- 1. 进行变换
- 2. 进行消耗
- 3. 对上一步的计算结果不关心,执行下一个操作。
- 4. 结合两个 CompletionStage 的结果,进行转化后返回
- 5. 结合两个 CompletionStage 的结果,进行消耗
- 6. 在两个 CompletionStage 都运行完执行。
- 7. 两个 CompletionStage,谁计算的快,我就用那个 CompletionStage 的结果进行下一步的转化操作。
- 8. 两个 CompletionStage,谁计算的快,我就用那个 CompletionStage 的结果进行下一步的消耗操作。
- 8. 两个 CompletionStage,任何一个完成了都会执行下一步的操作(Runnable)。
- 9. 当运行时出现了异常,可以通过 exceptionally 进行补偿。
- 10. 当运行完成时,对结果的记录。这里的完成时有两种情况,一种是正常执行,返回值。另外一种是遇到异常抛出造成程序的中断。这里为什么要说成记录,因为这几个方法都会返回 CompletableFuture,当 Action 执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的 CompletableFuture 的计算结果或者返回异常。所以不会对结果产生任何的作用。
- 11. 运行完成时,对结果的处理。这里的完成时有两种情况,一种是正常执行,返回值。另外一种是遇到异常抛出造成程序的中断。
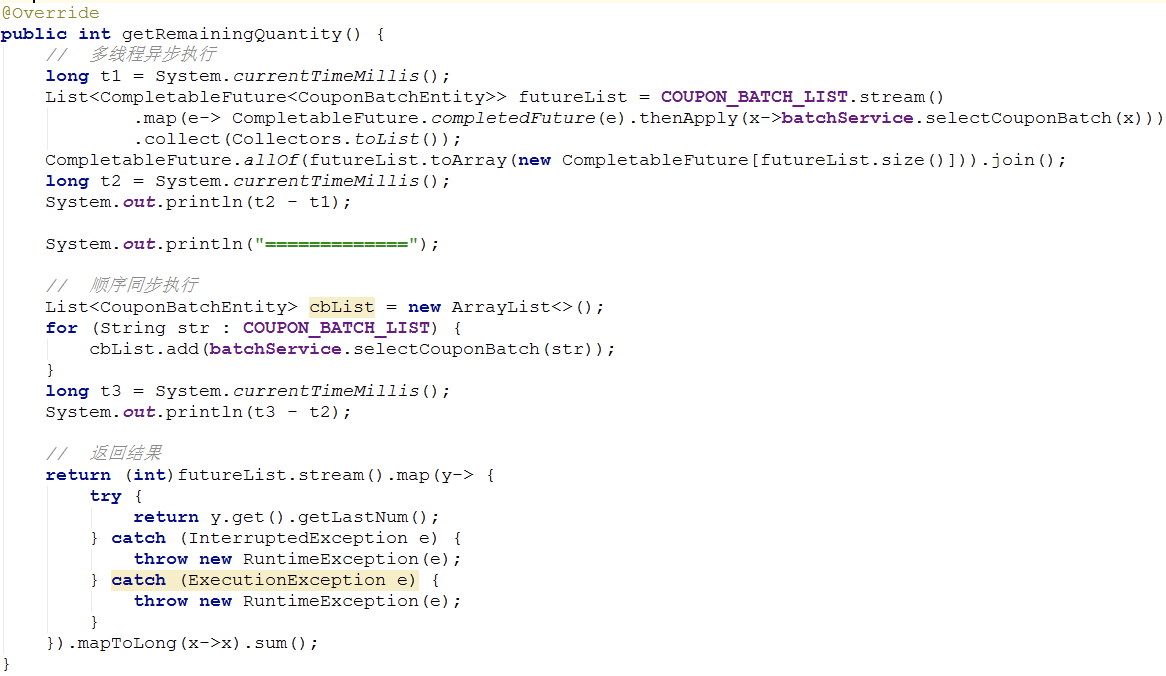
- 举个例子:
- 资料
本文由 简悦 SimpRead 转码, 原文地址 www.jianshu.com
CompletableFuture 类实现了 CompletionStage 和 Future 接口。Future 是 Java 5 添加的类,用来描述一个异步计算的结果,但是获取一个结果时方法较少, 要么通过轮询 isDone,确认完成后,调用 get() 获取值,要么调用 get() 设置一个超时时间。但是这个 get() 方法会阻塞住调用线程,这种阻塞的方式显然和我们的异步编程的初衷相违背。
为了解决这个问题,JDK 吸收了 guava 的设计思想,加入了 Future 的诸多扩展功能形成了 CompletableFuture。
CompletionStage 是一个接口,从命名上看得知是一个完成的阶段,它里面的方法也标明是在某个运行阶段得到了结果之后要做的事情。
1. 进行变换
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor);
首先说明一下已 Async 结尾的方法都是可以异步执行的,如果指定了线程池,会在指定的线程池中执行,如果没有指定,默认会在 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 中执行,下文中将会有好多类似的,都不详细解释了。关键的入参只有一个 Function,它是函数式接口,所以使用 Lambda 表示起来会更加优雅。它的入参是上一个阶段计算后的结果,返回值是经过转化后结果。
例如:
@Testpublic void thenApply() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello").thenApply(s -> s + " world").join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
hello world
2. 进行消耗
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
thenAccept 是针对结果进行消耗,因为他的入参是 Consumer,有入参无返回值。
例如:
@Testpublic void thenAccept(){CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello").thenAccept(s -> System.out.println(s+" world"));}
结果为:
hello world
3. 对上一步的计算结果不关心,执行下一个操作。
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
thenRun 它的入参是一个 Runnable 的实例,表示当得到上一步的结果时的操作。
例如:
@Testpublic void thenRun(){CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello";}).thenRun(() -> System.out.println("hello world"));while (true){}}
结果为:
hello world
4. 结合两个 CompletionStage 的结果,进行转化后返回
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
它需要原来的处理返回值,并且 other 代表的 CompletionStage 也要返回值之后,利用这两个返回值,进行转换后返回指定类型的值。
例如:
@Testpublic void thenCombine() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello";}).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "world";}), (s1, s2) -> s1 + " " + s2).join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
hello world
5. 结合两个 CompletionStage 的结果,进行消耗
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
它需要原来的处理返回值,并且 other 代表的 CompletionStage 也要返回值之后,利用这两个返回值,进行消耗。
例如:
@Testpublic void thenAcceptBoth() {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello";}).thenAcceptBoth(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "world";}), (s1, s2) -> System.out.println(s1 + " " + s2));while (true){}}
结果为:
hello world
6. 在两个 CompletionStage 都运行完执行。
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
不关心这两个 CompletionStage 的结果,只关心这两个 CompletionStage 执行完毕,之后在进行操作(Runnable)。
例如:
@Testpublic void runAfterBoth(){CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s1";}).runAfterBothAsync(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s2";}), () -> System.out.println("hello world"));while (true){}}
