链表(Linked)
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储单元,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。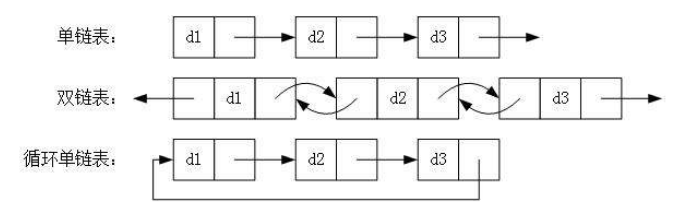
链表的特点
- 不要求逻辑上相连的两个元素物理上也相连
- 读取查询操作比数组难,链表结构无法通过指定索引位置来立即访问
- 插入、删除操作比数组简单,不需要移动元素,只需要修改“链”
- 在每一次插入和删除过程中,链表结构会调整大小,不需要额外的内存代价,不需要复制数据项
单链表(single linked)
链表结构的基本单位表示是节点,单链表的节点包括了:
- 一个数据项
- 到结构中下一个节点的一个链接
在单链表结构中,容易获取一个项的后继项,但不容易获取一个项的前驱项,用户通过沿着一个外部的头链接(head link)来访问第一个项,然后通过第一个项产生的、串联起来的、单个的链条,来访问其他项。
# 用python定义一个简单的单链表节点类class Node(object):def __init__(self, data, next=None):self.data = dataself.next = next# 用Node类创建一个含有5个节点的单链表结构head = None # head:指向链表头部的指针for i in range(5):head = Node(i, head)# Print the contents of the structurewhile head != None:print(head.data)head = head.next# 注:(1)指针head生成了链表结构,最近插入的项总是位于结构的开始处# (2)Print数据时,按照插入顺序相反出现# (3)Print数据时,head指针重新设置成下一个节点,直到变为None,# 所以这个过程后,节点从链表结构中删除,不可再用# 单链表结构上的操作# Create a single linkedhead = Nonefor i in range(5):head = Node(i, head)# (1)遍历(traversal) O(n)print('(1)遍历(traversal)')# 访问每一个节点而不删除它们,使用一个临时指针变量probprob = headwhile prob != None:print(prob.data)prob = prob.next# (2)搜索print('(2)搜索')targetItem = 9prob = headwhile prob != None and targetItem != prob.data:prob = prob.nextif prob != None:print("targetItem {} has been found".format(prob.data))else:print("targetItem {} is not in the linked".format(targetItem))# 访问链表中第i项 O(n)# Assumes 0 <= index < ndef read_data(head, index):prob = headwhile index > 0:prob = prob.nextindex -= 1return prob.dataprint(read_data(head, 0))# (3)替换print('(3)替换')# 替换一个给定项 O(n)targetItem = 0newItem = 10while head != None:head = head.nextfor i in range(5):head = Node(i, head)def print_linked(head):prob = headwhile prob != None:print(prob.data)prob = prob.nextprint_linked(head)# (4)插入print('在开始出插入') # O(1)head = Node(newItem, head)print_linked(head)print('在末尾插入') # O(n)newNode = Node(34)if head is None:head = newNodeelse:prob = headwhile prob.next != None:prob = prob.nextprob.next = newNodeprint_linked(head)print('在任何位置插入')idx = 2newItem = 'b'if head is None or idx <= 0:head = Node(newItem, head)else:prob = headwhile idx>1 and prob.next != None:prob = prob.nextidx -= 1prob.next = Node(newItem, prob.next)print_linked(head)#(5)删除print('从开始处删除') # O(1)removeItem = head.datahead = head.nextprint_linked(head)head.next.dataprob = headwhile prob != None and targetItem != prob.data:prob = prob.nextif prob != None:prob.data = newItemprint('Success')else:print('False')# 替换第i项 O(n)index = 1prob = headwhile index > 0:prob = prob.nextindex -= 1prob.data = newItem
双链表结构(doubly linked structure)
双链表结构的节点包括了:
- 一个数据项
- 到结构中下一个节点的一个链接
- 到结构中上一个节点的一个链接
双链表节点包括了两个方向的节点,所以用户很容易移动到一个节点的后继项和前驱项
# 双链表节点的python实现class TwoWayNode(Node):def __init__(self, data, previous=None, next=None):Node.__init__(self, data, next)self.previous = previous# Create a double linked structure with one nodehead = TwoWayNode(0)tail = head # tail:指向尾部的指针# Add four nodes to the end of the double linked structurefor i in range(1,5):tail = TwoWayNode(i, tail) # previous=tail# Print the contents of the double linked structure in reverse orderprob = tailwhile prob != None:print(prob.data)prob = prob.previous

