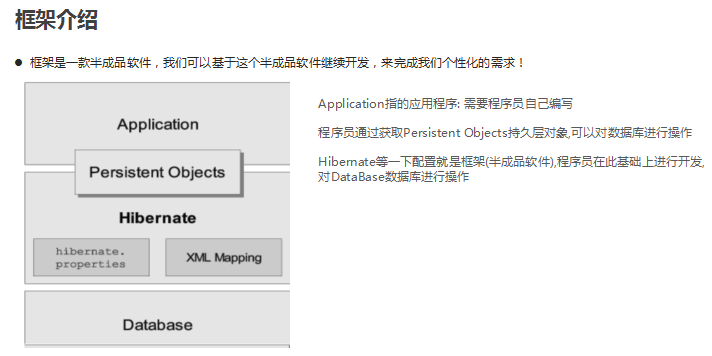
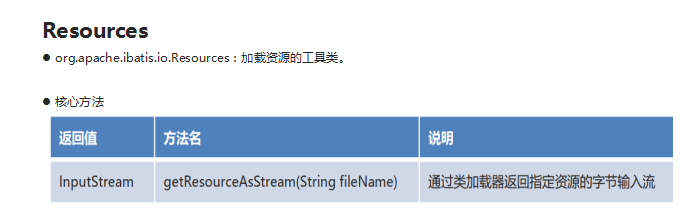
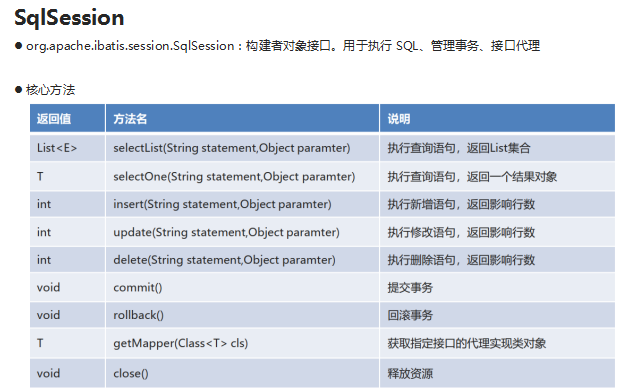
框架的介绍
映射规则:就是把对应表里的数据对应到java中对应的封装类中,表字段(列名)对应类中的属性, 表里封装的数据 也就是对象例如: 学生类中的姓名,年龄,学号组成的数据
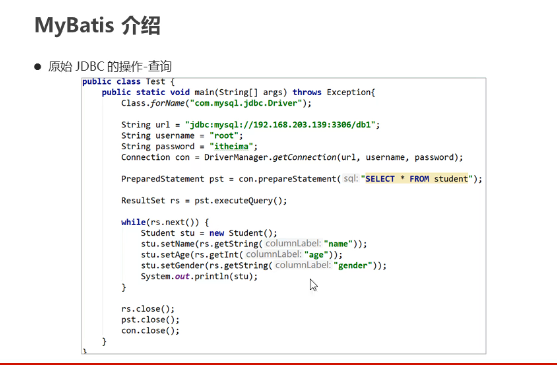
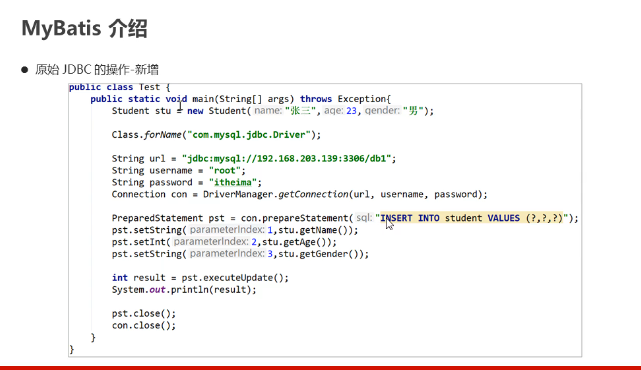
MyBatis介绍



映射配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="StudentMapper"><select id="select" resultType="com.itheima.dao.Teacher">select * from teacher</select></mapper>
核心配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><!--根标签--><configuration><!-- 配置数据库环境标签 ,环境可以有多个,default指定使用哪一个--><environments default="mysql"><!-- 配置数据库环境标签,这只是其中一个,用id来分辨 --><environment id="mysql"><transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.23.129:3306/db2"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="itheima888"/></dataSource></environment></environments><!-- 引入映射配置文件--><mappers><!-- mapper引入指定映射配置文件 resoutce属性指定配置文件名称--><mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
public class MyBatisTeacher {//查询全部@Testpublic void selectAll() throws Exception {//1.加载核心配置文件(核心配置文件)InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对想SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过SqlSession工厂对象获取SqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();//4.执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接受结果(映射配置文件中的,名称空间.id属性)List<Teacher> list = sqlSession.selectList("StudentMapper.select");//5.处理结果for (Teacher teacher : list) {System.out.println(teacher);}//6.释放结果sqlSession.close();is.close();}}
MyBatis相关的API类
1.Resources
2.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
3.SqlSessionFactory
4.SqlSession
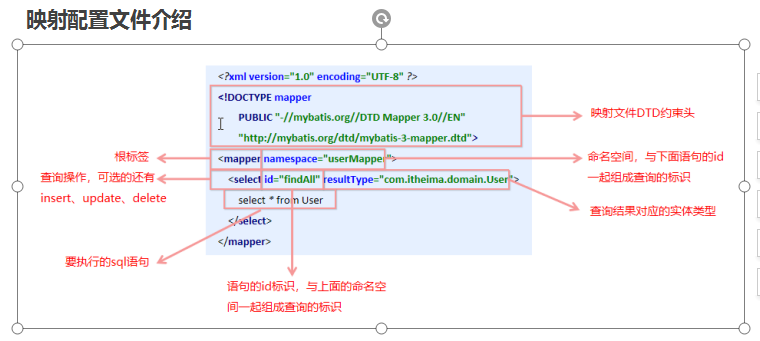
映射配置文件介绍
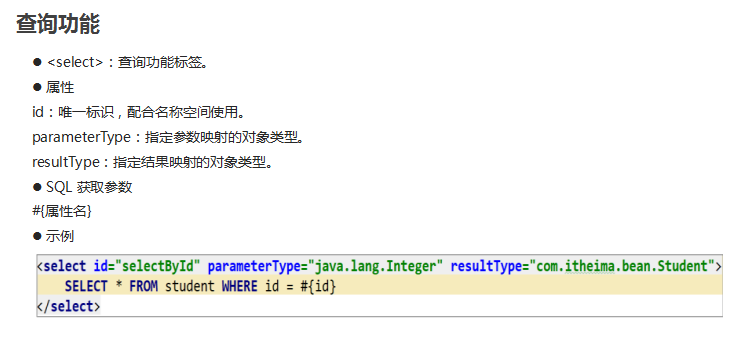
3.2 查询功能
- :查询功能标签。
- 属性
- id:唯一标识, 配合名称空间使用。
- parameterType:指定参数映射的对象类型。
- resultType:指定结果映射的对象类型。
- SQL 获取参数格式: #{属性名}
- 示例
3.3 新增功能
- :新增功能标签。
- 属性
- id:唯一标识, 配合名称空间使用。
- parameterType:指定参数映射的对象类型。
- resultType:指定结果映射的对象类型。
SQL 获取参数格式: #{属性名}
示例

3.4 修改功能
- :修改功能标签。
- 属性
- id:唯一标识, 配合名称空间使用。
- parameterType:指定参数映射的对象类型。
- resultType:指定结果映射的对象类型。
SQL 获取参数格式: #{属性名}
示例

3.5 删除功能
- :查询功能标签。
- 属性
- id:唯一标识, 配合名称空间使用。
- parameterType:指定参数映射的对象类型。
- resultType:指定结果映射的对象类型。
SQL 获取参数格式: #{属性名}
示例

- 总结: 大家可以发现crud操作,除了标签名称以及sql语句不一样之外,其他属性参数基本一致。
3.6 映射配置文件小结
