什么是JUC?
JUC就是java.util.concurrent包,这个包俗称JUC,里面都是解决并发问题的一些东西
该包的位置位于java下面的rt.jar包下面
4大常用并发工具类:
CountDownLatch
CyclicBarrier
Semaphore
ExChanger
CountDownLatch:
CountDownLatch,俗称闭锁,作用是类似加强版的Join,是让一组线程等待其他的线程完成工作以后才执行
就比如在启动框架服务的时候,我们主线程需要在环境线程初始化完成之后才能启动,这时候我们就可以实现使用CountDownLatch来完成
/*** Constructs a {@code CountDownLatch} initialized with the given count.** @param count the number of times {@link #countDown} must be invoked* before threads can pass through {@link #await}* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code count} is negative*/public CountDownLatch(int count) {if (count < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("count < 0");this.sync = new Sync(count);}
在源码中可以看到,创建CountDownLatch时,需要传入一个int类型的参数,将决定在执行几次扣减之后,等待的线程被唤醒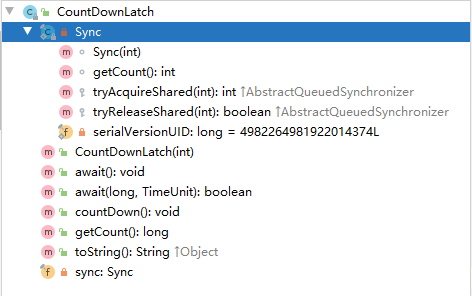
通过这个类图就可以知道其实CountDownLatch并没有多少东西
方法介绍:
CountDownLatch:初始化方法
await:等待方法,同时带参数的是超时重载方法
countDown:每执行一次,计数器减一,就是初始化传入的数字,也代表着一个线程完成了任务
getCount:获取当前值
toString:这个就不用说了
面的Sync是一个内部类,外面的方法其实都是操作这个内部类的,这个内部类继承了AQS,实现的标准方法,AQS将在后面的章节写
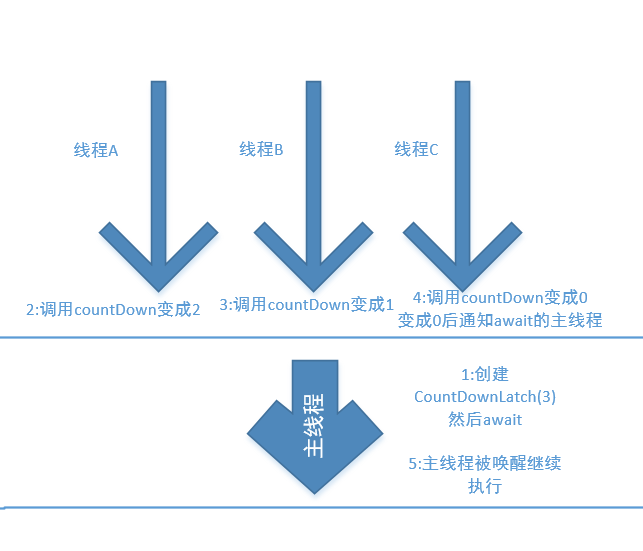
主线程中创建CountDownLatch(3),然后主线程await阻塞,然后线程A,B,C各自完成了任务,调用了countDown,之后,每个线程调用一次计数器就会减一,初始是3,然后A线程调用后变成2,B线程调用后变成1,C线程调用后,变成0,这时就会唤醒正在await的主线程,然后主线程继续执行
代码示例:
休眠工具类,之后的代码都会用到
package org.dance.tools;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** 类说明:线程休眠辅助工具类*/public class SleepTools {/*** 按秒休眠* @param seconds 秒数*/public static final void second(int seconds) {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}}/*** 按毫秒数休眠* @param seconds 毫秒数*/public static final void ms(int seconds) {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(seconds);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}}}
package org.dance.day2.util;import org.dance.tools.SleepTools;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;/*** CountDownLatch的使用,有五个线程,6个扣除点* 扣除完成后主线程和业务线程,才能执行工作* 扣除点一般都是大于等于需要初始化的线程的* @author ZYGisComputer*/public class UseCountDownLatch {/*** 设置为6个扣除点*/static CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(6);/*** 初始化线程*/private static class InitThread implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("thread_" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " ready init work .....");// 执行扣减 扣减不代表结束countDownLatch.countDown();for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {System.out.println("thread_" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + ".....continue do its work");}}}/*** 业务线程*/private static class BusiThread implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {// 业务线程需要在等初始化完毕后才能执行try {countDownLatch.await();for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {System.out.println("BusiThread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " do business-----");}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建单独的初始化线程new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {SleepTools.ms(1);System.out.println("thread_" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " ready init work step 1st.....");// 扣减一次countDownLatch.countDown();System.out.println("begin stop 2nd.....");SleepTools.ms(1);System.out.println("thread_" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " ready init work step 2nd.....");// 扣减一次countDownLatch.countDown();}}.start();// 启动业务线程new Thread(new BusiThread()).start();// 启动初始化线程for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {new Thread(new InitThread()).start();}// 主线程进入等待try {countDownLatch.await();System.out.println("Main do ites work.....");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
返回结果:
thread_13 ready init work .....thread_13.....continue do its workthread_13.....continue do its workthread_14 ready init work .....thread_14.....continue do its workthread_14.....continue do its workthread_15 ready init work .....thread_15.....continue do its workthread_11 ready init work step 1st.....begin stop 2nd.....thread_16 ready init work .....thread_16.....continue do its workthread_16.....continue do its workthread_15.....continue do its workthread_11 ready init work step 2nd.....Main do ites work.....BusiThread 12 do business-----BusiThread 12 do business-----BusiThread 12 do business-----
通过返回结果就可以很直接的看到业务线程是在初始化线程完全跑完之后,才开始执行的
CyclicBarrier:
CyclicBarrier,俗称栅栏锁,作用是让一组线程到达某个屏障,被阻塞,一直到组内的最后一个线程到达,然后屏障开放,接着,所有的线程继续运行
这个感觉和CountDownLatch有点相似,但是其实是不一样的,所谓的差别,将在下面详解
CyclicBarrier的构造参数有两个
/*** Creates a new {@code CyclicBarrier} that will trip when the* given number of parties (threads) are waiting upon it, and* does not perform a predefined action when the barrier is tripped.** @param parties the number of threads that must invoke {@link #await}* before the barrier is tripped* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parties} is less than 1*/public CyclicBarrier(int parties) {this(parties, null);}
/*** Creates a new {@code CyclicBarrier} that will trip when the* given number of parties (threads) are waiting upon it, and which* will execute the given barrier action when the barrier is tripped,* performed by the last thread entering the barrier.** @param parties the number of threads that must invoke {@link #await}* before the barrier is tripped* @param barrierAction the command to execute when the barrier is* tripped, or {@code null} if there is no action* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parties} is less than 1*/public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) {if (parties <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();this.parties = parties;this.count = parties;this.barrierCommand = barrierAction;}
很明显能感觉出来,上面的构造参数调用了下面的构造参数,是一个构造方法重载
首先这个第一个参数也是Int类型的,传入的是执行线程的个数,这个数量和CountDownLatch不一样,这个数量是需要和线程数量吻合的,CountDownLatch则不一样,CountDownLatch可以大于等于,而CyclicBarrier只能等于,然后是第二个参数,第二个参数是barrierAction,这个参数是当屏障开放后,执行的任务线程,如果当屏障开放后需要执行什么任务,可以写在这个线程中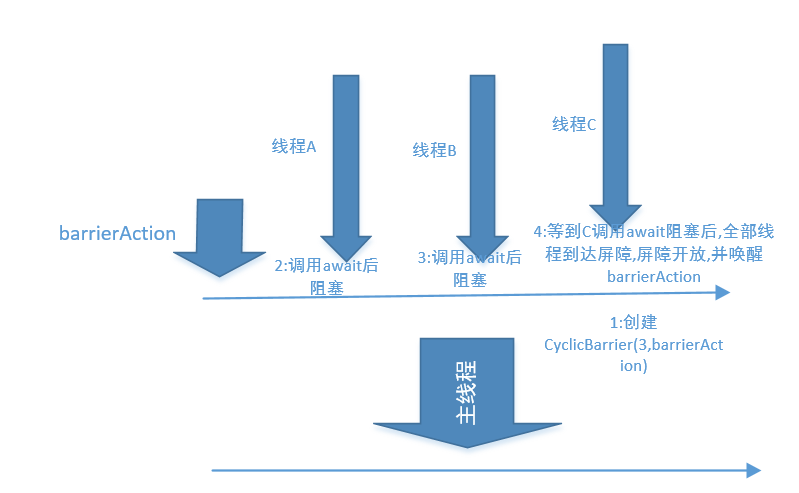
主线程创建CyclicBarrier(3,barrierAction),然后由线程开始执行,线程A,B执行完成后都调用了await,然后他们都在一个屏障前阻塞者,需要等待线程C也,执行完成,调用await之后,然后三个线程都达到屏障后,屏障开放,然后线程继续执行,并且barrierAction在屏障开放的一瞬间也开始执行
代码示例:
package org.dance.day2.util;import org.dance.tools.SleepTools;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Random;import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;/*** CyclicBarrier的使用** @author ZYGisComputer*/public class UseCyclicBarrier {/*** 存放子线程工作结果的安全容器*/private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Long> resultMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private static CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(5,new CollectThread());/*** 结果打印线程* 用来演示CyclicBarrier的第二个参数,barrierAction*/private static class CollectThread implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();for (Map.Entry<String, Long> workResult : resultMap.entrySet()) {result.append("[" + workResult.getValue() + "]");}System.out.println("the result = " + result);System.out.println("do other business.....");}}/*** 工作子线程* 用于CyclicBarrier的一组线程*/private static class SubThread implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {// 获取当前线程的IDlong id = Thread.currentThread().getId();// 放入统计容器中resultMap.put(String.valueOf(id), id);Random random = new Random();try {if (random.nextBoolean()) {Thread.sleep(1000 + id);System.out.println("Thread_"+id+"..... do something");}System.out.println(id+" is await");cyclicBarrier.await();Thread.sleep(1000+id);System.out.println("Thread_"+id+".....do its business");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(new SubThread());thread.start();}}}
返回结果:
