图-graph
组成:节点(Vertex),边(Edge)
有向图/无向图
常见的图
(1)图像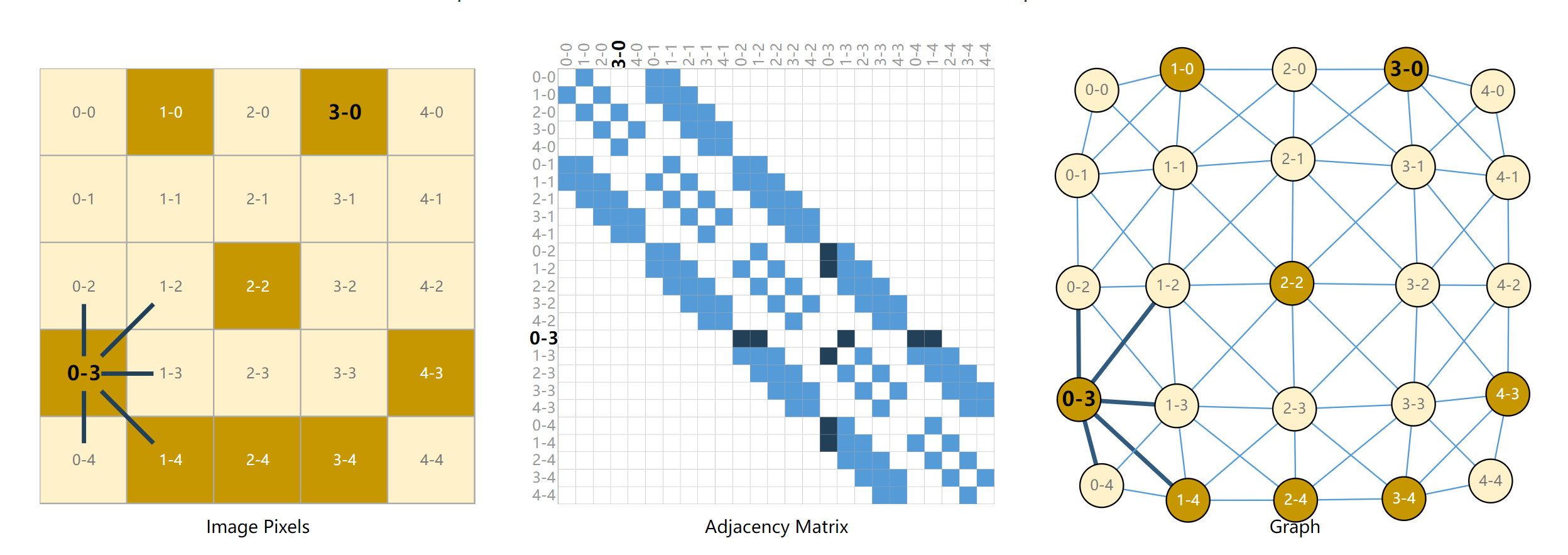
(2)文本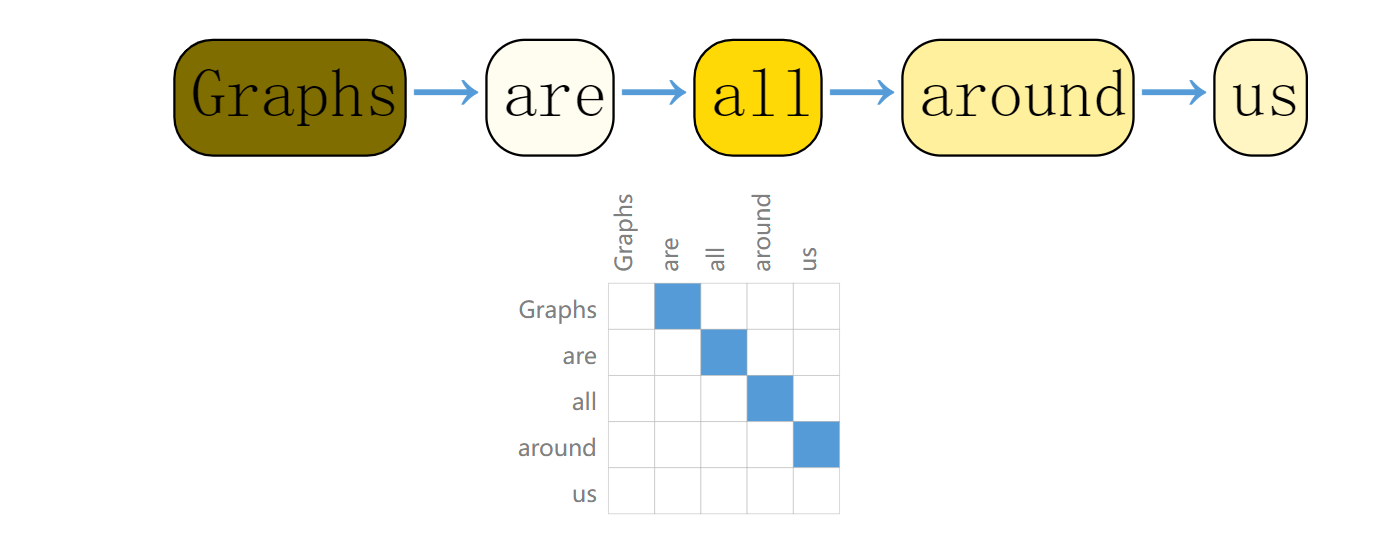
(3)分子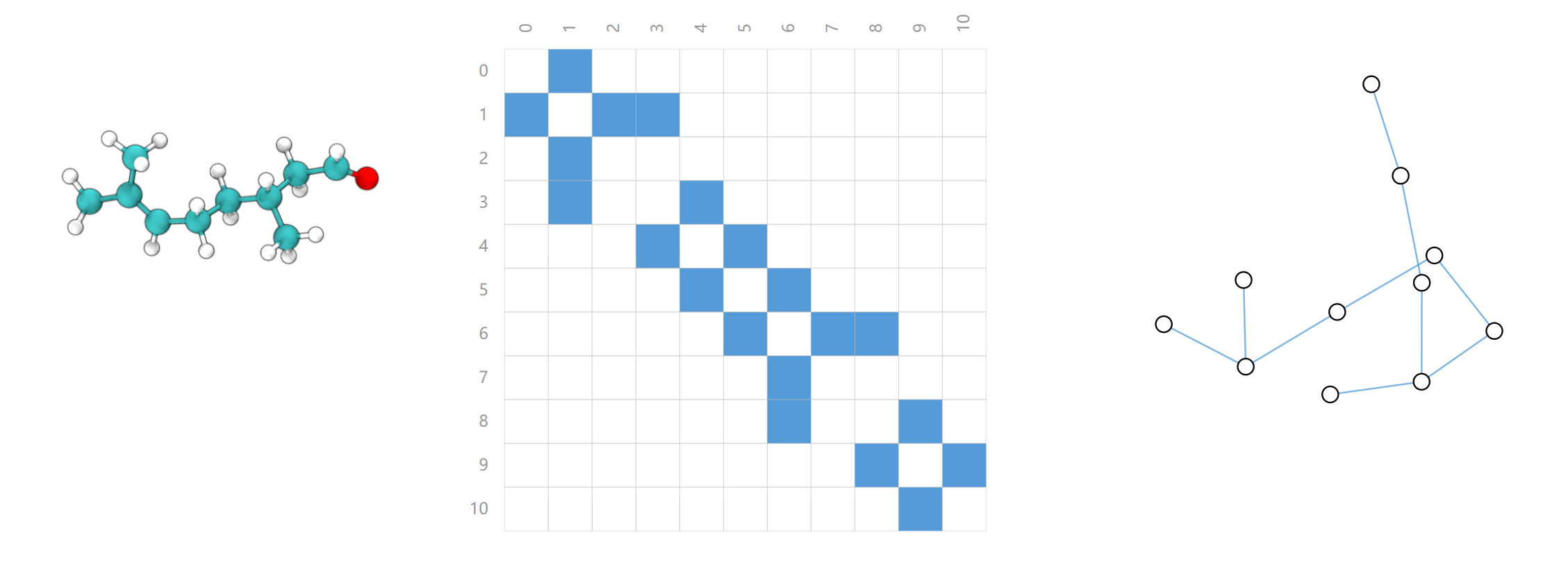