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.StudentMapper">注意下面的id属性值是可以随便起的,resultType是根据查询出来的数据要封装到哪所配置parameterType=是根据sql语句的查询参数来判断的他的数据类型,如果参数较多,数据是从来的就写那个类<!--查询所有--><select id="selectAll" resultType="Student" >select * from student</select><!--根据id查询--><select id="selectById" resultType="Student" parameterType="int">select * from student where id=#{id}</select><!--添加学生--><insert id="insert" parameterType="Student">insert into student (id,name,age) values (#{id},#{name},#{age})</insert><!--修改学生--><update id="update" parameterType="Student">update student set name=#{name},age=#{age} where id=#{id}</update><!--删除学生--><delete id="delete" parameterType="int">delete from student where id=#{id}</delete></mapper>
四.Mybatis核心配置文件介绍
4.1 核心配置文件介绍
核心配置文件包含了 MyBatis 最核心的设置和属性信息。如数据库的连接、事务、连接池信息等。
如下图:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!--MyBatis的DTD约束--><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><!--configuration 核心根标签--><configuration><!--environments配置数据库环境,环境可以有多个。default属性指定使用的是哪个--><environments default="mysql"><!--environment配置数据库环境 id属性唯一标识--><environment id="mysql"><!-- transactionManager事务管理。 type属性,采用JDBC默认的事务--><transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager><!-- dataSource数据源信息 type属性 连接池--><dataSource type="POOLED"><!-- property获取数据库连接的配置信息 --><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///db1" /><property name="username" value="root" /><property name="password" value="root" /></dataSource></environment></environments><!-- mappers引入映射配置文件 --><mappers><!-- mapper 引入指定的映射配置文件 resource属性指定映射配置文件的名称 --><mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
4.2 数据库连接配置文件引入
properties标签引入外部文件
- configuration跟标签下引入
<!--引入数据库连接的配置文件--><properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
- configuration跟标签下引入
具体使用,如下配置
- value=”${键名}”
<!-- property获取数据库连接的配置信息 --><property name="driver" value="${driver}" /><property name="url" value="${url}" /><property name="username" value="${username}" /><property name="password" value="${password}" />
- value=”${键名}”
4.3 起别名
- :为全类名起别名的父标签。
- :为全类名起别名的子标签。
- 属性
type:指定全类名
alias:指定别名 - :为指定包下所有类起别名的子标签。(别名就是类名)
- 通过name属性:name=”com.itheima.bean”
- 如下图:

- 具体如下配置
<!--起别名--><typeAliases><typeAlias type="com.itheima.bean.Student" alias="student"/><!--<package name="com.itheima.bean"/>--></typeAliase
4.4 总结
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!--MyBatis的DTD约束--><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><!--根标签--><configuration><properties resource="jdbc.properties"/><!--起别名--><typeAliases><typeAlias type="com.itheima.bean.Student" alias="student"/><!--给指定包下的类起别名,别名就是类名小写--><!-- <package name="com.itheima.bean"/>--></typeAliases><plugins><plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin></plugins><!