本文内容与上篇文章深入理解AuthenticationManagerBuilder(源码篇)内容强关联,所以强烈建议先学习上篇文章内容,再来看本文,就会好理解很多!
1、抛砖引玉
@Configurationpublic class SecurityConfig {@BeanUserDetailsService us() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withUsername("sang").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());return manager;}@Configuration@Order(1)static class DefaultWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {UserDetailsService us1() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withUsername("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin", "aaa", "bbb").build());return manager;}@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.antMatcher("/foo/**").authorizeRequests().anyRequest().hasRole("admin").and().formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/foo/login").permitAll().and().userDetailsService(us1()).csrf().disable();}}@Configuration@Order(2)static class DefaultWebSecurityConfig2 extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {UserDetailsService us2() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withUsername("江南一点雨").password("{noop}123").roles("user", "aaa", "bbb").build());return manager;}@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.antMatcher("/bar/**").authorizeRequests().anyRequest().hasRole("user").and().formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/bar/login").permitAll().and().csrf().disable().userDetailsService(us2());}}}
此处定义了两个过滤器链。但是在每个过滤器中,又都提供了一个UserDetailsService实例,然后在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中,配置了这个UserDetailsService实例。除了每一个过滤器链中都配置了一个UserDetailsService外,还提供了一个UserDetailsService的Bean,所以这里前前后后相当于一共有三个用户,那么我们在登录的时候,使用哪个用户可以登录成功呢?
先说结论:
- 当登录地址是
/foo/login,那么sang和javaboy两个用户可以登录成功 - 当登录地址是
/bar/login,那么sang和江南一点雨两个用户可以登录成功
也就是说,那个全局的,公共的UserDetailsService总是有效的,而针对不同过滤器链配置的UserDetailsService则只针对当前过滤器链生效。
2、源码分析
2.1、全局AuthenticationManager
首先大家注意,虽然定义了两个过滤器链,但是在两个过滤器链的定义中,都没有重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#congiure方法,结合上篇文章,没有重写这个方法,就意味着AuthenticationConfiguration中提供的全局AuthenticationManager是有效的,也就是说,系统默认提供的AuthenticationManager将作为其他局部AuthenticationManager的parent。
那么我们来看下全局的AuthenticationManager都配置了啥?
public AuthenticationManager getAuthenticationManager() throws Exception {if (this.authenticationManagerInitialized) {return this.authenticationManager;}AuthenticationManagerBuilder authBuilder = this.applicationContext.getBean(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);if (this.buildingAuthenticationManager.getAndSet(true)) {return new AuthenticationManagerDelegator(authBuilder);}for (GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter config : globalAuthConfigurers) {authBuilder.apply(config);}authenticationManager = authBuilder.build();if (authenticationManager == null) {authenticationManager = getAuthenticationManagerBean();}this.authenticationManagerInitialized = true;return authenticationManager;}
全局的配置中,有一步就是遍历globalAuthConfigurers,遍历全局的xxxConfigurer,并进行配置。全局的xxxConfigurer一共有三个,分别是:
- EnableGlobalAuthenticationAutowiredConfigurer
- InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer
- InitializeAuthenticationProviderBeanManagerConfigurer
其中,InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer看名字就是用来配置UserDetailsService:
@Order(InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer.DEFAULT_ORDER)class InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurerextends GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter {@Overridepublic void init(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {auth.apply(new InitializeUserDetailsManagerConfigurer());}class InitializeUserDetailsManagerConfigurerextends GlobalAuthenticationConfigurerAdapter {@Overridepublic void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {if (auth.isConfigured()) {return;}UserDetailsService userDetailsService = getBeanOrNull(UserDetailsService.class);if (userDetailsService == null) {return;}PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = getBeanOrNull(PasswordEncoder.class);UserDetailsPasswordService passwordManager = getBeanOrNull(UserDetailsPasswordService.class);DaoAuthenticationProvider provider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();provider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);if (passwordEncoder != null) {provider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder);}if (passwordManager != null) {provider.setUserDetailsPasswordService(passwordManager);}provider.afterPropertiesSet();auth.authenticationProvider(provider);}}}
