Nacos Config自定义nameSpace和group
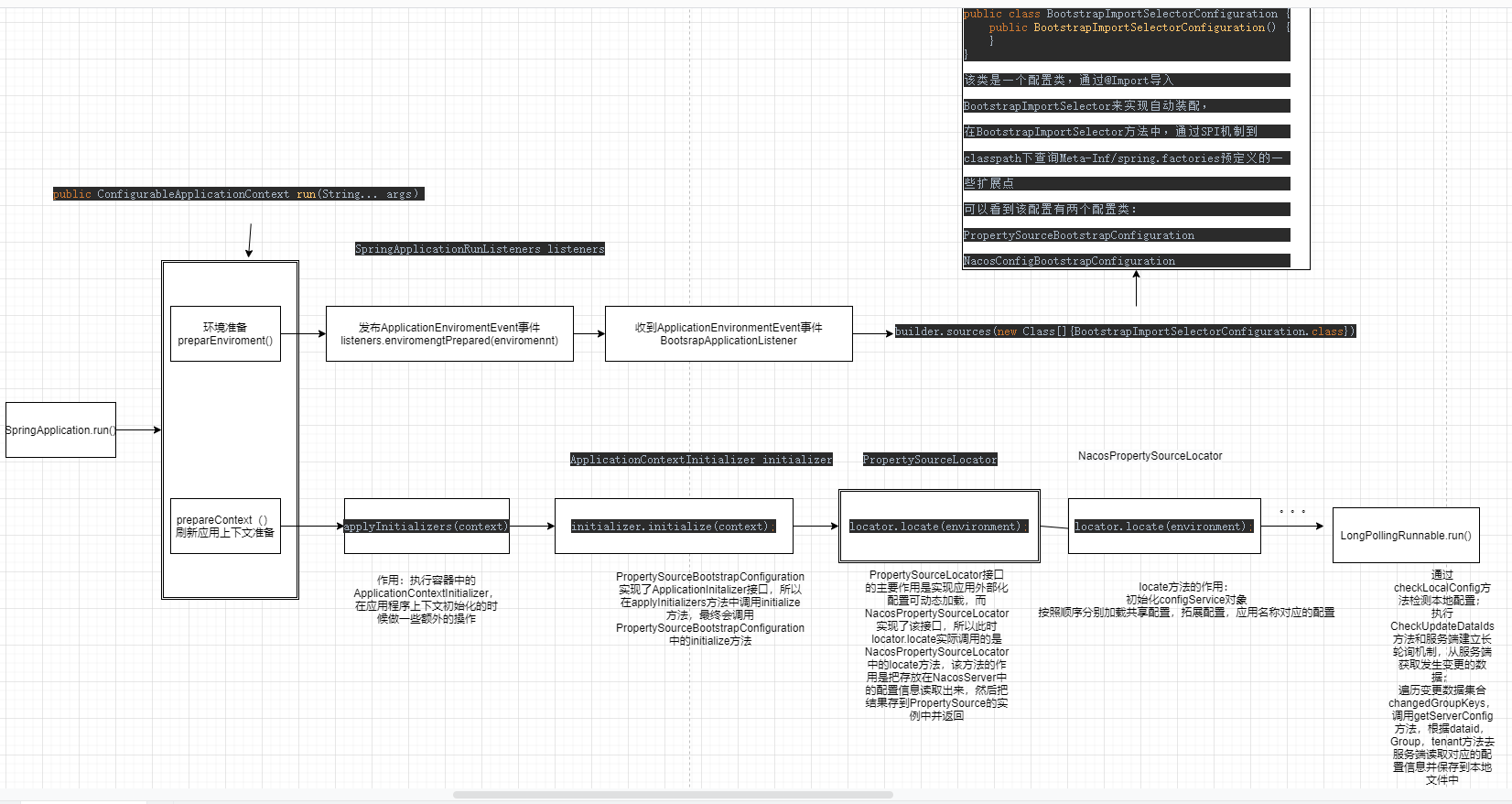
nacos数据模型
namespace:用于解决多环境及多组环数据的隔离问题,在不同的namespace下可以存在相同的group;
group:group是nacos中用来实现dataid 分组管理的机制,可以实现不同的service/dataid的隔离;对于group的用法,其实没有固定的规定,比如它可以实现不同 环境下的dataid的分组,也可以实现不同应用或者组件下使用相同配置类型的分组;
service、dataid:配置名称
配置的增删改查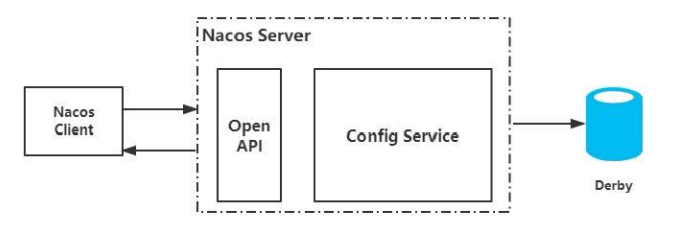
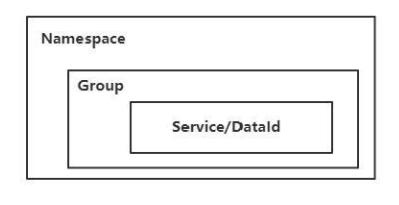
nacos配置中心
对于nacos Config来说,其实就是提供了配置的集中式管理功能,然后对外提供crud的访问接口是的应用系统可以完成配置的基本操作;
nacos服务端的数据存储默认采用的是Derby数据库,除此之外还支持mysql数据库;
配置的实时更新-动态监听
当nacos Config server上的配置发生变化时,需要让相关的应用程序感知配置的变化,需要客户端针对感兴趣的配置实现监听;
客户端与服务端之间的数据交互的两种方式
pull 表示客户端从服务端主动拉取数据
push 表示服务端主动把数据推送到客户端
push:服务端需要维持与可短短的长链接,如果客户端的数量比较多,那么服务端需要耗费大量的内存资源来保存每个连接,并且为了检测连接的有效性,还需要心跳机制来维持每个连接的状态;
pull:客户端需要定时从服务端拉取一次数据,由于定时任务会存在一定的时间间隔,所以不能保证实时性,并且在服务端配置长时间不更新的情况下,客户端的定时任务会做一些无效的pull;
nacos采用的是pull方式,但是不是一种简单的pull,而是一种长轮询机制,结合push与pull的优势;客户端采用长轮询的方式定时发起pull请求,去检查服务端配置是否发生了变更,如果发生了变更,则客户端会更会变更的数据获得最新的配置;所谓长轮询,是客户端发起轮询请求后,服务端如果有配置方式发生变更,就追返回;
Nacos Client 发起Pull请求
服务端如果没有配置发生变更则会Hold住这个请求,直到配置发生变化后或者29.5s后,服务端就会把这个hold住的请求返回;
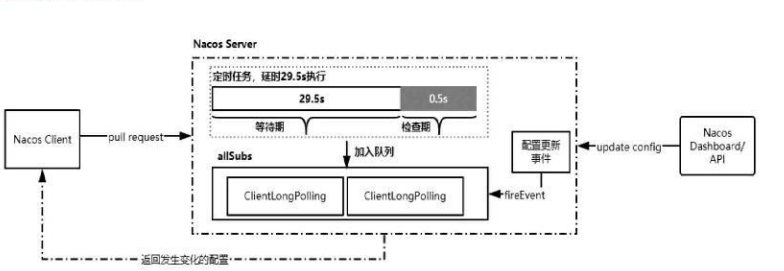
nacos的长轮询机制
Spring Cloud实现配置的加载
Spring cloud是基于Spring来进行扩展的,Spring原本提供了Environment接口,它抽象了一个Environment来表示Spring应用程序环境配置,整合了各种各样的外部环境,并且提供统一访问的方法getProperty(String key),在Spring启动时,会把配置加载到Environment中,当创建一个Bean时可以从Environment中把一些属性值通过@Value的形式注入业务代码。所以SpringCloud加载nacos配置的本质上是要如何解决如何讲远程配置加载到Environment中以及如何实时更新配置变更到Environment中
SpringBoot应用启动时调用SpringApplication.run()方法,在run方法中可以看到有一个prepareEnvironment()方法,具体代码如下
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {//省略部分代码try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments);//省略部分代码listeners.started(context);callRunners(context, applicationArguments);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}try {listeners.running(context);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}return context;}
在prepareEnvironment()方法中会发布一个ApplicationEnvironmentPrepareEvent事件,所有对这个时间感兴趣的Listener都会监听到该事件;
