));System.out.println("server start");// 监听accept事件,完全异步,不会阻塞serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {@Overridepublic void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, Object attachment) {try {System.out.println("accept new conn: " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());// 再次监听accept事件serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);// 消息的处理while (true) {ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);// 将数据读入到buffer中Future<Integer> future = socketChannel.read(buffer);if (future.get() > 0) {buffer.flip();byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];// 将数据读入到byte数组中buffer.get(bytes);String content = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");// 换行符会当成另一条消息传过来if (content.equals("\r\n")) {continue;}System.out.println("receive msg: " + content);}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}@Overridepublic void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {System.out.println("failed");}});// 阻塞住主线程System.in.read();}}
阻塞与非阻塞
数据就绪前要不要等待
阻塞: 没有数据传过来时,读会阻塞直到有数据,缓冲区满时,写操作也会阻塞
非阻塞遇到这些情况,都会直接返回。
同步与异步
数据就绪后,数据操作谁完成
数据就绪后需要自己去读取就是同步,数据就绪直接读好再回调给程序是异步。
为什么Netty 仅支持NIO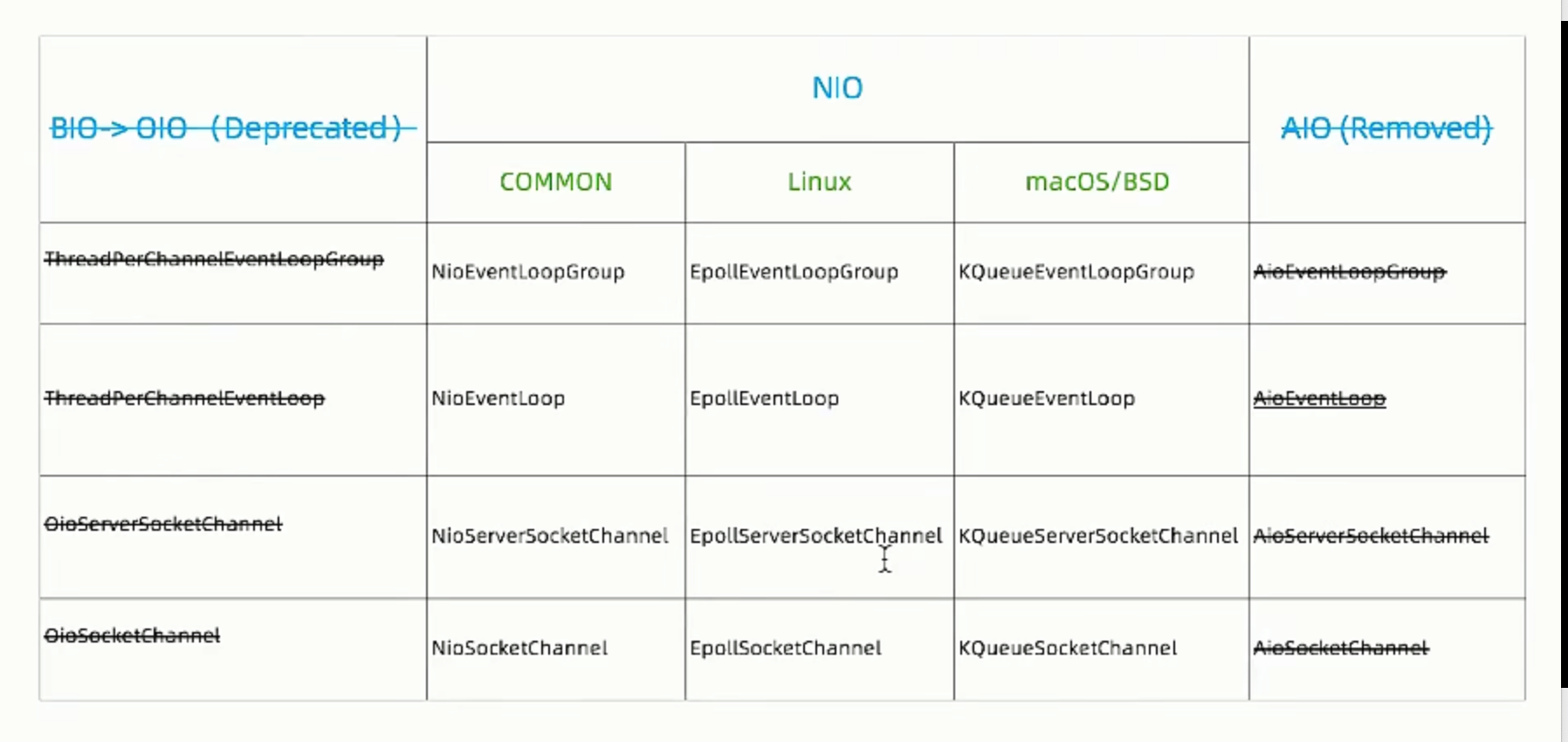
为什么不建议(deprdcate)阻塞I/O(BIO/OIO)
连接数高情况下:阻塞->消耗资源,效率低