-- 配置数据库环境标签 ,环境可以有多个,default指定使用哪一个--><environments default="mysql"><!-- 配置数据库环境标签,这只是其中一个,用id来分辨 --><environment id="mysql"><transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${driver}"/><property name="url" value="${url}"/><property name="username" value="${username}"/><property name="password" value="${password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments><!-- 引入映射配置文件--><mappers><!-- mapper引入指定映射配置文件 resoutce属性指定配置文件名称--><mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
五.Mybatis传统方式开发
5.1 Dao 层传统实现方式
- 分层思想:控制层(controller)、业务层(service)、持久层(dao)。
调用流程 ```sql / 持久层实现类 / public class StudentMapperImpl implements StudentMapper {
/*
查询全部
*/ @Override public List
selectAll() { List<Student> list = null;SqlSession sqlSession = null;InputStream is = null;try{//1.加载核心配置文件is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接收结果list = sqlSession.selectList("StudentMapper.selectAll");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//5.释放资源if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}if(is != null) {try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//6.返回结果return list;
}
/*
根据id查询
*/ @Override public Student selectById(Integer id) {
Student stu = null;SqlSession sqlSession = null;InputStream is = null;try{//1.加载核心配置文件is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接收结果stu = sqlSession.selectOne("StudentMapper.selectById",id);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//5.释放资源if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}if(is != null) {try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//6.返回结果return stu;
}
/*
新增功能
*/ @Override public Integer insert(Student stu) {
Integer result = null;SqlSession sqlSession = null;InputStream is = null;try{//1.加载核心配置文件is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接收结果result = sqlSession.insert("StudentMapper.insert",stu);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//5.释放资源if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}if(is != null) {try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//6.返回结果return result;
}
/*
修改功能
*/ @Override public Integer update(Student stu) {
Integer result = null;SqlSession sqlSession = null;InputStream is = null;try{//1.加载核心配置文件is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接收结果result = sqlSession.update("StudentMapper.update",stu);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//5.释放资源if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}if(is != null) {try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//6.返回结果return result;