(4)社交网络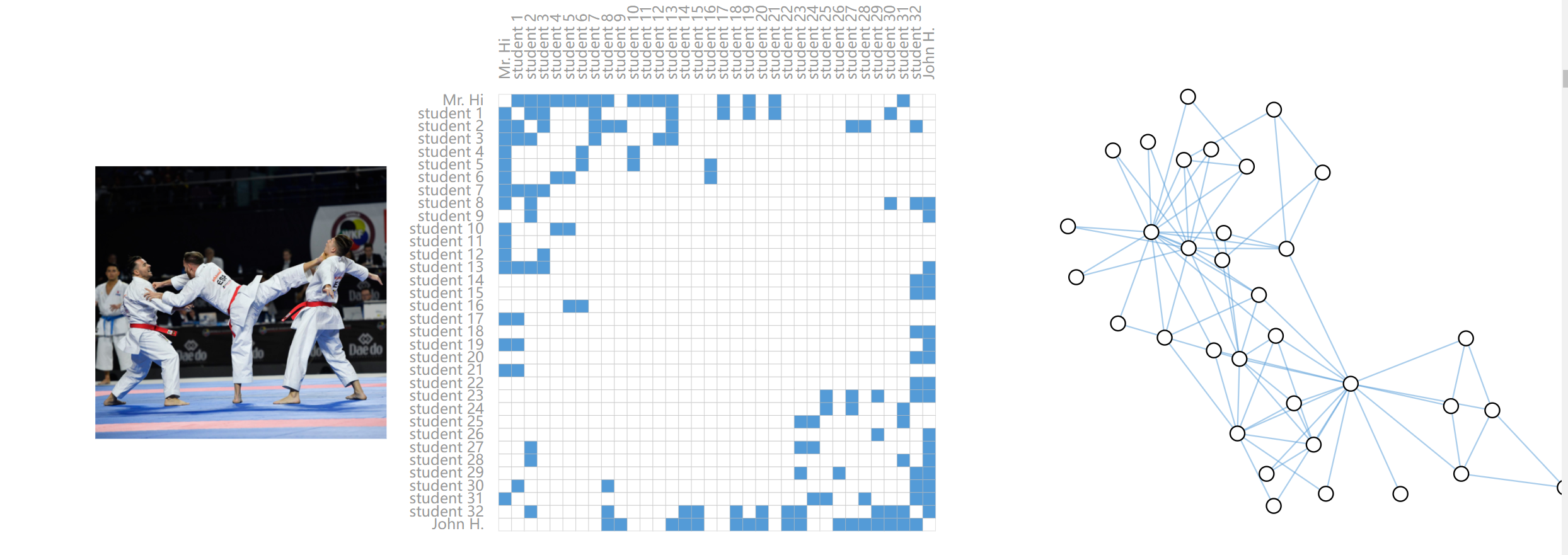
图的主要特性
基于图模型可以执行三种预测任务:graph-level, node-level, and edge-level
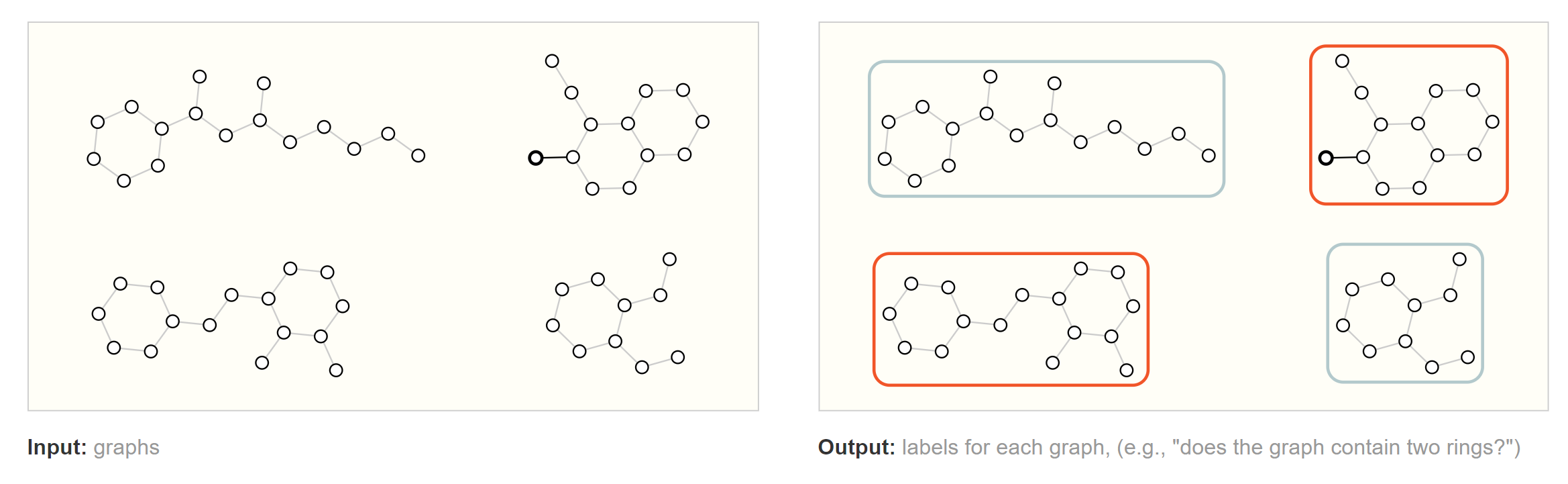
图级别的任务
预测整个图级别的属性
