前言
一对一、一对多、多对多,作为 NoSQL 领头羊的 MongoDB 中常用做法无非「内嵌」和「引用」两种,因为 Document 有 16MB 的大小限制且「内嵌」不适合复杂的多对多关系,「引用」是用得更广泛的关联方式,所以 MongoDB 官方称其为“Normalized Data Models”——标准化数据模型。
引用式的关联其实很简单,指文档与文档之间通过id字段的引用来进行关联,下图是在文章表中包含了分类和标签表中的id字段,作为外键存在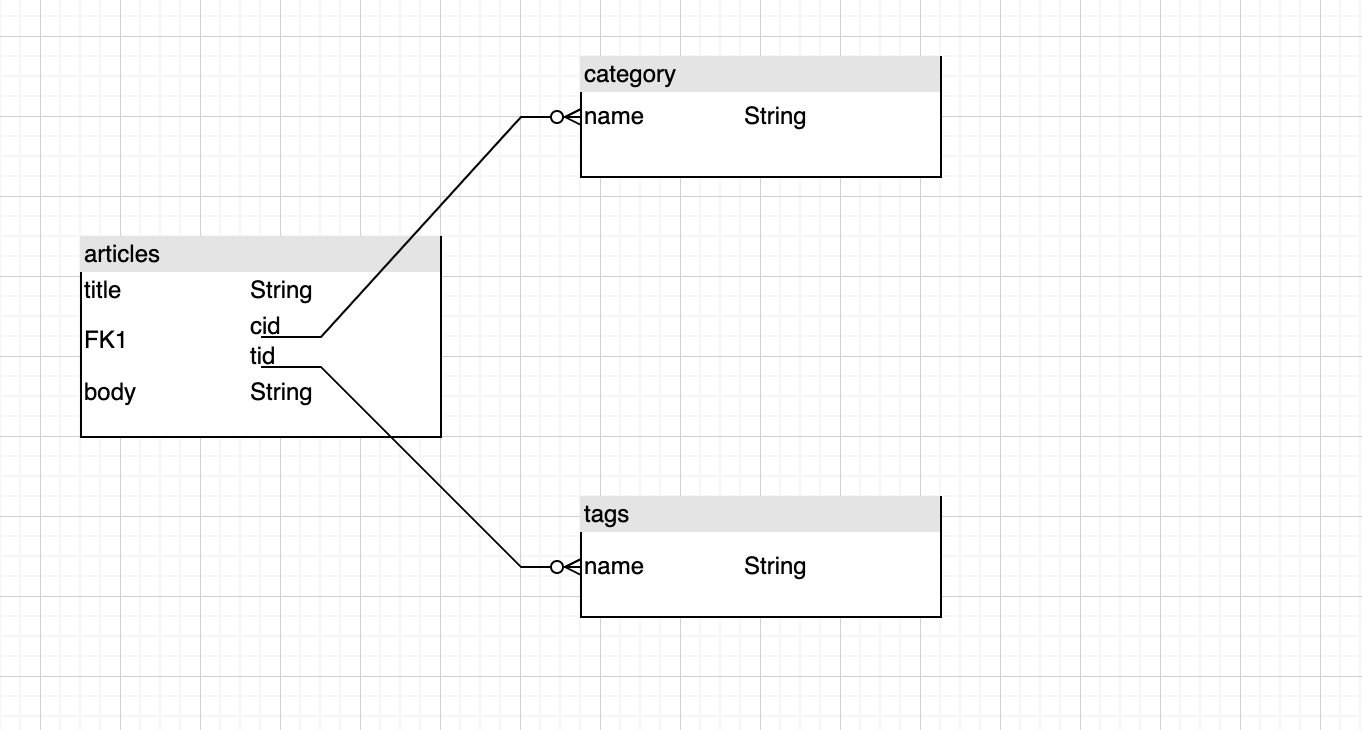
这里是三张不同的表:文章、分类、标签,mongoose的id会自动生成
下面我们会根据这张图中的关系分别使用populate和aggregate的方式进行查询
模拟数据
首先新增分类和标签模型内容
// 创建分类模型const CategorySchema = new mongoose.Schema({name: { type: String }})// 创建标签模型const TagsSchema = new mongoose.Schema({name: { type: String }})
// 新增分类await Category.insertMany([{ name: 'nodejs' },{ name: 'vuejs' },])await Tags.insertMany([{ name: 'JavaScript' },{ name: 'vue' },{ name: 'react' },{ name: 'html' },{ name: 'css' },])
新增文章并模拟数据关联
await Article.insertMany([{ title: '博客文章1', body: '内容1', cid: "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3ae", tid: "634144d3ec1d411217edf8f1" },{ title: '博客文章2', body: '内容2', cid: "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3af", tid: ["634144d3ec1d411217edf8f2", "634148e9aa35256326ce8f6a"] }])
关联查询
Populate
官方解释:
MongoDB在版本>= 3.2中有类似于联接的$查找聚合运算符。Mongoose有一个更强大的替代方案,称为populate(),它允许您引用其他集合中的文档。填充是自动用来自其他集合的文档替换文档中的指定路径的过程。我们可以填充单个文档、多个文档、一个普通对象、多个普通对象,或者从查询返回的所有对象
Mongoose的一切始于Schema,使用populate的重点也在于Schema中的设置
const ArticleSchema = new mongoose.Schema({title: { type: String },body: { type: String },author: { type: String },cid: {type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,ref: "Category"},tid: [{type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,ref: "Tags"}]})
这里是Article模型
下面在接口中使用populate():
router.get(`/api/article/article_list`, async (req, res) => {const result = await Article.find({}).populate('cid').populate('tid')res.json({code: CODE_SUCCESS,msg: "查询成功",data: {result}})})
返回的结果数据:
{"code": 0,"msg": "查询成功","data": {"result": [{"_id": "63414ae914a4ebfba8a14bf0","title": "博客文章1","body": "内容1","cid": {"_id": "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3ae","name": "nodejs","__v": 0},"tid": [{"_id": "634144d3ec1d411217edf8f1","name": "JavaScript","__v": 0}],"__v": 0},{"_id": "63414ae914a4ebfba8a14bf2","title": "博客文章3","body": "内容3","cid": {"_id": "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3af","name": "vuejs","__v": 0},"tid": [{"_id": "634144d3ec1d411217edf8f2","name": "vue","__v": 0},{"_id": "634148e9aa35256326ce8f6a","name": "react","__v": 0}],"__v": 0}]}}
aggregate
作为MongoDB官方推荐聚合查询方式,而要关联多个集合需要使用$lookup,如果一篇文章可以有多个标签(tags),划分到多个分类(categories),作为一对多的关联关系
使用aggregate的话不再需要指向对应的模型
cid: {type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,},tid: [{type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,}]
进行聚合查询
router.get(`/api/article/article_list`, async (req, res) => {const result = await Article.aggregate([{$lookup: {from: 'categories', // 数据库中关联的集合名称localField: 'cid', // article模型中关联的字段foreignField: '_id', // 需要关联categories中的字段as: 'categoryList' // 返回数据的别名字段},},{$lookup: {from: 'tags', // 数据库中关联的集合名称localField: 'tid', // article模型中关联的字段foreignField: '_id', // 需要关联tags中的字段as: 'tagList' // 返回数据的别名字段},},{$match: {} // 这里是查询时的筛选条件,查询全部设置为空,或者不用设置}])res.json({code: CODE_SUCCESS,msg: "查询成功",data: {result}})})
返回数据结果
{"code": 0,"msg": "查询成功","data": {"result": [{"_id": "63423143d78882b9d887224d","title": "博客文章1","body": "内容1","cid": "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3ae","tid": ["634144d3ec1d411217edf8f1"],"__v": 0,"categoryList": [{"_id": "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3ae","name": "nodejs","__v": 0}],"tagList": [{"_id": "634144d3ec1d411217edf8f1","name": "JavaScript","__v": 0}]},{"_id": "63423143d78882b9d887224f","title": "博客文章2","body": "内容2","cid": "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3af","tid": ["634144d3ec1d411217edf8f2","634148e9aa35256326ce8f6a"],"__v": 0,"categoryList": [{"_id": "634144ba02bb3f9e44b7b3af","name": "vuejs","__v": 0}],"tagList": [{"_id": "634148e9aa35256326ce8f6a","name": "react","__v": 0},{"_id": "634144d3ec1d411217edf8f2","name": "vue","__v": 0}]}]}}
参考链接:
MongoDB 中的关联查询