}
/*
删除功能
*/ @Override public Integer delete(Integer id) {
Integer result = null;SqlSession sqlSession = null;InputStream is = null;try{//1.加载核心配置文件is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.执行映射配置文件中的sql语句,并接收结果result = sqlSession.delete("StudentMapper.delete",id);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//5.释放资源if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}if(is != null) {try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//6.返回结果return result;
} }
<a name="d63ca79a"></a>#### 5.2 LOG4J的配置和使用- 在日常开发过程中,排查问题时难免需要输出 MyBatis 真正执行的 SQL 语句、参数、结果等信息,我们就可以借助 LOG4J 的功能来实现执行信息的输出。- 使用步骤:- <a name="Dzq8A"></a>## 核心配置文件中```sql<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!--MyBatis的DTD约束--><!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><!--根标签--><configuration><!-- 数据库连接配置文件引入--><properties resource="jdbc.properties"/><!-- 配置LOG4J--><settings><setting name="logImpl" value="log4j"/></settings><!--起别名--><typeAliases><typeAlias type="com.itheima.bean.Student" alias="student"/><!--给指定包下的类起别名,别名就是类名小写--><!-- <package name="com.itheima.bean"/>--></typeAliases><plugins><plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin></plugins><!-- 配置数据库环境标签 ,环境可以有多个,default指定使用哪一个--><environments default="mysql"><!-- 配置数据库环境标签,这只是其中一个,用id来分辨 --><environment id="mysql"><transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${driver}"/><property name="url" value="${url}"/><property name="username" value="${username}"/><property name="password" value="${password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments><!-- 引入映射配置文件--><mappers><!-- mapper引入指定映射配置文件 resoutce属性指定配置文件名称--><mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
LOG4J配置文件
# Global logging configurationlog4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout# Console output...log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppenderlog4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayoutlog4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
一.接口代理方式实现Dao
1.1 代理开发方式介绍
采用 Mybatis 的代理开发方式实现 DAO 层的开发,这种方式是我们后面进入企业的主流。
Mapper 接口开发方法只需要程序员编写Mapper 接口(相当于Dao 接口),由Mybatis 框架根据接口定义创建接口的动态代理对象,代理对象的方法体同上边Dao接口实现类方法。
Mapper 接口开发需要遵循以下规范:
1) Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的全限定名相同
2) Mapper接口方法名和Mapper.xml中定义的每个statement的id相同
3) Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的parameterType的类型相同
4) Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同
总结:
接口开发的方式: 程序员只需定义接口,就可以对数据库进行操作,那么具体的对象怎么创建?
