- WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter:
- SecurityContextPersistenceFilter:
- HeaderWriterFilter:
- CsrfFilter
- LogoutFilter
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
- createSuccessAuthentication()
- ConcurrentSessionFilter
- RequestCacheAwareFilter
- SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestFilter
- AnonymousAuthenticationFilter
- SessionManagementFilter
- ExceptionTranslationFilter
- FilterSecurityInteceptor
Spring security 是一种基于Spring Aop和Servlet 过滤器的安全框架。
在ApplicationFilterChain 中通过DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean创建DelegatingFilterProxy:
DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean:
@Overridepublic Filter getFilter() {return new DelegatingFilterProxy(this.targetBeanName,getWebApplicationContext()) {@Overrideprotected void initFilterBean() throws ServletException {// Don't initialize filter bean on init()}};}
通过调用AbstractFilterRegistrationBean的onStartup 方法调用DelegatingFilterProxy中具体的filter方法:
AbstractFilterRegistrationBean:
@Overridepublic void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {Filter filter = getFilter();Assert.notNull(filter, "Filter must not be null");String name = getOrDeduceName(filter);if (!isEnabled()) {this.logger.info("Filter " + name + " was not registered (disabled)");return;}FilterRegistration.Dynamic added = servletContext.addFilter(name, filter);if (added == null) {this.logger.info("Filter " + name + " was not registered "+ "(possibly already registered?)");return;}configure(added);}
最后通过DelegatingFilterProxy 执行FilterChainProxy的doFilterInternal方法。
在doFilterInternal方法中首先会根据request获取所有的filter
/*** Returns the first filter chain matching the supplied URL.返回第一个匹配的url的过滤器** @param request the request to match* @return an ordered array of Filters defining the filter chain*/private List<Filter> getFilters(HttpServletRequest request) {for (SecurityFilterChain chain : filterChains) {if (chain.matches(request)) {return chain.getFilters();}}return null;}
filterchains中的filter 是通过以下方法配置:
@Configurationpublic class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Autowiredprivate MyFilterSecurityInterceptor myFilterSecurityInterceptor;@Autowiredprivate LoginSuccessHandler loginSuccessHandler;@Autowiredprivate CustomLogoutSuccessHandler logoutSuccessHandler;@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {loginSuccessHandler.setDefaultTargetUrl("/");loginSuccessHandler.setForwardToDestination(false);logoutSuccessHandler.setDefaultTargetUrl("/login");http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated().and().formLogin().successHandler(loginSuccessHandler).permitAll().and().logout().logoutSuccessHandler(logoutSuccessHandler).permitAll();http.sessionManagement().maximumSessions(1);http.addFilterBefore(myFilterSecurityInterceptor, FilterSecurityInterceptor.class);http.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/403").authenticationEntryPoint(new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login"));}@Overridepublic void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {web.ignoring().antMatchers("/resources/static/**") //这会被解析成一个SecurityFilterChain.and().ignoring().antMatchers("/static/**").and().ignoring().antMatchers("/bootstrap/**").and().ignoring().antMatchers("/fragments/**").and().ignoring().antMatchers("/**/*.js").and().ignoring().antMatchers("/**/*.css").and().ignoring().antMatchers("/**/*.woff");}}
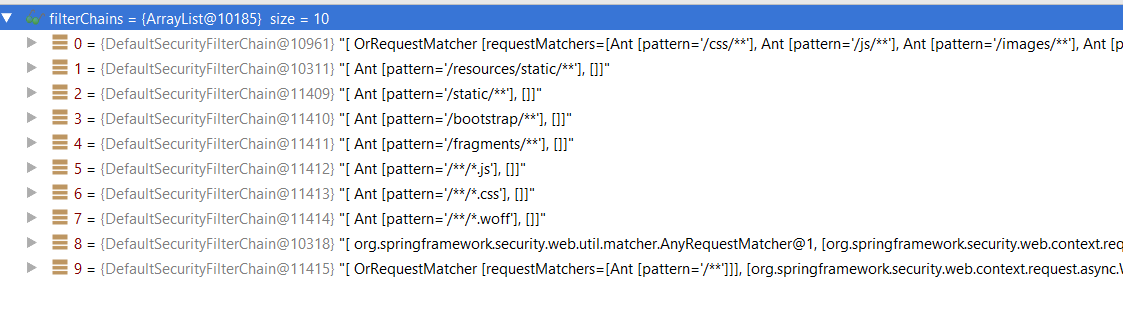 spring security 默认有13个filter, 通过下面配置可添加自己额外的filter:
spring security 默认有13个filter, 通过下面配置可添加自己额外的filter:
http.addFilterBefore(myFilterSecurityInterceptor, FilterSecurityInterceptor.class);
之后将这13个filter 封装在VirtualFilterChain 中:
VirtualFilterChain vfc = new VirtualFilterChain(fwRequest, chain, filters);vfc.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
下面讲解这13个Filter各自的作用(按顺序执行):
