前言
CopyOnWriteArrayList 是 ArrayList 的线程安全版本,内部也是通过数组实现,每次对数组的修改都会完全拷贝一份新的数组来修改,修改完之后再替换到老数组,这样保证了只阻塞写操作,不阻塞读操作。
为了防止并发修改导致的数组错误,写操作必须加锁,读操作不用加锁。
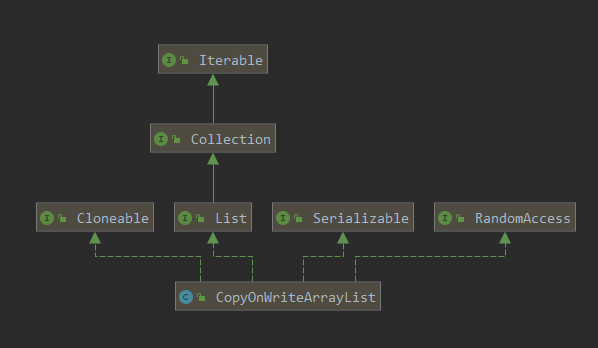
CopyOnWriteArrayList 类结构图
源码分析
成员变量
CopyOnWriteArrayList 的成员变量就只有两个,而且连最基本的 size 属性都没有。这是因为每次写操作时会复制一份新的数组,只需要让新的数组长度加 1 即可。
/** 用于修改时加锁 */final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();/** 保存元素的数组,仅通过 getArray/setArray 方法访问*/private transient volatile Object[] array;
构造方法
public CopyOnWriteArrayList() {// 所有对array的操作都是通过setArray()和getArray()进行setArray(new Object[0]);}final void setArray(Object[] a) {array = a;}public CopyOnWriteArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {Object[] elements;if (c.getClass() == CopyOnWriteArrayList.class)elements = ((CopyOnWriteArrayList<?>)c).getArray();else {elements = c.toArray();// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elements.getClass() != Object[].class)elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, elements.length, Object[].class);}setArray(elements);}
add
添加前给程序加锁,新建一个数组,并把所有的元素复制到新数组中。然后把需要添加的元素添加到新数组的尾部,最后释放锁。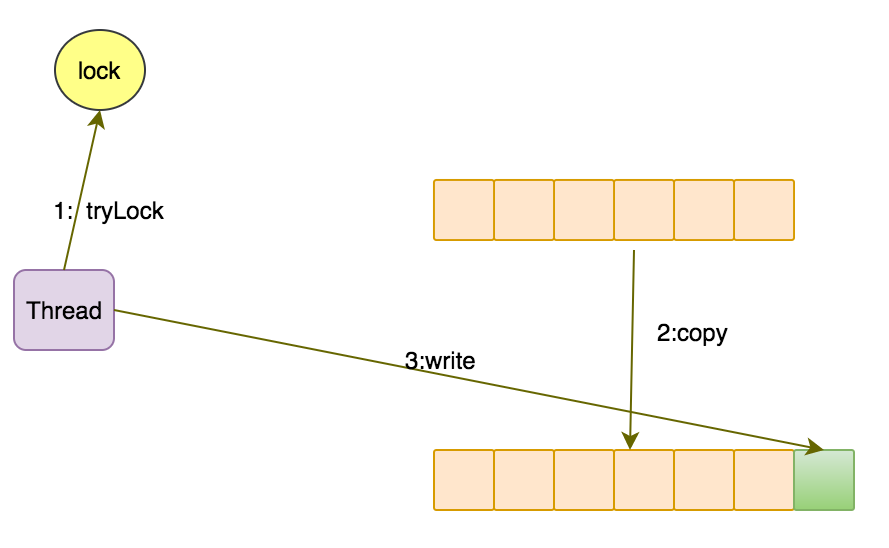
/*** Appends the specified element to the end of this list** @param e element to be appeded to this list* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/@Overridepublic boolean add(E e) {/*** 增加元素 e 到数组的末尾* 操作步骤:* 1. 获取全局的 reentrantLock* 2. 将原来的 array1 copy 到一个 array.length + 1 的数组 array2 里面* 3. 将 先添加的元素e添加到新数组 array2 的最后一个空间里面 (array2[array2.length - 1] = e)* 4. 将 新数组 array2 赋值给 CopyOnWriteArrayList 中的 array*/final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock(); // 1. 获取 全局 locktry{Object[] elements = getArray(); // 2. 获取原来的数组int len = elements.length;Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); // 3. 新建一个 array2 将原来的数据赋值到这个新建的数组里面newElements[len] = e; // 4. 将 e 赋值给 array2的最后一个空间里面setArray(newElements); // 5. 将新数组 array2 赋值给 CopyOnWriteArrayList 中的 arrayreturn true;}finally {lock.unlock(); // 6. 释放锁}}
Arrays#copyOf
copyOf 内部调用了 System.arraycopy 方法。
copyOf 在内部新建一个数组,并从原数组中复制一份,指定新数组长度(newLength),最后返回新数组。
方法参数:
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| original | 要复制的数组 |
| newLength | 要返回的副本的长度 |
| newType | 要返回的副本的类型 |
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)? (T[]) new Object[newLength]: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,Math.min(original.length, newLength));return copy;}
添加元素到数组的指定位置