1.程序员负责定义接口
2.在操作数据库,mybatis框架根据接口,通过动态代理的方式生成代理对象,负责数据库的crud操作
1.2.编写StudentMapper接口
dao层代码
public interface StudentMapper {//动态根据多个id查询public abstract List<Student> selectByIds(List<Integer> ids);//动态sql查询public abstract List<Student> selectNothing(Student stu);//根据名字或者年龄查询public abstract List<Student> selectByNameOrAge(@Param("p1") String name, @Param("p2") Integer age);//查询全部public abstract List<Student> selectAll();//根据id查询public abstract com.itheima.bean.Student selectById(Integer id);//新增数据public abstract Integer insert(Student stu);//修改数据public abstract Integer update(Student stu);//删除数据public abstract Integer delete(Integer id);}
service层代码
实现类
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {@Overridepublic List<Student> selectAll() {//获取sqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();//获取持久层接口的实现类的对象StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//调用实现类中方法执行操作List<Student> list= mapper.selectAll();//释放资源sqlSession.close();//返回结果return list;}@Overridepublic com.itheima.bean.Student selectById(Integer id) {//获取sqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();//获取持久层接口的实现类的对象StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//调用实现类中方法执行操作Student student = mapper.selectById(id);//释放资源sqlSession.close();//返回结果return student;}@Overridepublic Integer insert(Student stu) {//获取sqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();//获取持久层接口的实现类的对象StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//调用实现类中方法执行操作Integer result = mapper.insert(stu);//释放资源sqlSession.close();//返回结果return result;}@Overridepublic Integer update(Student stu) {//获取sqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();//获取持久层接口的实现类的对象StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//调用实现类中方法执行操作Integer result = mapper.update(stu);//释放资源sqlSession.close();//返回结果return result;}@Overridepublic Integer delete(Integer id) {//获取sqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = MyBatisUtils.getSqlSession();//获取持久层接口的实现类的对象StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//调用实现类中方法执行操作Integer result = mapper.delete(id);//释放资源sqlSession.close();//返回结果return result;}}
接口
public interface StudentService {//查询全部public abstract List<com.itheima.bean.Student> selectAll();//根据id查询public abstract com.itheima.bean.Student selectById(Integer id);//新增数据public abstract Integer insert(Student stu);//修改数据public abstract Integer update(Student stu);//删除数据public abstract Integer delete(Integer id);}
controller层代码
public class StudentController {//创建业务层对象private StudentService service=new StudentServiceImpl();//查询全部功能测试@Testpublic void selectAll(){List<Student> students = service.selectAll();for (Student stu :students){System.out.println(stu);}}//根据id查询功能测试@Testpublic void selectById(){Student stu = service.selectById(3);System.out.println(stu);}//新增功能测试@Testpublic void insert(){Student stu = new Student(null,"'朝朝'",18);Integer result = service.insert(stu);System.out.println(result);}//修改功能@Testpublic void update(){Student stu = new Student(5,"朝朝",26);Integer result = service.update(stu);System.out.println(result);}//删除功能@Testpublic void delete(){Integer result = service.delete(6);System.out.println(result);}}
1.3 测试代理方式
public Student selectById(Integer id) {Student stu = null;SqlSession sqlSession = null;InputStream is = null;try{//1.加载核心配置文件is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.获取StudentMapper接口的实现类对象StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); // StudentMapper mapper = new StudentMapperImpl();//5.通过实现类对象调用方法,接收结果stu = mapper.selectById(id);} catch (Exception e) {} finally {//6.释放资源if(sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}if(is != null) {try {is.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}//7.返回结果return stu;}
1.4 源码分析
- 分析动态代理对象如何生成的?
通过动态代理开发模式,我们只编写一个接口,不写实现类,我们通过 getMapper() 方法最终获取到 org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy 代理对象,然后执行功能,而这个代理对象正是 MyBatis 使用了 JDK 的动态代理技术,帮助我们生成了代理实现类对象。从而可以进行相关持久化操作。 - 分析方法是如何执行的?
