1、类加载器的创建
JAR 启动是由系统类加载器加载 JarLauncher 启动的,因此在JarLauncher 的main方法中,可以看到
public class JarLauncher extends ExecutableArchiveLauncher {static final String BOOT_INF_CLASSES = "BOOT-INF/classes/";static final String BOOT_INF_LIB = "BOOT-INF/lib/";public JarLauncher() {}protected JarLauncher(Archive archive) {super(archive);}@Overrideprotected boolean isNestedArchive(Archive.Entry entry) {if (entry.isDirectory()) {return entry.getName().equals(BOOT_INF_CLASSES);}return entry.getName().startsWith(BOOT_INF_LIB);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {new JarLauncher().launch(args);}}
调用的JarLauncher的无参构造器,JarLauncher 继承 ExecutableArchiveLauncher ,并调用 ExecutableArchiveLauncher的无参构造函数方法, 该方法中调用 createArchive 尝试构造 Archive,Archive 是压缩,存档的意思。
public ExecutableArchiveLauncher() {try {this.archive = createArchive();}catch (Exception ex) {throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}}protected final Archive createArchive() throws Exception {ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = getClass().getProtectionDomain();CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource();URI location = (codeSource != null) ? codeSource.getLocation().toURI() : null;// 这里的path指的就是启动的绝对路径String path = (location != null) ? location.getSchemeSpecificPart() : null;if (path == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive");}// 判断该JAR文件是否存在File root = new File(path);if (!root.exists()) {throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive from " + root);}// 如果是目录的话,构造的是展开的归档,否则就是JAR的归档return (root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root) : new JarFileArchive(root));}
在构造 JarLauncher 完成之后,会创建一个归档,然后执行JarLauncher 的launch() 方法
protected void launch(String[] args) throws Exception {JarFile.registerUrlProtocolHandler();// 重点 创建自定义的构造器,getClassPathArchives返回了classes目录和多个内部Lib的信息ClassLoader classLoader = createClassLoader(getClassPathArchives());launch(args, getMainClass(), classLoader);}// getClassPathArchives 方法是ExecutableArchiveLauncher的一个方法,返回的是是JAR和classes嵌套目录// 这里调用了 getClassPathArchives,这个方法是子类实现的方法,内容如下,标识是否是嵌套的Archiveprotected ClassLoader createClassLoader(List<Archive> archives) throws Exception {// 根据类路径的数据,创建等同大小的集合并搜索URLList<URL> urls = new ArrayList<>(archives.size());for (Archive archive : archives) {urls.add(archive.getUrl());}// urls 形式如同// jar:file:/Users/zhoutao/workspace/MyGithub/SpringBoot/build/libs/springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar!/BOOT-INF/classes!/// jar:file:/Users/zhoutao/workspace/MyGithub/SpringBoot/build/libs/springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar!/BOOT-INF/lib/spring-boot-starter-web-2.2.6.RELEASE.jar!/return createClassLoader(urls.toArray(new URL[0]));}/*** Create a classloader for the specified URLs.* @param urls the URLs* @return the classloader* @throws Exception if the classloader cannot be created*/protected ClassLoader createClassLoader(URL[] urls) throws Exception {// 创建自定义类加载器 LaunchedURLClassLoader ,这和上篇文章中打印出来的加载器一致// 显然这也是符合类的双亲委派机制,显然这里LaunchedURLClassLoader的父级类加载器为应用类加载器return new LaunchedURLClassLoader(urls, getClass().getClassLoader());}
