上篇文章深入理解Spring Security配置与构建(源码篇)已经介绍了SecurityBuilder以及它的一个重要实现HttpSecurity,在SecurityBuilder的实现类里面,还有一个重要的分支,那就是AuthenicationManagerBuilder,看名字就知道是用来构建AuthenticationManager的,那么就来看看AuthenticationManager是怎么被一步一步构建的。
1、AuthenticationManager
public interface AuthenticationManager {Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;}
在捋一遍登录Spring Security登录流程(源码篇)一文中,用户进行登录认证的时候,用来处理身份认证的类就是AuthenticationManager,我们也称之为认证管理器。AuthenticationManager中规范了 Spring Security 中的过滤器要如何执行身份认证,并在身份认证成功后返回一个经过认证的Authentication对象。AuthenticationManager是一个接口,我们可以自定义它的实现,但是通常我们使用更多的是系统提供的ProviderManager。
2、ProviderManager
ProviderManager是最常用的AuthenticationManager实现类。ProviderManager管理了一个AuthenticationProvider集合,每个AuthenticationProvider都是一个认证器,不同的AuthenticationProvider用来处理不同的Authentication对象的认证。一次完整的认证可能会经过多个AuthenticationProvider。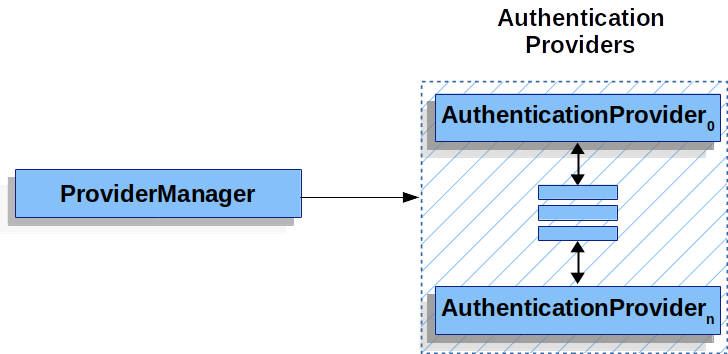
3、AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider定义了 Spring Security 中的验证逻辑:
public interface AuthenticationProvider {Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)throws AuthenticationException;boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);}
可以看到,就两个方法:
authenticate方法用来验证用户身份supports方法用来判断当前的AuthenticationProvider是否支持需要的认证的Authentication
最常用的AuthenticationProvider实现类就是DaoAuthenticationProvider
4、parent
每一个ProviderManager管理多个AuthenticationProvider,同时每一个ProviderManager都可以配置一个parent,如果当前的ProviderManager中认证失败了,还可以去它的parent中继续进行认证,所谓的parent实例,一般也是ProviderManager,即ProviderManager的parent还是ProviderManager。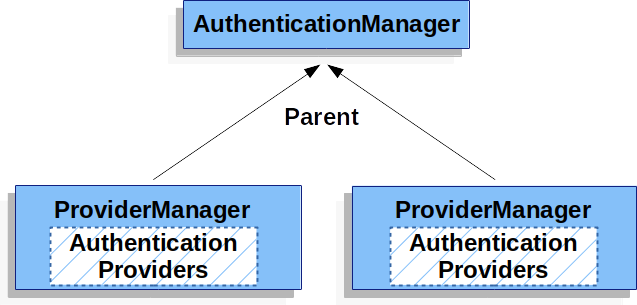
5、源码分析
先来看看AuthenicationManagerBuilder的一个继承关系类图: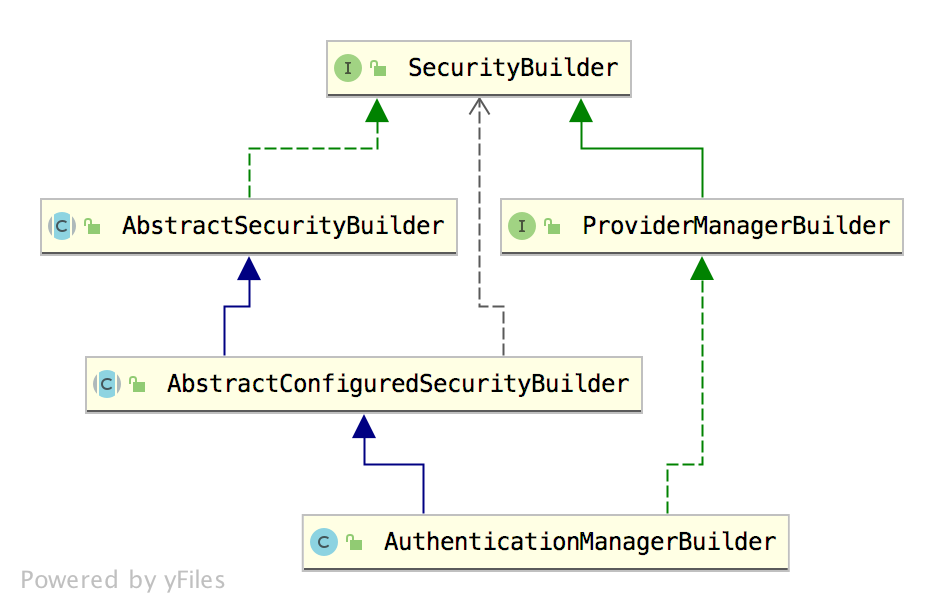
可以看到,上篇文章中介绍的全是AuthenicationManagerBuilder的父类,所以AuthenicationManagerBuilder已经自动具备了其父类的功能。
public class AuthenticationManagerBuilderextendsAbstractConfiguredSecurityBuilder<AuthenticationManager, AuthenticationManagerBuilder>implements ProviderManagerBuilder<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> {public AuthenticationManagerBuilder(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) {super(objectPostProcessor, true);}public AuthenticationManagerBuilder parentAuthenticationManager(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {if (authenticationManager instanceof ProviderManager) {eraseCredentials(((ProviderManager) authenticationManager).isEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication());}this.parentAuthenticationManager = authenticationManager;return this;}public InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> inMemoryAuthentication()throws Exception {return apply(new InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<>());}public JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> jdbcAuthentication()throws Exception {return apply(new JdbcUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<>());}public <T extends UserDetailsService> DaoAuthenticationConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder, T> userDetailsService(T userDetailsService) throws Exception {this.defaultUserDetailsService = userDetailsService;return apply(new DaoAuthenticationConfigurer<>(userDetailsService));}@Overrideprotected ProviderManager performBuild() throws Exception {if (!isConfigured()) {logger.debug("No authenticationProviders and no parentAuthenticationManager defined. Returning null.");return null;}ProviderManager providerManager = new ProviderManager(authenticationProviders,parentAuthenticationManager);if (eraseCredentials != null) {providerManager.setEraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication(eraseCredentials);}if (eventPublisher != null) {providerManager.setAuthenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);}providerManager = postProcess(providerManager);return providerManager;}}
