概念:出现在其他语句内部的select语句,称为子
查询或内查询
内部嵌套其他select语句的查询,称为外查询或主
查询
分类:
按子查询出现的位置:
select后面
仅仅支持标量查询
from后面
支持表子查询
where或having后面
标量子查询(单行),
列子查询(多行),
行子查询
exists后面(相关子查询)
表子查询
按结果集的行列数不同:
标量子查询(结果只有一行一列)
列子查询(结果集只有一列多行)
行子查询(结果集有一行多列)
表子查询(一般为多行多列)
一、where或having后面
1、标量子查询(单行子查询)
2、列子查询(多行子查询)
3、行子查询(多列多行、一行多列)
特点:
1.子查询放在小括号内
2.子查询一般放在条件的右侧
3.标量子查询,一般搭配着单行操作符使用
>< >= <= = <>
列子查询,一般搭配着多行操作符使用
IN /NOT IN、ANY/SOME、ALL
4.子查询的执行优先于主查询执行,主查询的条件用到了子查询结果
1.标量子查询
案例一:
谁的工资比 Abel高?
1.先查询Abel的工资
selectsalaryfromemployeeswherelast_name = 'Abel'select *fromemployeeswheresalary>(selectsalaryfromemployeeswherelast_name = 'Abel')
执行单行子查询(标量子查询)
题目:
返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary比143号员工多的员工
姓名,job_id 和工资。
1.先找141号员工的job_id
selectjob_idfromemployeeswhereemployee_id=141;
2.然后找143号的员工的salary
selectsalaryfromemployeeswhereemployee_id=143
3.然后找job_id=1,salary>2的员工的姓名,job_id 和工资。
selectlast_name,job_id,salaryfromemployeeswherejob_id=(selectjob_idfromemployeeswhereemployee_id=141)andsalary>(selectsalaryfromemployeeswhereemployee_id=143);
2.多行子查询(列子查询)
返回多行比较操作符
IN /NOT IN、ANY/SOME、ALL
案例:
返回其它部门中比job_id为‘IT_PROG’部门所有工资都低的员工的员工号、姓名、job_id 以及salary
selectlast_name,employee_id,job_id,salaryfromemployeeswheresalary<all(select distinctsalaryfromemployeeswherejob_id = 'IT_PROG')andjob_id<>'IT_PROG';
行子查询(结果集一行多列或多行多列)
二、放在select后面
三、放在from后面
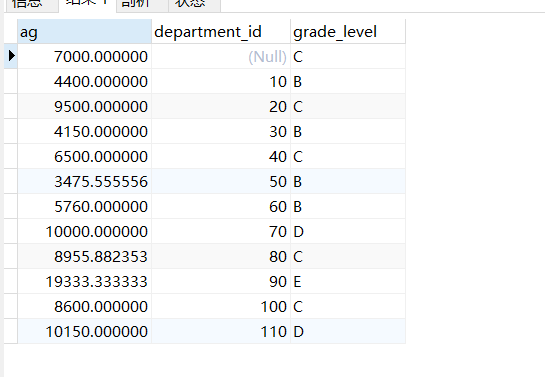
案例:查询每个部门的平均工资的工资等级
首先查询每个部门的平均工资
selectAVG(salary),department_idfromemployeesgroup bydepartment_id;
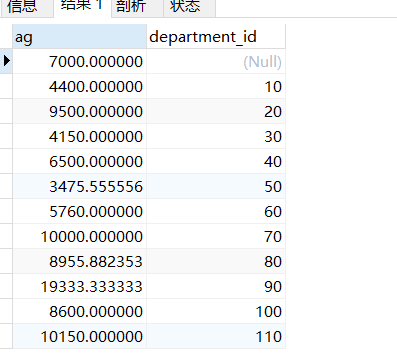
然后将上表与job_grades表连接起来
selectsa.*,grade_levelfrom( selectAVG(salary) ag,department_idfromemployeesgroup bydepartment_id) saJOINjob_grades gonsa.ag BETWEEN lowest_sal and highest_sal;
案例练习
子查询练习
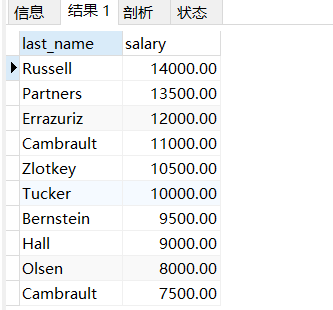
一、查询和Zlotkey相同部门的员工姓名和工资
1、查询Zlotkey的部门
selectdepartment_idfromemployeeswherelast_name = 'Zlotkey';
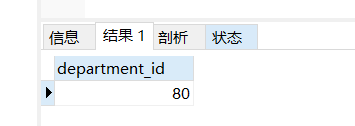
单行单列,判断是标量子查询
然后查询姓名和工资
SELECTlast_name,salaryfromemployeeswheredepartment_id=(selectdepartment_idfromemployeeswherelast_name = 'Zlotkey');
二、查询各部门工资比本部平均工资高的员工的员工号,姓名和工资
1.首先查询
各个部门的平均工资
SELECTdepartment_id,AVG(salary)fromemployeesGROUP BYdepartment_idHAVINGdepartment_id is not null;
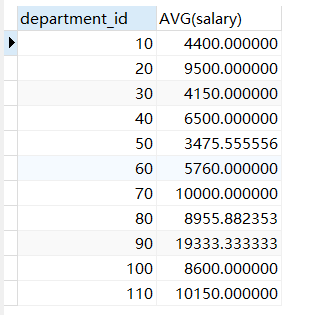
2连接1结果集和employees表,进行筛选
SELECTe.employee_id,last_name,e.salaryfromemployees ejoin(SELECTdepartment_id,AVG(salary) salfromemployeesGROUP BYdepartment_idHAVINGdepartment_id is not null) saone.department_id = sa.department_idwheree.salary>sal;