最终自定义的CLassLoader创建完成之后,我们在调试界面可以看到如下内容,可以看到新的类加载器为LauncherURLClassLoader ,其父类为常规的应用类加载器,应用类加载器的父类为拓展类加载器。所以SpringBoot的类加载器也是符合双亲委派机制的。
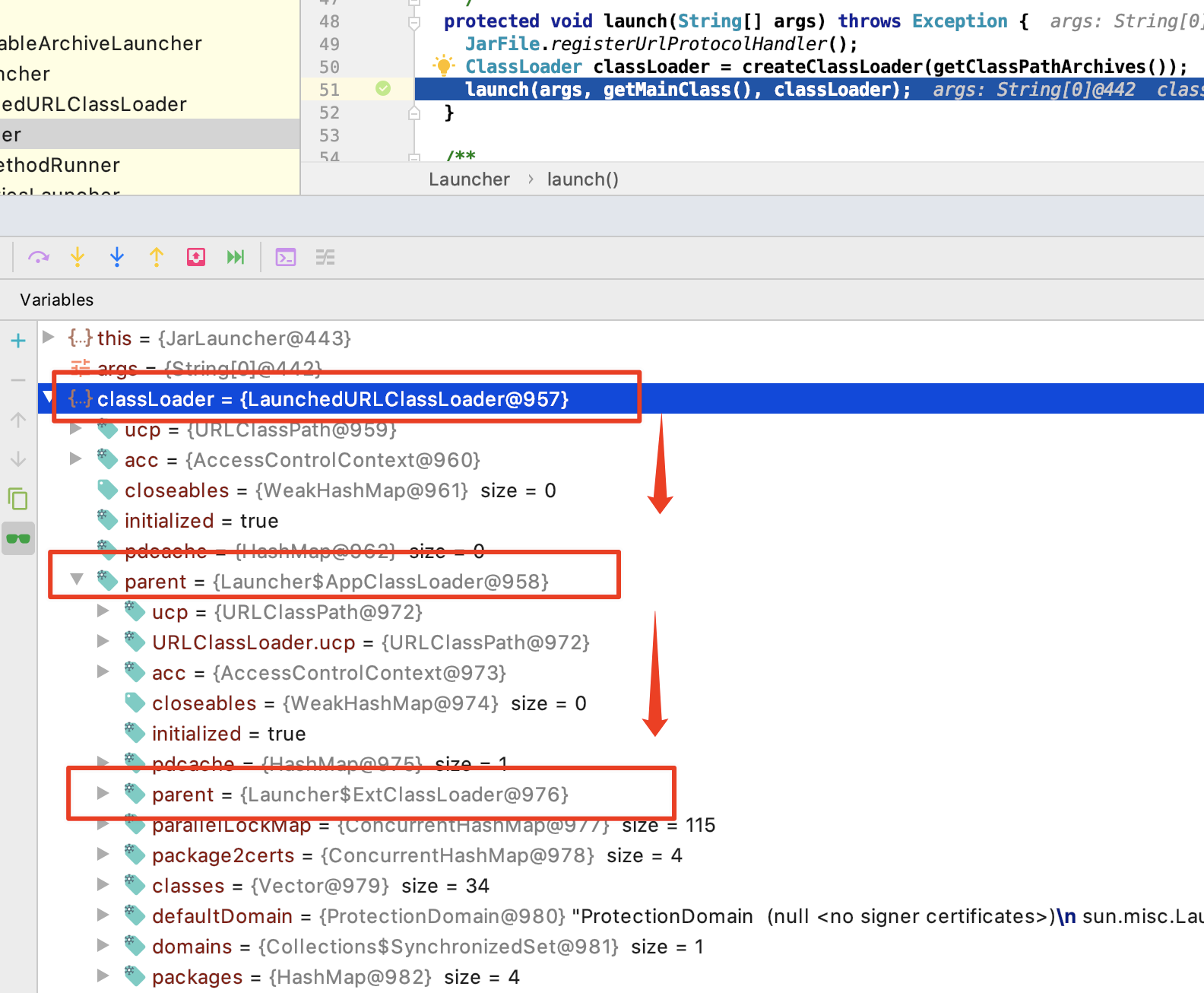
2、启动luancher方法
在创建类加载器完成之后,程序继续运行,调用getMainClass() 方法,这个方法是获取JAR文件中MAINFEST.MF 文件中的Start-class 属性,也就是启动的类名。
@Overrideprotected String getMainClass() throws Exception {Manifest manifest = this.archive.getManifest();String mainClass = null;if (manifest != null) {mainClass = manifest.getMainAttributes().getValue("Start-Class");}if (mainClass == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("No 'Start-Class' manifest entry specified in " + this);}// 此时值为: com.zhoutao123.spring.springboot.SpringbootApplicationreturn mainClass;}/* MAINFEST.MF 内容如下$ cat ./build/libs/springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT/META-INF/MANIFEST.MFManifest-Version: 1.0Start-Class: com.zhoutao123.spring.springboot.SpringbootApplicationSpring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/Spring-Boot-Version: 2.2.6.RELEASEMain-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher */
获取到启动类的全类名之后,继续调用 launch(String[] args, String mainClass, ClassLoader classLoader) 方法,并尝试创建 MainMethodRunner 对象
/*** Launch the application given the archive file and a fully configured classloader.* @param args the incoming arguments* @param mainClass the main class to run* @param classLoader the classloader* @throws Exception if the launch fails*/protected void launch(String[] args, String mainClass, ClassLoader classLoader) throws Exception {Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);createMainMethodRunner(mainClass, args, classLoader).run();}/*** Create the {@code MainMethodRunner} used to launch the application.* @param mainClass the main class* @param args the incoming arguments* @param classLoader the classloader* @return the main method runner*/protected MainMethodRunner createMainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args, ClassLoader classLoader) {return new MainMethodRunner(mainClass, args);}/** MainClass 值得调用就是Start-class的main()方法在run方法中通过 反射获取main方法,然后将args参数传递,并调用 mainMethod.invoke 指定StartClass的main方法*/public class MainMethodRunner {private final String mainClassName;private final String[] args;/*** Create a new {@link MainMethodRunner} instance.* @param mainClass the main class* @param args incoming arguments*/public MainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args) {this.mainClassName = mainClass;this.args = (args != null) ? args.clone() : null;}public void run() throws Exception {Class<?> mainClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(this.mainClassName);Method mainMethod = mainClass.getDeclaredMethod("main", String[].class);// 调用静态方法(也就是类的方法,而非实例的方法,instance可以不需要,设置为null即可)mainMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { this.args });}}
需要注意的是launcher 方法中
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);将自定的classLoader设置为当前上下文类加载器,然后Class<?> mainClass = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().loadClass(this.mainClassName);获取到了类加载器,加载MainClass 这里也在一次说明了SpringBoot应用的加载器确实是SpringBoot的自定义类加载器而非JDK的应用类加载器