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// Create and configure the environmentConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);bindToSpringApplication(environment);if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());}ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);return environment;}
其中BootstrapApplicationListener会收到该事件并进行处理
public class BootstrapApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered {public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();if ((Boolean)environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled", Boolean.class, true)) {if (!environment.getPropertySources().contains("bootstrap")) {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;String configName = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap}");Iterator var5 = event.getSpringApplication().getInitializers().iterator();while(var5.hasNext()) {ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer = (ApplicationContextInitializer)var5.next();if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) {context = this.findBootstrapContext((ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer)initializer, configName);}}if (context == null) {context = this.bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(), configName);event.getSpringApplication().addListeners(new ApplicationListener[]{new BootstrapApplicationListener.CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener(context)});}this.apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment);}}}}
在bootstrapServiceContext方法中
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, final SpringApplication application, String configName) {//省略部分代码builder.sources(new Class[]{BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class});ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run(new String[0]);context.setId("bootstrap");this.addAncestorInitializer(application, context);bootstrapProperties.remove("bootstrap");this.mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);return context;}
可以看到 builder.sources(new Class[]{BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class});方法,查看BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration类发现在该类上使用了@Import引入了BootstrapImportSelector类,在该类中的selectImport方法又可以看到Spring的SPI机制,可以到classpath路径下查找META-INF/spring.factories预定义的一些扩展点,其中key为BootstrapConfiguration
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,\org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.encrypt.EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration,\org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration,\org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
至此,准备工作就完成了,
从新回到run方法中,
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments);prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,printedBanner);return context;}
在方法中可以看到prepareContext()方法,该方法进行刷新应用上下文的主备阶段,接着调用applyInitializers()方法
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {//省略部分代码listeners.contextPrepared(context);//省略部分代码}
该方法主要会执行容器中的ApplicationContextInitzalizer,它的作用是在应用程序上下文初始化的时候做一些额外的操作
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");initializer.initialize(context);}}
该方法的类为PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration实现了ApplicationContextInitalizer接口,所以在applyInitizers方法中调用initalizer方法,最终会调用PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration中的initialize方法
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {PropertySourceLocator locator = (PropertySourceLocator)var5.next();//省略部分代码source = locator.locate(environment);//省略部分代码}
PropertySourceLocator接口的主要作用是实现应用外部化配置可动态加载,而NacosProPertySourceLocator实现了了该接口,所以此时locator.locate实际调用的是NacosPropertySourceLocator中的locate方法,在NacosPropertySourceLocator的locate方法中把存放在Nacos Server中的配置信息读取出来,然后把结果存到PropertySource的实例中并返回;在该方法的实现中海油一个longPollingRunable.run方法,LongpollingRunable实际上是一个线程,run方法的作用如下
通过checkLocalConfig方法来检查本地配置
执行checkUpdateDataIds方法和在服务端建立长轮询机制,从服务端获取发生变更的数据
遍历变更数据集合changedGroupKeys,调用getServerConfig方法,根据DataId,group。tenant去服务端读取对应的配置信息并保存到本地文件中。
总结: