导学
之前我们学习过过滤器,过滤器是针对于请求过滤。而今天我们要学习的监听器,就像汽车的自动刹停技术,监听汽车与前方物体的距离,从而采取措施。JavaWeb中的监听器也是如此,监听事物变化,从而采取措施。
监听器入门
监听器介绍
- 监听器(Listener)是J2EE Servlet模块下的组件
- Listener的作用对Web应用对象的行为进行监控
- 通过Listener监听Web应用对象功能状态的变化,自动触发指定的功能代码
三种监听对象
- ServletContext-对全局ServletContext及其属性进行监听
- HttpSession-对用户会话及其属性操作进行监听
- ServletRequest-对请求及属性操作进行监听
过滤器与监听器的区别
- 实现XxxListener接口,不同接口对应不同监听对象
- 实现每个接口中独有的方法,实现触发监听的后续操作
- 在web.xml中配置
<listener>使监听器生效 ``` /**
针对ServletContext对象进行监听,不同接口对应不同监听对象 **/ //@WebListener //只要这个注解就可以了,无需其他的属性。更推荐使用配置的形式 public class FirstListener implements ServletContextListener{
//因为ServletContext在Web应用启动时创建,所以该监听器在应用启动的时候就进行监听 @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("ServletContext已初始化");
} @Override public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.out.println("ServletContext已销毁");
} }
```<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"><display-name>first-listener</display-name><welcome-file-list><welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file><welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file><welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file></welcome-file-list><listener><listener-class>com.dodoke.listener.FirstListener</listener-class></listener><context-param><param-name>app_name</param-name><param-value>Listener Web</param-value></context-param><context-param><param-name>version</param-name><param-value>1.0</param-value></context-param></web-app>
对象监听器与属性监听器
监听器的实现需要实现监听器接口,每种监听器接口对应不同的监听器对象。其实在监听器中存在六种监听器接口:
内置对象监听器接口
- ServletContextListener - 监听ServletContext对象创建、销毁等操作
- HttpSessionListener - 监听HttpSession对象创建、销毁等操作
- ServletRequestListener - 监听HttpServletRequest对象创建、销毁
属性监听接口
- ServletContextAttributeListener - 监听全局属性操作
- HttpSessionAttributeListener- 监听用户会话属性操作
ServletRequestAttributeListener- 监听请求属性操作
@WebServlet("/hello")public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;public HelloServlet() {super();}protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {response.getWriter().println("Hello World!");//在ServletContext,HttpSession,HttpServletRequest对象中添加删除属性request.getServletContext().setAttribute("sc-attr1", "sc-attr-value1");request.getServletContext().removeAttribute("sc-attr1");request.getSession().setAttribute("session-attr1", "session-attr-value1");request.setAttribute("request-attr1", "request-attr-value1");}protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}
public class WebAttributeListener implements ServletContextAttributeListener,HttpSessionAttributeListener ,ServletRequestAttributeListener{@Overridepublic void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent event) {System.out.println("ServletContext新增属性:" + event.getName() + "->" + event.getValue());}@Overridepublic void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent event) {}@Overridepublic void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent event) {}@Overridepublic void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {System.out.println("HttpSession新增属性:" + event.getName() + "->" + event.getValue());}@Overridepublic void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}@Overridepublic void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {}@Overridepublic void attributeAdded(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) {System.out.println("Request新增属性:" + srae.getName() + "->" + srae.getValue());}@Overridepublic void attributeRemoved(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) {}@Overridepublic void attributeReplaced(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae) {}}
public class WebListener implements ServletContextListener,HttpSessionListener,ServletRequestListener{@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {System.out.println("ServletContext已初始化");}@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {System.out.println("ServletContext已被销毁");}@Overridepublic void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se) {HttpSession session = se.getSession();System.out.println("Session已被创建,SessionId:" + session.getId());}@Overridepublic void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se) {System.out.println("Session已被销毁");}@Overridepublic void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {System.out.println("HttpServletRequest已被销毁");}@Overridepublic void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)sre.getServletRequest();System.out.println("HttpServletRequest已被创建,URI:" + request.getRequestURI());}}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"><display-name>listener-interface</display-name><welcome-file-list><welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file><welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file><welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file><welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file></welcome-file-list><listener><listener-class>com.dodoke.listener.WebListener</listener-class></listener><listener><listener-class>com.dodoke.listener.WebAttributeListener</listener-class></listener></web-app>
web应用程序执行过程
- 一个请求时 tomcat处理的过程:Web应用启动时,ServletContext被初始化,启动成功后访问地址时,一个HttpServletRequest对象被创建。同时因为是一个新的浏览器窗口,所以tomcat会创建一个session对象,网页处理完成后HttpServletRequest被销毁。
- 第二次请求(当浏览器窗口刷新后),session 并没有被创建,因为session id 已存在,通过确认session id 的存在,所以并不会创建新的session。此时,HttpServletRequest 又经历了一次创建与销毁的过程。