提供了对securityContext和WebAsyncManager的集成。方式是通过SecurityContextCallableProcessingInterceptor的beforeConcurrentHandling(NativeWebRequest, Callable)方法来讲SecurityContext设置到Callable上。
这个过滤器主要是加载或者创建新的SecurityContext,并把它保存到全局的SecurityContextHolder中去。
看如下代码:
HttpRequestResponseHolder holder = new HttpRequestResponseHolder(request,response);//1. 加载或创建SecurityContextSecurityContext contextBeforeChainExecution = repo.loadContext(holder);try {//2. 保存securityContext 到 SecurityContextHolder中去SecurityContextHolder.setContext(contextBeforeChainExecution);chain.doFilter(holder.getRequest(), holder.getResponse());}finally {SecurityContext contextAfterChainExecution = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();// Crucial removal of SecurityContextHolder contents - do this before anything// else.SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();repo.saveContext(contextAfterChainExecution, holder.getRequest(),holder.getResponse());request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);if (debug) {logger.debug("SecurityContextHolder now cleared, as request processing completed");}}
在看loadContext()方法的实现,这个方法的默认实现在HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository类中:
代码如下:
public SecurityContext loadContext(HttpRequestResponseHolder requestResponseHolder) {HttpServletRequest request = requestResponseHolder.getRequest();HttpServletResponse response = requestResponseHolder.getResponse();HttpSession httpSession = request.getSession(false);// 1. 从session中读取securitycontext,//实际调用httpSession.getAttribute("SPRING_SECURITY_CONTEXT");SecurityContext context = readSecurityContextFromSession(httpSession);if (context == null) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("No SecurityContext was available from the HttpSession: "+ httpSession + ". " + "A new one will be created.");}//2. 如果session中不存在securityContext, 则会创建一个empty securitycontext,具体如何创建,往下看context = generateNewContext();}//3. 下面代码将response封装成SaveToSessionResponseWrapper对象,// 如果是servlet3, 则将response封装成Servlet3SaveToSessionRequestWrapper对象:SaveToSessionResponseWrapper wrappedResponse = new SaveToSessionResponseWrapper(response, request, httpSession != null, context);requestResponseHolder.setResponse(wrappedResponse);if (isServlet3) {requestResponseHolder.setRequest(new Servlet3SaveToSessionRequestWrapper(request, wrappedResponse));}return context;}
如果session中不存在securityContext , spring会根据3中不同的策略创建空的securityContext:
GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
InheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy
ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy(默认使用)
我们可以在application.properties 中通过配置 spring.security.strategy 来选择使用哪个strategy来创建空的securityContext;
下面是ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy创建securityContext的代码:
public SecurityContext createEmptyContext() {
return new SecurityContextImpl();
}
这个过滤器主要是在response中加入一些spring security关于安全的头部信息,默认会有以下5中HeaderWriter需要写入头信息:
XContentTypeOptionsHeaderWriter
XXssProtectionHeaderWriter
CacheControlHeaderWriter
HstsHeaderWriter
XFrameOptionsHeaderWriter
接下来看每一种HeaderWriter都写入了哪些头信息:
a. XContentTypeOptionsHeaderWriter
这个写入了”X-Content-Type-Options” = “nosniff”, 这个设置可防止内容嗅探攻击,详细解释请自行百度
public final class XContentTypeOptionsHeaderWriter extends StaticHeadersWriter {
/**
* Creates a new instance
*/
public XContentTypeOptionsHeaderWriter() {
super("X-Content-Type-Options", "nosniff");
}
}
public StaticHeadersWriter(String headerName, String... headerValues) {
this(Collections.singletonList(new Header(headerName, headerValues)));
}
b. XXssProtectionHeaderWriter
这个写入 X-XSS-Protection = 1;mode=block, 这个设置可以阻止用户在地址栏中执行插入的脚本,详细解释请自行百度
public void writeHeaders(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setHeader(XSS_PROTECTION_HEADER, headerValue);
}
c. CacheControlHeaderWriter
这个写入三个header, 分别是Cache-Control, Expires, Pragma
private static List<Header> createHeaders() {
List<Header> headers = new ArrayList<Header>(2);
headers.add(new Header(CACHE_CONTROL,