11 is await14 is await15 is awaitThread_12..... do something12 is awaitThread_13..... do something13 is awaitthe result = [11][12][13][14][15]do other business.....Thread_11.....do its businessThread_12.....do its businessThread_13.....do its businessThread_14.....do its businessThread_15.....do its business
通过返回结果可以看出前面的11 14 15三个线程没有进入if语句块,在执行到await的时候进入了等待,而另外12 13两个线程进入到了if语句块当中,多休眠了1秒多,然后当5个线程同时到达await的时候,屏障开放,执行了barrierAction线程,然后线程组继续执行
CountDownLatch和CyclicBarrier的区别:
首先就是CountDownLatch的构造参数传入的数量一般都是大于等于线程的数量,因为他是有第三方控制的,可以扣减多次,然后就是CyclicBarrier的构造参数第一个参数传入的数量一定是等于线程的个数的,因为他是由一组线程自身控制的
CountDownLatch CyclicBarrier<br />控制 第三方控制 自身控制<br />传入数量 大于等于线程数量 等于线程数量
Semaphore:
Semaphore,俗称信号量,作用于控制同时访问某个特定资源的线程数量,用在流量控制
一说特定资源控制,那么第一时间就想到了数据库连接..
示例:用Semaphone写一个数据库连接池
/*** Creates a {@code Semaphore} with the given number of* permits and nonfair fairness setting.** @param permits the initial number of permits available.* This value may be negative, in which case releases* must occur before any acquires will be granted.*/public Semaphore(int permits) {sync = new NonfairSync(permits);}
在源码中可以看到在构建Semaphore信号量的时候,需要传入许可证的数量,这个数量就是资源的最大允许访问的线程数
接下里用信号量实现一个数据库连接池
连接对象
package org.dance.day2.util.pool;import org.dance.tools.SleepTools;import java.sql.*;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Properties;import java.util.concurrent.Executor;/*** 数据库连接* @author ZYGisComputer*/public class SqlConnection implements Connection {/*** 获取数据库连接* @return*/public static final Connection fetchConnection(){return new SqlConnection();}@Overridepublic void commit() throws SQLException {SleepTools.ms(70);}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {SleepTools.ms(1);return null;}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {return false;}@Overridepublic void rollback() throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic void close() throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {return false;}@Overridepublic DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {return false;}@Overridepublic void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic String getCatalog() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {return 0;}@Overridepublic SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic int getHoldability() throws SQLException {return 0;}@Overridepublic Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Clob createClob() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {return false;}@Overridepublic void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {}@Overridepublic void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {}@Overridepublic String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic String getSchema() throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {}@Overridepublic int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {return 0;}@Overridepublic <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {return null;}@Overridepublic boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {return false;}}
连接池对象
package org.dance.day2.util.pool;import java.sql.Connection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;/*** 使用信号量控制数据库的链接和释放** @author ZYGisComputer*/public class DBPoolSemaphore {/*** 池容量*/private final static int POOL_SIZE = 10;/*** useful 代表可用连接* useless 代表已用连接* 为什么要使用两个Semaphore呢?是因为,在连接池中不只有连接本身是资源,空位也是资源,也需要记录*/private final Semaphore useful, useless;/*** 连接池*/private final static LinkedList<Connection> POOL = new LinkedList<>();/*** 使用静态块初始化池*/static {for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) {POOL.addLast(SqlConnection.fetchConnection());}}public DBPoolSemaphore() {// 初始可用的许可证等于池容量useful = new Semaphore(POOL_SIZE);// 初始不可用的许可证容量为0useless = new Semaphore(0);}/*** 获取数据库连接** @return 连接对象*/public Connection takeConnection() throws InterruptedException {// 可用许可证减一useful.acquire();Connection connection;synchronized (POOL) {connection = POOL.removeFirst();}// 不可用许可证数量加一useless.release();return connection;}/*** 释放链接** @param connection 连接对象*/public void returnConnection(Connection connection) throws InterruptedException {if(null!