字符串散列
强大的算法将帮助您进行有关 String 操作的采访。
字符串哈希是一种将字符串转换为哈希数的技术。我们为什么需要那?有时我们需要比较大的字符串,但是相反,我们可以比较生成的哈希值来比较字符串。
想象一下,您必须比较下两个字符串:
const A = "imagine that this is a string of 200 characters"const B = "imagine that this is a string of 200 characterz"`
两个字符串都有 200 个字符。暴力匹配是比较每个字符并查看它们是否匹配。就像是:
const A = "imagine that this is a string of 200 characters"const B = "imagine that this is a string of 200 characterz"function equal(A, B) {let i;for(i = 0; i < A.length; i++){if (A[i] !== B[i]) {return false;}}return true;}console.log(equal(A,B));`
由于它的O(min(A, B))性能,这对于大字符串不是最佳的。
当然,我们可以O(n)通过添加一个比较 A 大小和 B 大小的条件来做到这一点。就像是:
function equal(A, B) {if (A.lenght !== B.length) return false;let i;for(i = 0; i < A.length; i++){if (A[i] !== B[i]) {return false;}}return true;}`
就像我说的那样,最糟糕的情况是O(n),但是可以想象我们必须比较一个非常大的字符串。
字符串散列是一种技术,我们可以将字符串转换为将用作哈希数的整数。因此,我们将比较hash(A) == hash(B)这将要考虑的两个散列O(1)。这是比较两个字符串的最佳选择。
字符串哈希公式
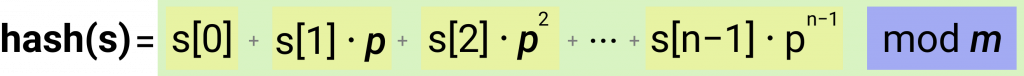
其中p和m是质数,并且s[0], s[1], s[2]...是每个字符的值,在这种情况下为 char 码。
p: 它是一个质数,大约等于所用不同字符的数量。例如,如果我们要计算仅包含英文字母小写字符的单词的哈希值,则31是一个很好的数字。但是,如果我们将大写字母包括在内,则53是一个合适的选项。
m: 这个数字越大,我们碰撞两个随机字符串的机会就越少。此变量也应该是质数。10 ^ 9 + 9是常见的选择。
让我们使用以下数据:
p = 31m = 1e9 + 9word = 'apple'`
我们想知道单词的哈希码是什么apple,因此,如果将数据添加到公式中,我们将得到以下内容:

然后

然后我们得到了 char 代码:
"a" = 97"p" = 112"p" = 112"l" = 108"e" = 101`
并将其替换为公式:

然后我们减少公式:

最后

JavaScript 的实现
function hash(word) {var p = 31;var m = 1e9 + 9;var hash_value = 0;for(var i = 0; i < word.length; i++) {var letter = word[i];var charCode = letter.charCodeAt();hash_value = hash_value + (charCode * Math.pow(p, i))}return hash_value % m;}console.log(hash("apple"));`
Java实现
private long hash(String word) {int p = 31;long m = (long) (Math.pow(10, 9) + 9);long hashValue = 0;char[] chars = word.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {char letter = chars[i];hashValue = (long) (hashValue + (letter * Math.pow(p, i)));}return hashValue % m;}