可以看到,InitializeUserDetailsBeanManagerConfigurer中定义了内部类,在其内部类的configure方法中,通过getBeanOrNull去从容器中查找UserDetailsService实例,查找到后,创建DaoAuthenticationProvider,并最终配置给AuthenticationManagerBuilder对象。
这里的getBeanOrNull方法从容器中查找到的,实际上就是Spring容器中的Bean,也就是我们一开始配置了sang用户的那个Bean,这个Bean被交给了全局的AuthenticationManager,也就是所有局部AuthenticationManager的parent。
2.2、局部AuthenticationManager
从上篇文章中可以知道所有HttpSecurity在构建的过程中,都会传递一个局部的AuthenticationManagerBuilder进来,这个局部的AuthenticationManagerBuilder一旦传入进来就存入了共享对象中,以后需要用的时候再从共享对象中取出来,部分代码如下:
public HttpSecurity(ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor,AuthenticationManagerBuilder authenticationBuilder,Map<Class<?>, Object> sharedObjects) {super(objectPostProcessor);Assert.notNull(authenticationBuilder, "authenticationBuilder cannot be null");setSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class, authenticationBuilder);//省略}private AuthenticationManagerBuilder getAuthenticationRegistry() {return getSharedObject(AuthenticationManagerBuilder.class);}
所以,在HttpSecurity中配置UserDetailsService,实际上是给这个AuthenticationManagerBuilder配置的:
public HttpSecurity userDetailsService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService)throws Exception {getAuthenticationRegistry().userDetailsService(userDetailsService);return this;}
也就是局部AuthenticationManager。至此,整个流程就很清晰了。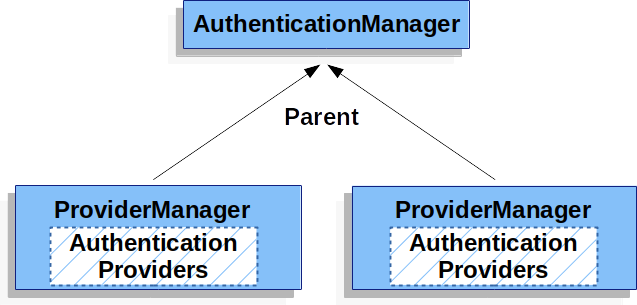
再结合上面的图说明一下,每一个过滤器链都会绑定一个自己的ProviderManager,即AuthenticationManager的实现,而每一个ProviderManager中都通过DaoAuthenticationProvider持有一个UserDetailsService对象,当开始认证的时候,首先由过滤器链所持有的局部ProviderManager去认证,要是认证失败了,则调用ProviderManager的parent去认证,此时就会用到全局AuthenticationManager中DaoAuthenticationProvider中的UserDetailsService对象了。
结合一开始的案例,例如你的登录地址是/foo/login,如果你的登录用户是sang/123,那么先去HttpSecurity的局部ProviderManager中去认证,结果验证失败(局部的ProviderManager中对应的用户是javaboy),此时就会进入局部ProviderManager的parent去认证,也就是全局认证,全局的ProviderManager中所对应的用户就是sang了,此时就认证成功!
3、再抛
再次修改SecurityConfig的定义,如下:
@Configurationpublic class SecurityConfig {@BeanUserDetailsService us() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withUsername("sang").password("{noop}123").roles("admin").build());return manager;}@Configuration@Order(1)static class DefaultWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {UserDetailsService us1() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withUsername("javaboy").password("{noop}123").roles("admin", "aaa", "bbb").build());return manager;}@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {auth.userDetailsService(us1());}@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.antMatcher("/foo/**").authorizeRequests().anyRequest().hasRole("admin").and().formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/foo/login").permitAll().and().csrf().disable();}}@Configuration@Order(2)static class DefaultWebSecurityConfig2 extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {UserDetailsService us2() {InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();manager.createUser(User.withUsername("江南一点雨").password("{noop}123").roles("user", "aaa", "bbb").build());return manager;}@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {auth.userDetailsService(us2());}@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.antMatcher("/bar/**").authorizeRequests().anyRequest().hasRole("user").and().formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/bar/login").permitAll().and().csrf().disable();}}}
和前面相比,这段代码的核心变化,就是我重写了WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#congiure方法,根据上篇文章的介绍,重写了该方法之后,默认的全局AuthenticationManager就失效了,也就是说sang这个用户定义失效了,换言之,无论是/foo/login还是/bar/login,使用sang/123现在都无法登录了。
在每一个HttpSecurity过滤器链中,都重写了WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#congiure方法,并且配置了UserDetailsService,这个重写,相当于我在定义parent级别的ProviderManager。而每一个HttpSecurity过滤器链则不再包含UserDetailsService。
当用户登录时,先去找到HttpSecurity过滤器链中的ProviderManager去认证,结果认证失败了,然后再找到ProviderManager的parent去认证,就成功了!

