Java.lang提供Java语言程序设计的基础类,可以不通过import直接使用。
Object
Java中处理基本类型,剩下的都是对象。Object类是所有类的超类,所有对象都继承了Object的方法,必要时可以重写这些方法。
public class Object {private static native void registerNatives();static {registerNatives();}/*** equals* ‘==’ 对于基本数据类型,比较的是其值是否相等;对于引用类型则比较是否为同一对象* 如果没有对equals进行重写,则使用的是object中的equals方法,比较是否为同以对象*/public boolean equals(Object obj) {return (this == obj);}/*** System.out.print打印命令会调用toString方法*/public String toString() {return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode());}/*** finalize* 对象被GC回收时会调用的方法*/protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }/*** Causes the current thread to wait until either another thread invokes the* notify() or notifyAll() method for this object or* a specified amount of time has elapsed* The current thread must own this object's monitor.*/public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;/*** Wakes up a single thread that is waiting on this object's monitor.** This method should only be called by a thread that is the owner* of this object's monitor.*/public final native void notify();/*** Wakes up all threads that are waiting on this object's monitor. A* thread waits on an object's monitor by calling one of the* {@code wait} methods.*/public final native void notifyall();/*** getClass()* 返回该对象的类对象*/public final native Class<?> getClass();/*** hashCode* 根据对象内存地址或者字符串或者数字算出来int类型的数值*/public native int hashCode();/*** clone* 该对象需要实现Cloneable接口,否则会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常* Object实现的clone(super.clone)方法为浅克隆,只能克隆对象本身和对象中的基本变量;* 如果要克隆引用对象,需要自己实现。* https://www.jianshu.com/p/ea8f7b1fbbb1*/protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;}
MATH
- floor
- ceil
- round
String
String对象保存在堆中,当以引号出现的时候保存在StringPool中
java.lang.string
- string.substring() 获取子串
- String join(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence… elements)
- char[] toCharArray()
- boolean equals(0bject other)
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String other)
- char string.charAt()
- boolean startsWith(String prefix)
- boolean endsWith(String suffix)
- String trim()
- intern() 将字符放入StringPool中,如果调用的字符“abc”已经在池中,则返回池中的字符串地址。否则,新建一个常量加入池中,并返回地址
System
System类由final修饰,不能被继承;构造器由private修饰,不允许被实例化,方法都是static修饰的静态方法。
- 标准输入输出流
- public final static InputStream in 标准输入流
- public final static PrintStream out 标准输出流
- public final static PrintStream err 标准错误输出流
- arraycopy,数组复制
- exit() 退出虚拟机
- System.currentTimeMillis, 获取系统当前时间
- System.gc(), 主动进行垃圾回收
- System.getProperties(), 获取系统属性,包括Java工作目录,os架构,jvm版本等信息
Exception
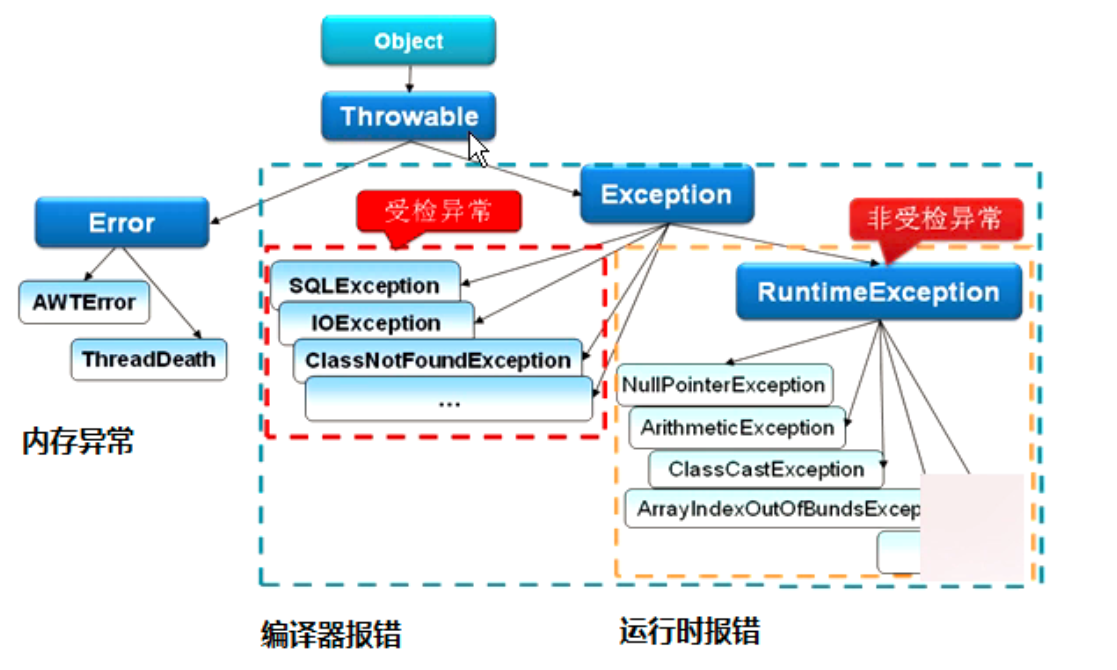
- Throwable
- Exceptrion
- 可查异常,在代码中必须被捕获,不然编译器会报错,要求在方法的末尾表明可能抛出的异常。
- 运行时异常 ,不要求强制捕获,之所以会设计运行时异常的原因之一,是因为下标越界,空指针这些运行时异常太过于普遍,如果都需要进行捕捉,代码的可读性就会变得很糟糕。
- Exceptrion
- Error 描述了Java运行系统中的内部错误以及资源耗尽的情形。应用程序不应该抛出这种类型的对象.一般是由虚拟机抛出。
参考:
错误信息的阅读:https://www.yuque.com/zhanghang-xhy01/gc0uxk/kofdmy/edit
https://blog.csdn.net/yshysh8/article/details/80015789