/*** Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this* list. Shifts the lement currently at that position (if any) and* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices)*/@Overridepublic void add(int index, E element) {/*** 将元素 e 插入到数组 指定的索引下标 index 下* 操作步骤:* 1. 获取全局的锁* 2. 获取 CopyOnWriteArrayList 的 array, 及 array.length* 3. 进行参数校验 (index > len || index < 0) 则直接抛异常 -> 说明元素的插入只能在 0 - array.length 之间(包含两个端点)* 4. 获取插入点 index 与 array.length 之间的步长, 进行分类讨论* 1) 插入的数据正好在 原array数组的后一个节点 (numMoved = len), 则直接新建一个 array, 将原来的 array copy 过来* 2) 插入的 index 满足 0 <= index <= len - 1, 则新建一个数组, 原来 o -> index(index不包含) 拷贝来, index后面的数据拷贝到新数组的 index + 1 的空间* 5. 将 e 设置到 新 array 的 index 位置* 6. 将 新 array 设置到 CopyOnWriteArrayList 里面*/final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock(); // 1. 获取全局的锁try{Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;if(index > len || index < 0){throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index + ", Size:" + len);}Object[] newElements;int numMoved = len - index;if(numMoved == 0){ // 走到这一步, 说明 数据是插入到 oldArray.length(这个值是指下标) 位置上的元素newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); // 直接拷贝原数组到一个新的 array 数组中, 这个数组的长度是 len + 1}else{newElements = new Object[len + 1];System.arraycopy(elements, 0, newElements, 0, index); // 将原数组 index 前的数组都拷贝到新的数组里面System.arraycopy(elements, index, newElements, index + 1, numMoved); // 将原数组 index 以后的元素都 copy到新的数组里面(包括index位置的元素)}newElements[index] = element; // 将 index 赋值 elementsetArray(newElements); // 将 新的 array set到 CopyOnWriteArrayList 上}finally {lock.unlock();}}
remove
删除指定索引 index 上的元素。
/*** Removes the element at the specified position in this list.* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their* indices). Returns the lement that was removed from the list*/@Overridepublic E remove(int index) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try{Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;E oldValue = get(elements, index);int numMoved = len - index - 1;if(numMoved == 0){ // 说明删除的元素的位置在 len - 1 上, 直接拷贝原数组的前 len - 1 个元素setArray(Arrays.copyOf(elements, len - 1));}else{Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1];System.arraycopy(elements, 0, newElements, 0, index); // 拷贝原数组 0 - index之间的元素 (index 不拷贝)System.arraycopy(elements, index + 1, newElements, index, numMoved); // 拷贝原数组 index+1 到末尾之间的元素 (index+1也进行拷贝)setArray(newElements);}}finally {lock.unlock();}return null;}
直接删除
直接删除的方式比较复杂。先要找到元素在数组中的索引,根据索引去删除对应位置的元素。
根据对象的值去查找元素需要遍历数组,所以这在大数组中是个耗时的操作,而且遍历的时候并不会加锁,所以得到数组的索引后再加锁,这个元素也有可能被其它线程修改。为了使程序正常运行,所以后面会加上 snapshot != current 的判断,如果数组发生变化,重新计算索引在新数组中位置。