动态代理实现类对象在执行方法的时候最终调用了 mapperMethod.execute() 方法,这个方法中通过 switch 语句根据操作类型来判断是新增、修改、删除、查询操作,最后一步回到了 MyBatis 最原生的 SqlSession 方式来执行增删改查。
1.5 知识小结
接口代理方式可以让我们只编写接口即可,而实现类对象由 MyBatis 生成。
实现规则 :
- 映射配置文件中的名称空间必须和 Dao 层接口的全类名相同。
- 映射配置文件中的增删改查标签的 id 属性必须和 Dao 层接口的方法名相同。
- 映射配置文件中的增删改查标签的 parameterType 属性必须和 Dao 层接口方法的参数相同。
- 映射配置文件中的增删改查标签的 resultType 属性必须和 Dao 层接口方法的返回值相同。
- 获取动态代理对象 SqlSession 功能类中的 getMapper() 方法。
二. 动态sql语句
2.1 动态sql语句概述
Mybatis 的映射文件中,前面我们的 SQL 都是比较简单的,有些时候业务逻辑复杂时,我们的 SQL是动态变化的,此时在前面的学习中我们的 SQL 就不能满足要求了。
参考的官方文档,描述如下:

2.2 动态 SQL 之<if>
我们根据实体类的不同取值,使用不同的 SQL语句来进行查询。比如在 id如果不为空时可以根据id查询,如果username 不同空时还要加入用户名作为条件。这种情况在我们的多条件组合查询中经常会碰到。
如下图:
<select id="findByCondition" parameterType="student" resultType="student">select * from student<where><if test="id!=0">and id=#{id}</if><if test="username!=null">and username=#{username}</if></where></select>
当查询条件id和username都存在时,控制台打印的sql语句如下:
… … …//获得MyBatis框架生成的StudentMapper接口的实现类StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper( StudentMapper.class);Student condition = new Student();condition.setId(1);condition.setUsername("lucy");Student student = mapper.findByCondition(condition);… … …

当查询条件只有id存在时,控制台打印的sql语句如下:
… … …//获得MyBatis框架生成的UserMapper接口的实现类StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper( StudentMapper.class);Student condition = new Student();condition.setId(1);Student student = mapper.findByCondition(condition);… … …

总结语法:
<where>:条件标签。如果有动态条件,则使用该标签代替 where 关键字。<if>:条件判断标签。<if test=“条件判断”>查询条件拼接</if>
2.3 动态 SQL 之<foreach>
循环执行sql的拼接操作,例如:SELECT * FROM student WHERE id IN (1,2,5)。
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="student">select * from student<where><foreach collection="array" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">#{id}</foreach></where></select>
测试代码片段如下:
… … …//获得MyBatis框架生成的UserMapper接口的实现类StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);int[] ids = new int[]{2,5};List<Student> sList = mapper.findByIds(ids);System.out.println(sList);… … …
总结语法:
<foreach>:循环遍历标签。适用于多个参数或者的关系。<foreach collection=“”open=“”close=“”item=“”separator=“”>获取参数</foreach>
属性
collection:参数容器类型, (list-集合, array-数组)。
open:开始的 SQL 语句。
close:结束的 SQL 语句。
item:参数变量名。
separator:分隔符。
2.4 SQL片段抽取
Sql 中可将重复的 sql 提取出来,使用时用 include 引用即可,最终达到 sql 重用的目的
<!--抽取sql片段简化编写--><sql id="selectStudent" select * from student</sql><select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="student"><include refid="selectStudent"></include> where id=#{id}</select><select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultType="student"><include refid="selectStudent"></include><where><foreach collection="array" open="id in(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">#{id}</foreach></where></select>
总结语法:
我们可以将一些重复性的 SQL 语句进行抽取,以达到复用的效果。