"no-cache, no-store, max-age=0, must-revalidate"));
headers.add(new Header(PRAGMA, "no-cache"));
headers.add(new Header(EXPIRES, "0"));
return headers;
}
d. HstsHeaderWriter
这个写入Strict-Transport-Security = “max-age=31536000;includeSubDomains”, 具体解释请自行百度
private static final String HSTS_HEADER_NAME = "Strict-Transport-Security";
public void writeHeaders(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
if (this.requestMatcher.matches(request)) {
response.setHeader(HSTS_HEADER_NAME, this.hstsHeaderValue);
}
else if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger
.debug("Not injecting HSTS header since it did not match the requestMatcher "
+ this.requestMatcher);
}
}
private void updateHstsHeaderValue() {
String headerValue = "max-age=" + this.maxAgeInSeconds;
if (this.includeSubDomains) {
headerValue += " ; includeSubDomains";
}
this.hstsHeaderValue = headerValue;
}
e.XFrameOptionsHeaderWriter
这个写入 X-Frame-Options = DENY, 这个响应头为了阻止CSRF 攻击,具体解释请自行百度
public enum XFrameOptionsMode {
DENY("DENY"), SAMEORIGIN("SAMEORIGIN"), ALLOW_FROM("ALLOW-FROM");
}
public void writeHeaders(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
if (XFrameOptionsMode.ALLOW_FROM.equals(frameOptionsMode)) {
String allowFromValue = allowFromStrategy.getAllowFromValue(request);
if (allowFromValue != null) {
response.setHeader(XFRAME_OPTIONS_HEADER,
XFrameOptionsMode.ALLOW_FROM.getMode() + " " + allowFromValue);
}
}
else {
response.setHeader(XFRAME_OPTIONS_HEADER, frameOptionsMode.getMode());
}
}
这个过滤器主要防止网站CSRF攻击, 具体逻辑看下面代码:
//通过HttpSessionCsrfTokenRepository.loadToken() 去session中
// 去加载 key = org.springframework.security.web.csrf.HttpSessionCsrfTokenRepository.CSRF_TOKEN
//的值
CsrfToken csrfToken = this.tokenRepository.loadToken(request);
final boolean missingToken = csrfToken == null;
if (missingToken) {
//如果session中不存在Csrf Token,则自动生成并存入tokenRepository中
csrfToken = this.tokenRepository.generateToken(request);
this.tokenRepository.saveToken(csrfToken, request, response);
}
//将csrfToken 加入request属性中
request.setAttribute(CsrfToken.class.getName(), csrfToken);
request.setAttribute(csrfToken.getParameterName(), csrfToken);
//如果request不需要csrf检查,则跳过这个filter
if (!this.requireCsrfProtectionMatcher.matches(request)) {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
// 从请求头不中获取csrf Token 的信息,
String actualToken = request.getHeader(csrfToken.getHeaderName());
if (actualToken == null) {
//如果请求头部不存在,再从请求参数中获取
actualToken = request.getParameter(csrfToken.getParameterName());
}
// 如果实际请求的csrf token 和repository中的token不一致,则拒绝访问
if (!csrfToken.getToken().equals(actualToken)) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Invalid CSRF token found for "
+ UrlUtils.buildFullRequestUrl(request));
}
if (missingToken) {
this.accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
new MissingCsrfTokenException(actualToken));
}
else {
this.accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
new InvalidCsrfTokenException(csrfToken, actualToken));
}
return;
}
首先根据请求url 是否匹配/logout 并且 requestMethod = Post 来判断是否需需要执行这个filter。
如果需要,看如下代码:
if (requiresLogout(request, response)) {
// 从SecurityContextHolder中获取当前登录用户的授权信息Authentication
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Logging out user '" + auth
+ "' and transferring to logout destination");
}
// this.handler = CompositeLogoutHandler, 它会遍历所有的LogoutHandler的实例,
//并执行他们各自的logout方法。 logoutHandler可在WebSecurityConfig配置
this.handler.logout(request, response, auth);
// logoutSuccessHandler 在所有logoutHandler执行完成后用户需要执行额外的逻辑
// 这个handler 也可以通过在WebSecurityConfig 配置
logoutSuccessHandler.onLogoutSuccess(request, response, auth);
return;
}
首先判断请求的url是否需要授权,默认执行AntPathRequestMatcher.matches(request)去验证。默认/login 才需要授权验证
public UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter() {
super(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/login", "POST"));
}
如果是/login访问,则首先调用 attempAuthentication(request,response)方法尝试获取Authentication.