- 首先,我们可以通过
parentAuthenticationManager方法来给一个AuthenticationManager设置parent。 inMemoryAuthentication、jdbcAuthentication以及userDetailsService方法作用就是为了配置数据源。- 最后就是
performBuild方法,这个方法的作用就是根据当前AuthenicationManagerBuilder来构建一个AuthenticationManager,AuthenticationManager本身是一个接口,它的默认实现是ProviderManager,所以构建出来的ProviderManager。在构建ProviderManager时,一方面传入authenticationProviders,就是该ProviderManager所管理的所有的AuthenticationProvider,另一方面传入ProviderManager的parent(其实也就是一个ProviderManager)。
AuthenicationManagerBuilder还有一个实现类叫做DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder,作为内部类分别定义在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter和AuthenticationConfiguration中,不过DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder中的内容比较简单,重写了父类AuthenicationManagerBuilder的几个方法,配置了新的PasswordEncoder,这里就不列出源码了。但是这并不表示DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder类就不重要,因为在后面的使用中,基本上都是使用AuthenicationManagerBuilder的子类DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder。
说了这么多,那么什么时候通过AuthenicationManagerBuilder来构建AuthenticationManager呢?🤔
在初始化流程中,得先介绍一个AuthenticationConfiguration类,这个类可以当作是一个全局配置类来理解,里面都是一些全局属性的配置:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)@Import(ObjectPostProcessorConfiguration.class)public class AuthenticationConfiguration {@Beanpublic AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationManagerBuilder(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor, ApplicationContext context) {LazyPasswordEncoder defaultPasswordEncoder = new LazyPasswordEncoder(context);AuthenticationEventPublisher authenticationEventPublisher = getBeanOrNull(context, AuthenticationEventPublisher.class);DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder result = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(objectPostProcessor, defaultPasswordEncoder);if (authenticationEventPublisher != null) {result.authenticationEventPublisher(authenticationEventPublisher);}return result;}@Beanpublic static GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter enableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {return new EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(context);}@Beanpublic static InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer initializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {return new InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer(context);}@Beanpublic static InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer initializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {return new InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer(context);}public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {if (this.authenticationManagerInitialized) {return this.authenticationManager;}AuthenticationManagerBuilder authBuilder = this.applicationContext.getBean(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);if (this.buildingAuthenticationManager.getAndSet(true)) {return new AuthenticationManagerDelegator(authBuilder);}for (GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter config : globalAuthConfigurers) {authBuilder.apply(config);}authenticationManager = authBuilder.build();if (authenticationManager == null) {authenticationManager = getAuthenticationManagerBean();}this.authenticationManagerInitialized = true;return authenticationManager;}@Autowiredpublic void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {this.applicationContext = applicationContext;}@Autowiredpublic void setObjectPostProcessor(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor) {this.objectPostProcessor = objectPostProcessor;}private static class EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer extendsGlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter {private final ApplicationContext context;private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer.class);EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer(ApplicationContext context) {this.context = context;}@Overridepublic void init(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {Map<String, Object> beansWithAnnotation = context.getBeansWithAnnotation(EnableGlobalAuthentication.class);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Eagerly initializing " + beansWithAnnotation);}}}}
- 这里首先构建了一个
AuthenicationManagerBuilder实例,这个实例就是用来构建全局AuthenticationManager,具体的构建过程在下面的getAuthenticationManager方法中。不过这里的这个全局的AuthenicationManagerBuilder并非总是有用,为什么这么说呢?请接着往下看。 - 另外还有一些
initializeXXX方法,这些方法可以作为一个了解,因为正常情况下是不会用到这几个Bean的,只有当getAuthenticationManager方法被调用时,这些默认的Bean才会被配置,而getAuthenticationManager方法被调用,意味着我们要使用系统默认配置的AuthenticationManager作为parent,而在实际使用中,我们一般不会使用系统默认配置的AuthenticationManager作为parent,我们多多少少都会重新定制一下(使用WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#congiure方法,为什么是这个方法,接着看)。
这些全局的Bean虽然一定会初始化,但是并非一定会用到。那么到底什么时候用到,什么时候用不到呢?这就和WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter有关了,在WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter中有三个重要的方法涉及到AuthenticationManager的初始化问题。
第一个是setApplicationContext方法:
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) {this.context = context;ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor = context.getBean(ObjectPostProcessor.class);LazyPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = new LazyPasswordEncoder(context);authenticationBuilder = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(objectPostProcessor, passwordEncoder);localConfigureAuthenticationBldr = new DefaultPasswordEncoderAuthenticationManagerBuilder(objectPostProcessor, passwordEncoder) {@Overridepublic AuthenticationManagerBuilder eraseCredentials(boolean eraseCredentials) {authenticationBuilder.eraseCredentials(eraseCredentials);return super.eraseCredentials(eraseCredentials);}@Overridepublic AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationEventPublisher(AuthenticationEventPublisher eventPublisher) {authenticationBuilder.authenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);return super.authenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);}};}
在这个方法中,创建了两个几乎一模一样的AuthenicationManagerBuilder实例,为什么会有两个呢?第一个authenticationBuilder是一个局部的AuthenicationManagerBuilder,将来会传入到HttpSecurity中去构建局部的AuthenticationManager;第二个localConfigureAuthenticationBldr则是一个用来构建全局AuthenticationManager的AuthenicationManagerBuilder。
📢在此处,有的小伙伴就会问了:构建全局的AuthenticationManager不是一开始就在AuthenticationConfiguration中创建了吗?为什么这里还会有一个?是的,当前这个localConfigureAuthenticationBldr是可以禁用的,如果禁用了,就会使用AuthenticationConfiguration中提供的AuthenticationManager,如果没有禁用的话,就是用localConfigureAuthenticationBldr来构建全局的AuthenticationManager。
另一个方法是getHttp方法:
protected final HttpSecurity getHttp() throws Exception {if (http != null) {return http;}AuthenticationEventPublisher eventPublisher = getAuthenticationEventPublisher();localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.authenticationEventPublisher(eventPublisher);AuthenticationManager authenticationManager = authenticationManager();authenticationBuilder.parentAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager);Map<Class<?>, Object> sharedObjects = createSharedObjects();http = new HttpSecurity(objectPostProcessor, authenticationBuilder,sharedObjects);//省略return http;}
在getHttp方法中,会首先调用authenticationManager方法去获取一个全局的AuthenticationManager,并调用parentAuthenticationManager方法给上面局部的authenticationBuilder中的parentAuthenticationManager属性设置parent,即全局的AuthenticationManager,然后在构建HttpSecurity的时候将局部authenticationBuilder传入进去。