public boolean remove(Object o){Object[] snapshot = getArray();// 获取 index 在 snapshot 中的位置, -1 表示不存在int index = indexOf(o, snapshot, 0, snapshot.length);return (index < 0) ? false : remove(o, snapshot, index);}/*** A version of remove(Object) using the strong hint that given* recent snapshot contains o at the given index*/private boolean remove(Object o, Object[] snapshot, int index){final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {Object[] current = getArray();int len = current.length;// findIndex: <- 这个用法平时用的比较少, 在这里, 只要 break findIndex, 那 if(snapshot != current) 这里括号里面的其他代码就不执行了, 直接跳到括号外面, 建议写个小demo试一下if(snapshot != current) findIndex:{ // snapshot != current 表示数组被另外一个线程操作过, 有变化/*** 下面的操作是发生在 调用方法 "remove(Object o)" 中的 "indexOf"后 , 数组 array 发生变化而做的查询修正工作* 主要分 下面 4 中情况:* 1. 从 index,len 中取出一个较小的值 prefix, 从 current的prefix前个元素中寻找元素 o, 找到后, 直接 break, 执行下面的操作* 2. 若 index >= len, 则说明 元素 o 在另外的线程中已经被删除, 直接 return* 3. current[index] = o, 则说明, index 位置上的元素 o 还在那边, 直接 break* 4. 最后 在 index 与 len 之间寻找元素, 找到位置直接接下来的代码, 没找到 直接 return*/int prefix = Math.min(index, len);for(int i = 0; i < prefix; i++){// 找出 current 数组里面 元素 o 所在的位置 i, 并且赋值给 indexif(current[i] != snapshot[i] && eq(o, current[i])){index = i;break findIndex;}}if(index >= len){ // index >= len 表示元素 o 已经被删除掉return false;}if(current[index] == o){ // 元素 o 也在数组 current 的 index 位置break findIndex;}index = indexOf(o, current, index, len); // 在 current 中寻找元素 o 所在的位置 (这里不会出现 index > len 的情况, 上面的代码中已经做了判断)if(index < 0){ // 要删除的元素 在另外的线程中被删除掉了, 直接 return falsereturn false;}}Object[] newElements = new Object[len - 1]; // 新建一个 len - 1 长度的数组System.arraycopy(current, 0, newElements, 0, index); // 拷贝老数组前 index 个元素System.arraycopy(current, index + 1, newElements, index, len - index - 1); // 拷贝 老数组 index + 1 后的元素 ( index + 1 包含)setArray(newElements);return true;}finally {lock.unlock();}}
元素替换 set 方法
/*** Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the* specified element*/@Overridepublic E set(int index, E element) {/*** 将数组 array 指定位置 index 用元素 element 进行替代* 操作步骤:* 0. 获取全局的 ReentrantLock* 1. 获取数组指定下标 index 上的元素* 2. 判断 element 是否与来源数组中的元素一致* 1) 不一致, 则获取原数组的 一个 snapshot, 并且将对应位置 index 进行替换* 2) 一致, setArray(elements) <- 这个其实是说明都没做* 3. 在 finally 中释放 锁**/final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock(); // 0. 获取锁try {Object[] elements = getArray();E oldValue = get(elements, index); // 1. 获取原数组中对应index位置的元素if(oldValue != element){int len = elements.length;Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len); // 2. 获取原数组的一个 snapshot 版本newElements[index] = element; // 3. 在 index 位置进行 set 新的值setArray(newElements); // 4. 将 snapshot 版本的数组覆盖原来的数组}else{// Not quite a no-op; ensures volatile write semanticssetArray(elements);}}finally {lock.unlock(); // 5. 释放锁}return null;}