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(
"Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
String password = obtainPassword(request);
if (username == null) {
username = "";
}
if (password == null) {
password = "";
}
username = username.trim();
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
username, password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
获取Authentication的主要逻辑在这句话中
this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
this.getAuthenticationManager()返回的是ProviderManager对象, 接下来看ProviderManager 是如何实现authenticate 方法的:
首先在ProviderManager中要获取AuthenticationProvider, 第一个ProviderManager找到的是AnonymousAuthenticationProvider,它的父ProviderManager找到的是DaoAuthenticationProvider
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
Authentication result = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
// 当前的toTest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,
// 所以只有支持这个token的authenticationProvider才能执行authenticate()
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
.............
//如果当前的providerManager 没有找到合适AuthenticateProvider ,则从父的providerManager中查找
if (result == null && parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
result = parent.authenticate(authentication);
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException e) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
}
......................
.........................
}
DaoAuthenticationProvider:
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
// Determine username
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
//查找用户,通过userDetailsService 接口查找user ,
//用户可自己实现UserDetailsService接口的loadUserByUsername();
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
....................
try {
//预检查user 的 授权信息, 比如用户是否账号被锁,用户账号是否可用,用户账号是否过期
preAuthenticationChecks.check(user);
//密码MD5校验
additionalAuthenticationChecks(user,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
}
....................
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
createSuccessAuthentication()
private GrantedAuthoritiesMapper authoritiesMapper = new NullAuthoritiesMapper();
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal,
Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) {
// Ensure we return the original credentials the user supplied,
// so subsequent attempts are successful even with encoded passwords.
// Also ensure we return the original getDetails(), so that future
// authentication events after cache expiry contain the details
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
principal, authentication.getCredentials(),
// user.getAuthorities()返回的是GrantedAuthority
authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails());
return result;
}
authoritiesMapper有三种实现: NullAuthorititesMapper(默认),RoleHierarchyAuthoritiesMapper,SimpleAuthorityMapper
接下来执行successfulAuthentication()来更新SecurityContextHolder中Authentication的信息
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Authentication success. Updating SecurityContextHolder to contain: "
+ authResult);
}
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult);
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
// Fire event
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(
authResult, this.getClass()));
}
//最后调用sucessHandler 来处理 authentication成功之后的跳转逻辑
successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}
@Override
public HttpServletRequest create(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
//this.rolePrefix == “ROLE_“
return new Servlet3SecurityContextHolderAwareRequestWrapper(request,
this.rolePrefix, response);
}
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
// 这里创建一个匿名的AuthenticationToken : AnonymousAuthenticationToken
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(
createAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) req));
}
static final String FILTER_APPLIED = "__spring_security_session_mgmt_filter_applied";
if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
else{
//如果HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository中没有这次请求对应的securityContext
if (!securityContextRepository.containsContext(request)) {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication();
//如果在SecurityContextHolder上下文中存在Authentication信息并且不是匿名的,
//证明这个用户在当前请求中已经被授权了,可只见调用sessionAuthenticationStrategy重新绑定request
//对应的authentication, RegisterSessionAuthenticationStrategy会调用
// sessionRegistry.registerNewSession(request.getSession().getId(),authentication.getPrincipal());
if (authentication != null && !trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication)) {
// The user has been authenticated during the current request, so call the
// session strategy
try {
sessionAuthenticationStrategy.onAuthentication(authentication,
request, response);
}
catch (SessionAuthenticationException e) {
// The session strategy can reject the authentication
logger.debug(
"SessionAuthenticationStrategy rejected the authentication object",
e);
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, e);
return;
}
// Eagerly save the security context to make it available for any possible
// re-entrant
// requests which may occur before the current request completes.
// SEC-1396.
securityContextRepository.saveContext(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(),
request, response);
}
else {
// No security context or authentication present. Check for a session
// timeout
if (request.getRequestedSessionId() != null
&& !request.isRequestedSessionIdValid()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Requested session ID "
+ request.getRequestedSessionId() + " is invalid.");
}
if (invalidSessionStrategy != null) {
invalidSessionStrategy
.onInvalidSessionDetected(request, response);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
如果在上述过滤器中出现Exception,都会在这个过滤器中拦截并跳转执行 handleSpringSecurityException()方法