=connection){// 打印日志System.out.println("当前有"+useful.getQueueLength()+"个线程等待获取连接,,"+"可用连接有"+useful.availablePermits()+"个");// 不可用许可证减一useless.acquire();synchronized (POOL){POOL.addLast(connection);}// 可用许可证加一useful.release();}}}
测试类:
package org.dance.day2.util.pool;import org.dance.tools.SleepTools;import java.sql.Connection;import java.util.Random;/*** 测试Semaphore* @author ZYGisComputer*/public class UseSemaphore {/*** 连接池*/public static final DBPoolSemaphore pool = new DBPoolSemaphore();private static class BusiThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {// 随机数工具类 为了让每个线程持有连接的时间不一样Random random = new Random();long start = System.currentTimeMillis();try {Connection connection = pool.takeConnection();System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"_获取数据库连接耗时["+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"]ms.");// 模拟使用连接查询数据SleepTools.ms(100+random.nextInt(100));System.out.println("查询数据完成归还连接");pool.returnConnection(connection);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {BusiThread busiThread = new BusiThread();busiThread.start();}}}
测试返回结果:
Thread_11_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_12_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_13_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_14_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_15_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_16_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_17_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_18_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_19_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.Thread_20_获取数据库连接耗时[0]ms.查询数据完成归还连接当前有40个线程等待获取连接,,可用连接有0个Thread_21_获取数据库连接耗时[112]ms.查询数据完成归还连接...................查询数据完成归还连接当前有2个线程等待获取连接,,可用连接有0个Thread_59_获取数据库连接耗时[637]ms.查询数据完成归还连接当前有1个线程等待获取连接,,可用连接有0个Thread_60_获取数据库连接耗时[660]ms.查询数据完成归还连接当前有0个线程等待获取连接,,可用连接有0个查询数据完成归还连接...................当前有0个线程等待获取连接,,可用连接有8个查询数据完成归还连接当前有0个线程等待获取连接,,可用连接有9个
通过执行结果可以很明确的看到,一上来就有10个线程获取到了连接,,然后后面的40个线程进入阻塞,然后只有释放链接之后,等待的线程就会有一个拿到,然后越后面的线程等待的时间就越长,然后一直到所有的线程执行完毕
最后打印的可用连接有九个不是因为少了一个是因为在释放之前打印的,不是错误
从结果中可以看到,我们对连接池中的资源的到了控制,这就是信号量的流量控制
Exchanger:
Exchanger,俗称交换器,用于在线程之间交换数据,但是比较受限,因为只能两个线程之间交换数据
/*** Creates a new Exchanger.*/public Exchanger() {participant = new Participant();}
这个构造函数没有什么好说的,也没有入参,只有在创建的时候指定一下需要交换的数据的泛型即可,下面看代码
package org.dance.day2.util;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Set;import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;/*** 线程之间交换数据* @author ZYGisComputer*/public class UseExchange {private static final Exchanger<Set<String>> exchanger = new Exchanger<>();public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {Set<String> aSet = new HashSet<>();aSet.add("A");aSet.add("B");aSet.add("C");try {Set<String> exchange = exchanger.exchange(aSet);for (String s : exchange) {System.out.println("aSet"+s);}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}.start();new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {Set<String> bSet = new HashSet<>();bSet.add("1");bSet.add("2");bSet.add("3");try {Set<String> exchange = exchanger.exchange(bSet);for (String s : exchange) {System.out.println("bSet"+s);}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}.start();}}
执行结果:
bSetAbSetBbSetCaSet1aSet2aSet3
通过执行结果可以清晰的看到,两个线程中的数据发生了交换,这就是Exchanger的线程数据交换了

