一、常见的几种继承方式
- 原型链继承
- 构造函数继承
- 组合继承
- 原型式继承
- 寄生继承
- 寄生组合继承
-
二、常见继承方式的优缺点
1 - 原型链继承
实现:手动绑定父类对象为子类的原型链,使用new关键字实例化子类
- 关键:子类和父类都是构造函数,不是具体的字面量表达式 ```javascript // 父类构造函数 function Parent1(){ this.name=’parent1’; this.friends = [‘Tom’,’Joly’,’Tim’]; } // 子类构造函数 function Child1(){ this.age = 12; } // 子类的原型 = 父类对象 Child1.prototype = new Parent1();
// 子类实例化 let child1 = new Child1(); console.log(child1.friends); // [‘Tom’,’Joly’,’Tim’] let child1_2 = new Child1(); child1_2.friends.push(“test”); console.log(child1.friends); // [ ‘Tom’, ‘Joly’, ‘Tim’, ‘test’ ] console.log(child1_2.friends); // [ ‘Tom’, ‘Joly’, ‘Tim’, ‘test’ ]
- 缺点:多个实例对象之间共享一个原型对象,当某个实例修改了原型对象中的数据时,其他的实例也随之改变。<a name="BIoWY"></a>### 2 - 构造函数继承- 实现:在子类的构造函数中硬绑定this指针的指向,从而在子类中也可以访问父类的属性和方法- 关键:父类和子类都是构造函数的形式- 缺点:子无法继承父类原型上的属性。```javascript// 父类构造函数function Parent2(){this.name = 'Parent2';this.friends = ['Tom','Joly','Tim'];}Parent2.prototype.getName = function (){return this.name};Parent2.prototype.type = "type";// 子类构造函数function Child3(){// 在子类构造函数中修改父类this指针的指向Parent2.call(this);this.age = 12;}// 实例化子类const child2 = new Child3();console.log(child2);console.log(child2.type) // undefined
3 - 组合继承
- 实现:集合了原型链继承和构造函数继承
- 关键:父类和子类都是构造函数形式
缺点:在子类中调用了两遍父类,影响性能问题。使得子类中的属性重复。
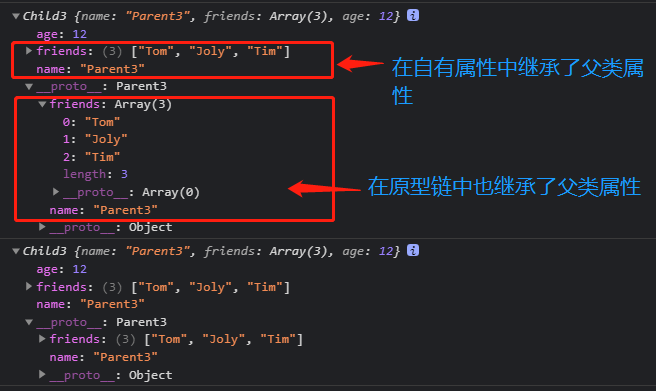
// 父类function Parent3(){this.name = 'Parent3';this.friends = ['Tom','Joly','Tim'];}Parent3.prototype.getName = function (){return this.name;}// 子类function Child3(){// 在子类中使用构造函数继承继承父类的自有属性Parent3.call(this);this.age = 12;}// 通过原型链继承,继承父类的原型链上的属性Child3.prototype = new Parent3();// 因为修改了prototype的指向,所以需要手动绑定constructor指针Child3.prototype.constructor = Child3;let child3_1 = new Child3();let child3_2 = new Child3();console.log(child3_1); // { name: 'Parent3', friends: [ 'Tom', 'Joly', 'Tim' ], age: 12 }console.log(child3_2); // { name: 'Parent3', friends: [ 'Tom', 'Joly', 'Tim' ], age: 12 }child3_1.friends.push("test");console.log(child3_1.friends); // [ 'Tom', 'Joly', 'Tim', 'test' ]console.log(child3_2.friends); // [ 'Tom', 'Joly', 'Tim' ]
4 - 原型式继承
实现:直接通过父对象创建子对象,使用object.create 实现原型继承
- 关键:父对象是字面量对象
- 缺点:多个子对象之间共享一个原型对象 ```javascript let parent4 = { name:’parent4’, friends:[‘Tom’,’Joly’,’Tim’], getName(){ return this.name } }; let child42_1 = Object.create(parent4); let child42_2 = Object.create(parent4); child42_1.friends.push(“child43_1”); child42_2.friends.push(“child42_2”) console.log(child42_2.friends); // [ ‘Tom’, ‘Joly’, ‘Tim’, ‘child43_1’, ‘child42_2’ ] console.log(child42_1.friends); // [ ‘Tom’, ‘Joly’, ‘Tim’, ‘child43_1’, ‘child42_2’ ]
<a name="MSP8K"></a>### 5 - 寄生式继承- 实现:寄生式继承在原型式继承的基础上新增了更多了方法- 关键:父对象是字面量对象- 缺点:多个子对象共享一个对象<a name="C9rFJ"></a>### 6 - 寄生组合式继承- 实现:基于组合继承的方式,使用Object.create() 代理 new 的原型链继承实现- 关键:父类和子类是构造函数- 目前主流的继承方式```javascript// 父类构造函数function Parent6(){this.name = 'Parent6';this.friends = ['Tom','Joly','Tim'];}Parent6.prototype.getName = function (){return this.name;}// 子类构造函数function Child6(){// 在子类中通过构造函数继承继承父类的自有属性Parent6.call(this);this.age = 12;}// 通过Object.create创建包含父类原型的新对象// 对组合继承的改进,防止执行两遍父类并且在子类中有重复的属性Child6.prototype = Object.create(Parent6.prototype);Child6.prototype.constructor = Child6;Child6.prototype.getFriend = function (){return this.friends;}let child6_1 = new Child6();let child6_2 = new Child6();child6_1.friends.push("child6_1");child6_2.friends.push("child6_2");console.log(child6_1.getFriend()); // [ 'Tom', 'Joly', 'Tim', 'child6_1' ]console.log(child6_2.getFriend()); // [ 'Tom', 'Joly', 'Tim', 'child6_2' ]
7 - ES6 中 extends 继承
class Parent7{constructor(name) {this.name = name}getName(){return this.name}}class Child7 extends Parent7{constructor(name,age) {super(name);this.age = age;}}const child7 = new Child7("tim",27);console.log(child7.getName());
- extends 关键字的注意事项:
- 在子类的构造函数中必须调用 super()关键字来初始化父类的属性和方法
- 如果子类中没有显示声明constructor,则super会被默认添加
- 在子类的构造函数中,只有调用了super后才可以使用this指针。因为子类的构建基于父类的实例。