- 当浏览器关闭重新打开一个新的窗口,再次访问这个网址,这时一个新的session被创建。原因是新的浏览器并没有包含任何session id,所以由新的浏览器窗口向tomcat发送请求后,会为其创建一个对应的session,原有的session并不会消失,只是原有的sessionid的凭证不存在了,30分钟后自然过期,或程序代码人为关闭。
- 当关闭应用时,ServletContext 才被销毁。
案例:请求流量分析
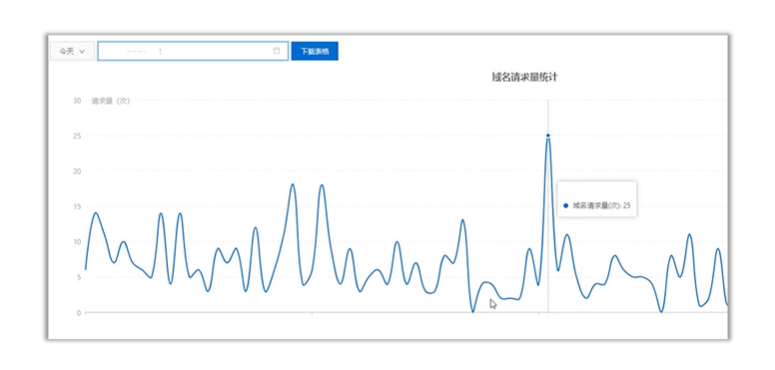
请求流量分析统计的统计功能实现:
- 利用全局对象监听器在启动应用创建全局对象时往对象添加两个属性,分别是请求对象的初始化的时间记录表和初始化的次数统计表,两者一一对应(存放时间的位置在次数统计表中对应的是该时间的请求次数)。
- 利用请求对象监听器在请求到来时对全局对象里的两个属性进行修改。
补充:采用图表展现数据,可以使用百度开发的echarts组件,该组件开源免费,并已加入Apache基金会开源项目。
访问请求测试页面:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Test Page</title></head><body><h1>I'm test page 1</h1></body></html>
可以多设置几个不同的测试页面
请求统计监听器
public class RequestTotalListener implements ServletContextListener,ServletRequestListener{@Overridepublic void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre) {}@Overridepublic void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre) {//流量统计页面的请求不计入流量的统计HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)sre.getServletRequest();String url = request.getRequestURL().toString();if(url.endsWith("/rt") == true) {return;}//先取出存放在全局对象中的时间和次数数据//TimeList: 10:02 10:03 10:04 10:05//ValueList: 5 7 10 2List<String> timeList = (List)sre.getServletContext().getAttribute("timeList");List<Integer> valueList = (List)sre.getServletContext().getAttribute("valueList");//产生请求时,获取当前时间Date date = new Date();SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm");String time = sdf.format(date);//10:05//实现记录每分钟的请求次数//原理:判断时间表中是否存在当前时间字符串,如果存在证明该次请求还是发生在一分钟内,进入代码段2,只针对次数加一//如果不存在,则证明本次请求为当前一分钟内的第一次请求,所以记录当前时间,并添加次数记录。if(timeList.indexOf(time) == -1) {//代码段1timeList.add(time);valueList.add(1);sre.getServletContext().setAttribute("timeList", timeList);sre.getServletContext().setAttribute("valueList", valueList);}else {//代码段2int index = timeList.indexOf(time);int value = valueList.get(index);valueList.set(index, value+1);sre.getServletContext().setAttribute("valueList", valueList);}}@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {}@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {//在全局对象初始化的时候,就设置请求时间和数据的存放表,并加入全局对象//时间数据List timeList = new ArrayList();//具体时间访问量数据List valueList = new ArrayList();//将这两个数据存放表存放到全局对象中sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("timeList", timeList);sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("valueList", valueList);}}
获取统计数据
@WebServlet("/rt")public class RequestTotalServlet extends HttpServlet {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;public RequestTotalServlet() {super();}protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {ServletContext context = request.getServletContext();List<String> timeList = (List)context.getAttribute("timeList");List<Integer> valueList = (List)context.getAttribute("valueList");response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");/*response.getWriter().println(timeList.toString());response.getWriter().println("<br/>");response.getWriter().println(valueList.toString());*///echarts要求x轴数据和series中数据一一对应Map result = new HashMap();result.put("timeList", timeList);result.put("valueList", valueList);String json = JSON.toJSONString(result);response.getWriter().println(json);}protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {doGet(request, response);}}
统计数据展示页面
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Insert title here</title><script type="text/javascript" src="js/echarts.min.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.3.3.1.min.js"></script></head><body><div id="main" style="width: 600px; height: 400px;"></div><script type="text/javascript">function showChart(){$.ajax({url:"./rt",type:"get",dataType:"json",success : function(json){console.log(json.timeList);console.log(json.valueList);// 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例var myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('main'));// 指定图表的配置项和数据var option = {title : {//标题项text : '请求流量分析统计'//标题文本},tooltip : {},legend : {data : [ '访问量' ]},xAxis : {//X坐标项data : json.timeList//X坐标数据},yAxis : {},//y轴没有设置,代表显示默认的数值series : [ {name : '访问量',type : 'line',//代表以折线图显示data : json.valueList//每个X轴数据对应的Y轴数据} ]};// 使用刚指定的配置项和数据显示图表。myChart.setOption(option);}})}window.setInterval("showChart()",1000);</script></body></html>
案例:静态数据预处理
在工程中,对于一些长期不会改变的数据,可以在服务器每次启动的时候利用上下文监听器在全局属性中写入。可以避免每次加载页面时都要从数据库获取数据
//频道类public class Channel {private String channelName;private String url;public Channel(String channelName, String url) {super();this.channelName = channelName;this.url = url;}public String getChannelName() {return channelName;}public void setChannelName(String channelName) {this.channelName = channelName;}public String getUrl() {return url;}public void setUrl(String url) {this.url = url;}}
public class StaticDataListener implements ServletContextListener{@Overridepublic void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {List list = new ArrayList();list.add(new Channel("Java" , "my Java"));list.add(new Channel("UI" , "my UI"));list.add(new Channel("Video" , "my Video"));sce.getServletContext().setAttribute("channelList", list);}@Overridepublic void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {}}
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %><!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Insert title here</title></head><body><c:forEach items="${applicationScope.channelList }" var="c"><a href="${c.url }">${c.channelName }</a> |</c:forEach><hr/></body></html>