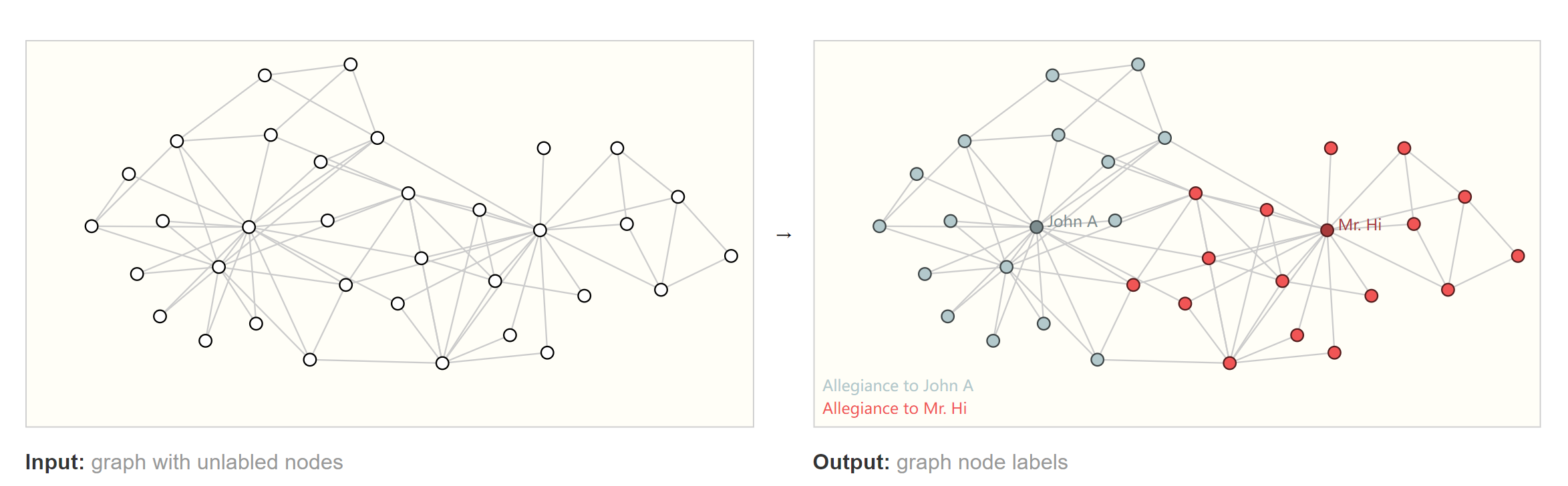
节点级别任务
预测每一个节点的身份或角色
边级别任务
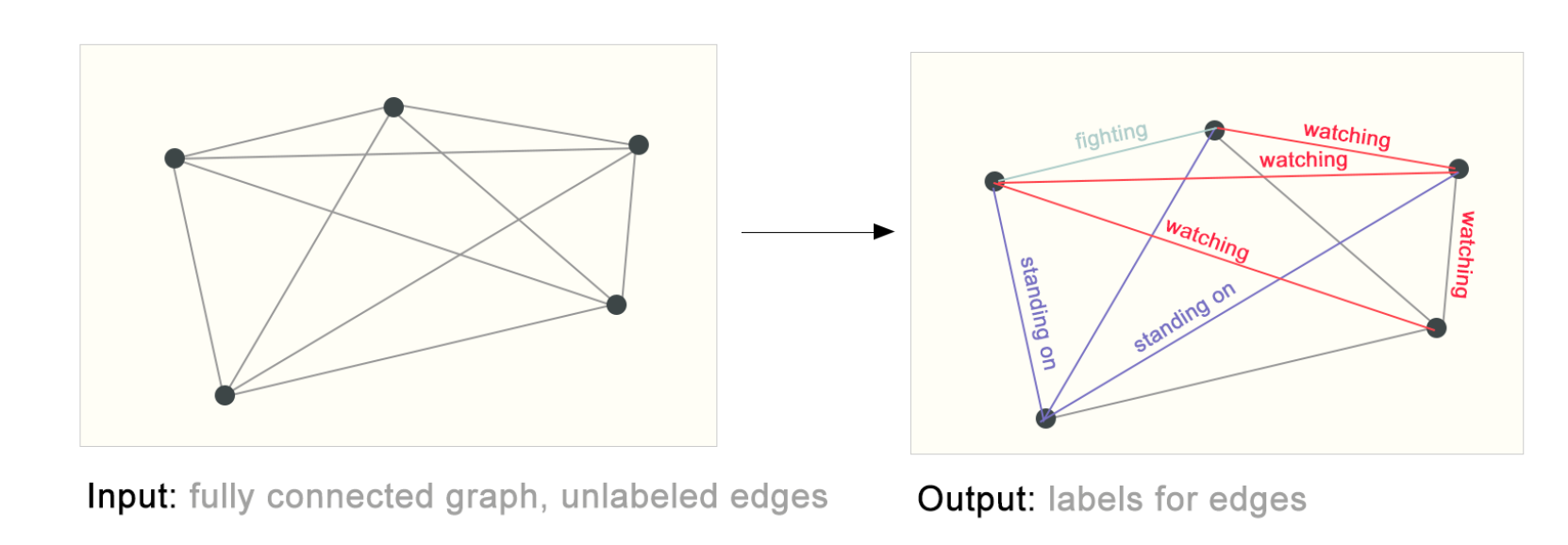
关系预测
GNN
定义:可优化的图变换,包括图的节点,边和全局属性,同时保持图的几何结构不变
最简单的GNN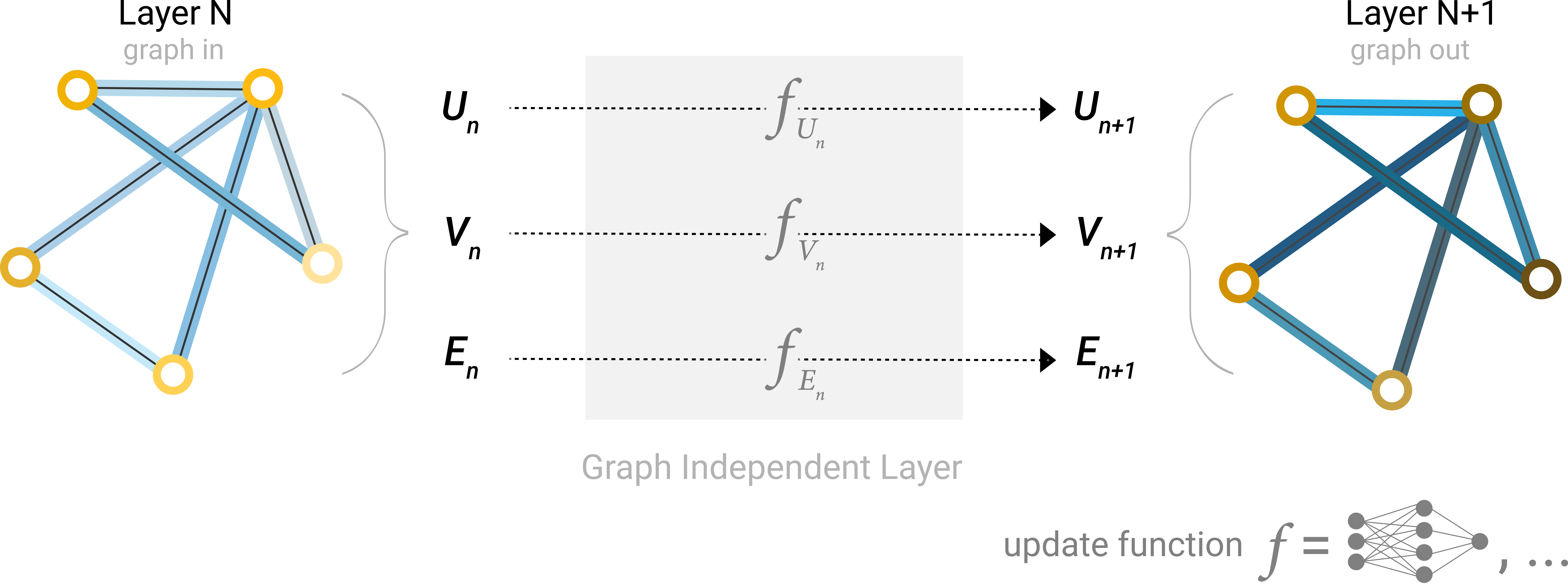
二分类问题
对每一个节点采用线性分类器
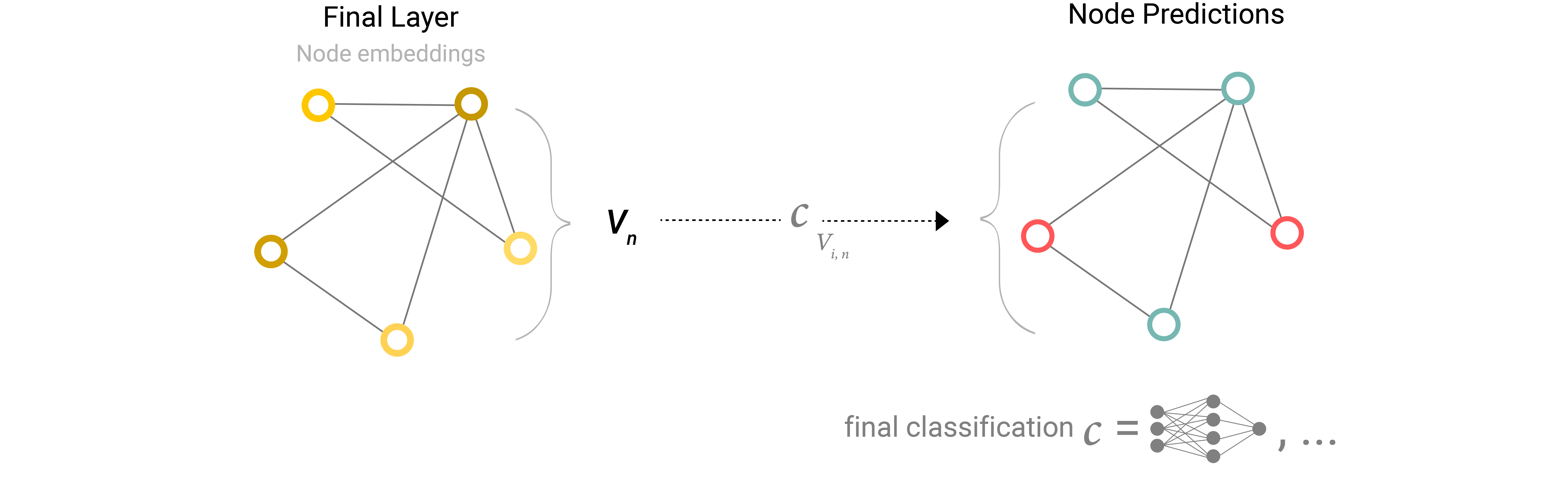
有些信息只保存在图的边上,节点上无信息,这个时候如果要对节点执行预测,需要有一种方式来收集边上的信息,叫做池化(Pooling),池化分为两步:
- For each item to be pooled, gather each of their embeddings and concatenate them into a matrix.
- The gathered embeddings are then aggregated, usually via a sum operation.
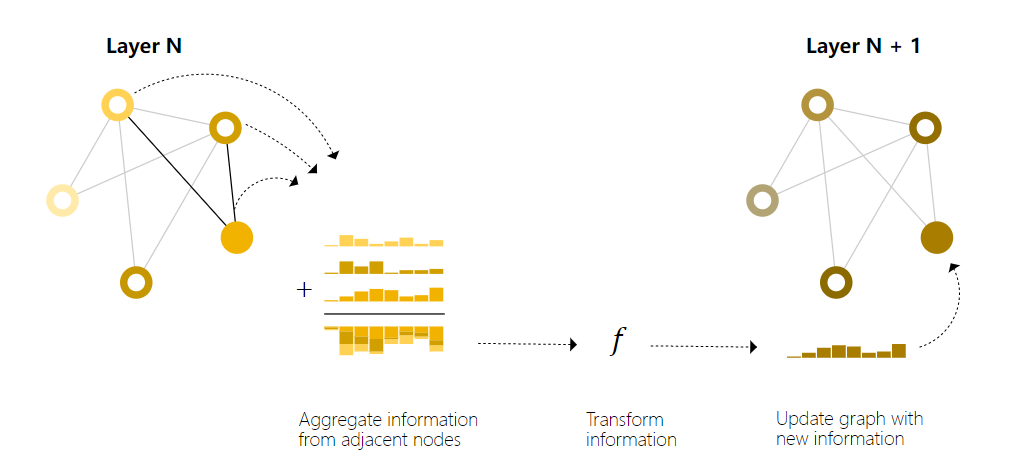
消息传递(message passing)
邻接节点,边相互交换信息,可以理解为信息聚合和计算
- For each node in the graph, gather all the neighboring node embeddings (or messages), which is the gg function described above.
- Aggregate all messages via an aggregate function (like sum).
- All pooled messages are passed through an update function, usually a learned neural network.
图卷积
图注意力网络