那么关键性的问题就是authenticationManager方法到底是怎么执行的了:
protected AuthenticationManager authenticationManager() throws Exception {if (!authenticationManagerInitialized) {configure(localConfigureAuthenticationBldr);if (disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr) {authenticationManager = authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();}else {authenticationManager = localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.build();}authenticationManagerInitialized = true;}return authenticationManager;}protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {this.disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr = true;}
可以看到,如果AuthenticationManager还没有初始化,那就先进行初始化。初始化首先调用configure方法,默认情况下,configure方法里面会把disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr变量设置为true,这样接下来就会进入到if分支中,这个configure方法不知道大家有没有觉得眼熟?我们在自定义的SecurityConfig配置类继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter时,一般都会重写该方法,一旦重写了这个方法,那么disableLocalConfigureAuthenticationBldr变量就不会变成true,依然是false,这样在获取AuthenticationManager的时候就会进入到else分支。
如果进入到if分支中,就意味着开发者并没有重写configure方法,AuthenicationManagerBuilder就使用默认的,大家可以看到,此时调用authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager()方法去获取AuthenticationManager,也就是一开始我们说的那个全局的配置。
如果开发者重写了configure方法,意味着开发者对AuthenicationManagerBuilder进行了一些定制,此时就不能继续使用AuthenticationConfiguration中配置的默认的AuthenticationManager了,而要根据开发者的具体配置,调用localConfigureAuthenticationBldr.build方法去构建全局的AuthenticationManager。
一句话,AuthenticationConfiguration中的配置有没有用上,全看开发着有没有重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#congiure方法,重写了,就用localConfigureAuthenticationBldr来构建parent级别的AuthenticationManager,没重写,就用AuthenticationConfiguration中的方法来构建。
这是扮演parent角色的AuthenticationManager的构建过程,当然,parent并非必须,如果你没有这个需求,也可以不配置parent。
最后来看下局部的AuthenticationManager是如何构建的,也就是和HttpSecurity绑定的那个AuthenticationManager。
根据前面的介绍,HttpSecurity在构建的时候就会传入AuthenicationManagerBuilder,如下:
public HttpSecurity(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor,AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationBuilder,Map<Class<?>, Object> sharedObjects) {super(objectPostProcessor);Assert.notNull(authenticationBuilder, "authenticationBuilder cannot be null");setSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class, authenticationBuilder);//省略}
传入进来的AuthenicationManagerBuilder,二话不说就存到SharedObject中,这个根据官方的解释,说它是一个在不同Configurer中共享的对象的工具,其实可以理解为一个缓存,现在存进去,需要的时候再取出来。
取出来的方法,在HttpSecurity中也已经定义好了,如下:
private AuthenticationManagerBuilder getAuthenticationRegistry() {return getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);}
在HttpSecurity中,凡是涉及到AuthenticationManager配置的,都会调用getAuthenticationRegistry方法,如下:
public HttpSecurity userDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService)throws Exception {getAuthenticationRegistry().userDetailsService(userDetailsService);return this;}public HttpSecurity authenticationProvider(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider) {getAuthenticationRegistry().authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);return this;}
最后在HttpSecurity的beforeConfigure方法中完成构建:
@Overrideprotected void beforeConfigure() throws Exception {setSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class, getAuthenticationRegistry().build());}
至此,无论是全局的AuthenticationManager,还是局部的AuthenticationManager就都和大家捋一遍了。
6、小结
为什么每一个HttpSecurity都要绑定一个AuthenticationManager呢?
因为在同一个系统中,我们可以配置多个HttpSecurity,也就是多个不同的过滤器链,既然有多个过滤器链,每个请求到来的时候,他需要进入到某一个过滤器链中去处理,每个过滤器链中又会涉及到AuthenticationProvider的管理,不同的过滤器链中的AuthenticationProvider肯定是各自管理最为合适,也就是不同的过滤器链中都有一个绑定的AuthenticationManager,及每一个HttpSecurity都要绑定一个AuthenticationManager。