结果为
hello world
7. 两个 CompletionStage,谁计算的快,我就用那个 CompletionStage 的结果进行下一步的转化操作。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor);
我们现实开发场景中,总会碰到有两种渠道完成同一个事情,所以就可以调用这个方法,找一个最快的结果进行处理。
例如:
@Testpublic void applyToEither() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s1";}).applyToEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello world";}), s -> s).join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
hello world
8. 两个 CompletionStage,谁计算的快,我就用那个 CompletionStage 的结果进行下一步的消耗操作。
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
例如:
@Testpublic void acceptEither() {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s1";}).acceptEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hello world";}), System.out::println);while (true){}}
结果为:
hello world
8. 两个 CompletionStage,任何一个完成了都会执行下一步的操作(Runnable)。
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
例如:
@Testpublic void runAfterEither() {CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s1";}).runAfterEither(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s2";}), () -> System.out.println("hello world"));while (true) {}}
结果为:
hello world
9. 当运行时出现了异常,可以通过 exceptionally 进行补偿。
public CompletionStage<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn);
例如:
@Testpublic void exceptionally() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (1 == 1) {throw new RuntimeException("测试一下异常情况");}return "s1";}).exceptionally(e -> {System.out.println(e.getMessage());return "hello world";}).join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
java.lang.RuntimeException: 测试一下异常情况hello world
10. 当运行完成时,对结果的记录。这里的完成时有两种情况,一种是正常执行,返回值。另外一种是遇到异常抛出造成程序的中断。这里为什么要说成记录,因为这几个方法都会返回 CompletableFuture,当 Action 执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的 CompletableFuture 的计算结果或者返回异常。所以不会对结果产生任何的作用。
public CompletionStage<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action,Executor executor);
例如:
@Testpublic void whenComplete() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (1 == 1) {throw new RuntimeException("测试一下异常情况");}return "s1";}).whenComplete((s, t) -> {System.out.println(s);System.out.println(t.getMessage());}).exceptionally(e -> {System.out.println(e.getMessage());return "hello world";}).join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
nulljava.lang.RuntimeException: 测试一下异常情况java.lang.RuntimeException: 测试一下异常情况hello world
这里也可以看出,如果使用了 exceptionally,就会对最终的结果产生影响,它没有口子返回如果没有异常时的正确的值,这也就引出下面我们要介绍的 handle。
11. 运行完成时,对结果的处理。这里的完成时有两种情况,一种是正常执行,返回值。另外一种是遇到异常抛出造成程序的中断。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn,Executor executor);
例如:
出现异常时
@Testpublic void handle() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (1 == 1) {throw new RuntimeException("测试一下异常情况");}return "s1";}).handle((s, t) -> {if (t != null) {return "hello world";}return s;}).join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
hello world
未出现异常时
@Testpublic void handle() {String result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "s1";}).handle((s, t) -> {if (t != null) {return "hello world";}return s;}).join();System.out.println(result);}
结果为:
s1
上面就是 CompletionStage 接口中方法的使用实例,CompletableFuture 同样也同样实现了 Future,所以也同样可以使用 get 进行阻塞获取值,总的来说,CompletableFuture 使用起来还是比较爽的,看起来也比较优雅一点。