- <sql>:抽取 SQL 语句标签。- <include>:引入 SQL 片段标签。<sql id=“片段唯一标识”>抽取的 SQL 语句</sql> <include refid=“片段唯一标识”/>
2.5 知识小结
MyBatis映射文件配置:
<select>:查询<insert>:插入<update>:修改<delete>:删除<where>:where条件<if>:if判断<foreach>:循环<sql>:sql片段抽取
三. 分页插件
3.1 分页插件介绍

- 分页可以将很多条结果进行分页显示。
- 如果当前在第一页,则没有上一页。如果当前在最后一页,则没有下一页。
- 需要明确当前是第几页,这一页中显示多少条结果。
- MyBatis分页插件总结
- 在企业级开发中,分页也是一种常见的技术。而目前使用的 MyBatis 是不带分页功能的,如果想实现分页的 功能,需要我们手动编写 LIMIT 语句。但是不同的数据库实现分页的 SQL 语句也是不同的,所以手写分页 成本较高。这个时候就可以借助分页插件来帮助我们实现分页功能。
- PageHelper:第三方分页助手。将复杂的分页操作进行封装,从而让分页功能变得非常简单。
3.2 分页插件的使用
MyBatis可以使用第三方的插件来对功能进行扩展,分页助手PageHelper是将分页的复杂操作进行封装,使用简单的方式即可获得分页的相关数据
开发步骤:
①导入与PageHelper的jar包
②在mybatis核心配置文件中配置PageHelper插件
<!-- 注意:分页助手的插件 配置在通用mapper之前 --><plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"><!-- 指定方言 --><property name="dialect" value="mysql"/></plugin>
③测试分页数据获取
@Testpublic void testPageHelper(){//设置分页参数PageHelper.startPage(1,2);List<User> select = userMapper2.select(null);for(User user : select){System.out.println(user);}}
3.3 分页插件的参数获取
获得分页相关的其他参数:
//其他分页的数据PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(select);System.out.println("总条数:"+pageInfo.getTotal());System.out.println("总页数:"+pageInfo.getPages());System.out.println("当前页:"+pageInfo.getPageNum());System.out.println("每页显示长度:"+pageInfo.getPageSize());System.out.println("是否第一页:"+pageInfo.isIsFirstPage());System.out.println("是否最后一页:"+pageInfo.isIsLastPage());
3.4 分页插件知识小结
分页:可以将很多条结果进行分页显示。
- 分页插件 jar 包: pagehelper-5.1.10.jar jsqlparser-3.1.jar
- :集成插件标签。
- 分页助手相关 API
1.PageHelper:分页助手功能类。- startPage():设置分页参数
- PageInfo:分页相关参数功能类。
- getTotal():获取总条数
- getPages():获取总页数
- getPageNum():获取当前页
- getPageSize():获取每页显示条数
- getPrePage():获取上一页
- getNextPage():获取下一页
- isIsFirstPage():获取是否是第一页
- isIsLastPage():获取是否是最后一页
四.MyBatis的多表操作
4.1 多表模型介绍
我们之前学习的都是基于单表操作的,而实际开发中,随着业务难度的加深,肯定需要多表操作的。
- 多表模型分类 一对一:在任意一方建立外键,关联对方的主键。
- 一对多:在多的一方建立外键,关联一的一方的主键。
- 多对多:借助中间表,中间表至少两个字段,分别关联两张表的主键。
4.2 多表模型一对一操作
- 一对一模型: 人和身份证,一个人只有一个身份证
- 代码实现
- 步骤一: sql语句准备 ```sql CREATE TABLE person( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(20), age INT ); INSERT INTO person VALUES (NULL,’张三’,23); INSERT INTO person VALUES (NULL,’李四’,24); INSERT INTO person VALUES (NULL,’王五’,25);
CREATE TABLE card( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, number VARCHAR(30), pid INT, CONSTRAINT cp_fk FOREIGN KEY (pid) REFERENCES person(id) ); INSERT INTO card VALUES (NULL,’12345’,1); INSERT INTO card VALUES (NULL,’23456’,2); INSERT INTO card VALUES (NULL,’34567’,3);
- 步骤二:配置文件```xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.itheima.table01.OneToOneMapper"><!--配置字段和实体对象属性的映射关系--><resultMap id="oneToOne" type="card"><id column="cid" property="id" /><result column="number" property="number" /><!--association:配置被包含对象的映射关系property:被包含对象的变量名javaType:被包含对象的数据类型--><association property="p" javaType="person"><id column="pid" property="id" /><result column="name" property="name" /><result column="age" property="age" /></association></resultMap><select id="selectAll" resultMap="oneToOne">SELECT c.id cid,number,pid,NAME,age FROM card c,person p WHERE c.pid=p.id</select></mapper>
步骤三:测试类
@Testpublic void selectAll() throws Exception{//1.加载核心配置文件InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.获取OneToOneMapper接口的实现类对象OneToOneMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToOneMapper.class);//5.调用实现类的方法,接收结果List<Card> list = mapper.selectAll();//6.处理结果for (Card c : list) {System.out.println(c);}//7.释放资源sqlSession.close();is.close();}
3.一对一配置总结:
<resultMap>:配置字段和对象属性的映射关系标签。id 属性:唯一标识type 属性:实体对象类型<id>:配置主键映射关系标签。<result>:配置非主键映射关系标签。column 属性:表中字段名称property 属性: 实体对象变量名称<association>:配置被包含对象的映射关系标签。property 属性:被包含对象的变量名javaType 属性:被包含对象的数据类型
4.3 多表模型一对多操作
- 一对多模型: 一对多模型:班级和学生,一个班级可以有多个学生。
- 代码实现
- 步骤一: sql语句准备 ```sql CREATE TABLE classes( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(20) ); INSERT INTO classes VALUES (NULL,’黑马一班’); INSERT INTO classes VALUES (NULL,’黑马二班’);
CREATE TABLE student( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(30), age INT, cid INT, CONSTRAINT cs_fk FOREIGN KEY (cid) REFERENCES classes(id) ); INSERT INTO student VALUES (NULL,’张三’,23,1); INSERT INTO student VALUES (NULL,’李四’,24,1); INSERT INTO student VALUES (NULL,’王五’,25,2); INSERT INTO student VALUES (NULL,’赵六’,26,2);
- 步骤二:配置文件```xml<mapper namespace="com.itheima.table02.OneToManyMapper"><resultMap id="oneToMany" type="classes"><id column="cid" property="id"/><result column="cname" property="name"/><!--collection:配置被包含的集合对象映射关系property:被包含对象的变量名ofType:被包含对象的实际数据类型--><collection property="students" ofType="student"><id column="sid" property="id"/><result column="sname" property="name"/><result column="sage" property="age"/></collection></resultMap><select id="selectAll" resultMap="oneToMany">SELECT c.id cid,c.name cname,s.id sid,s.name sname,s.age sage FROM classes c,student s WHERE c.id=s.cid</select></mapper>
步骤三:测试类
@Testpublic void selectAll() throws Exception{//1.加载核心配置文件InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.获取OneToManyMapper接口的实现类对象OneToManyMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OneToManyMapper.class);//5.调用实现类的方法,接收结果List<Classes> classes = mapper.selectAll();//6.处理结果for (Classes cls : classes) {System.out.println(cls.getId() + "," + cls.getName());List<Student> students = cls.getStudents();for (Student student : students) {System.out.println("\t" + student);}}//7.释放资源sqlSession.close();is.close();}
3.一对多配置文件总结:
<resultMap>:配置字段和对象属性的映射关系标签。id 属性:唯一标识type 属性:实体对象类型<id>:配置主键映射关系标签。<result>:配置非主键映射关系标签。column 属性:表中字段名称property 属性: 实体对象变量名称<collection>:配置被包含集合对象的映射关系标签。property 属性:被包含集合对象的变量名ofType 属性:集合中保存的对象数据类型
4.4 多表模型多对多操作
- 多对多模型:学生和课程,一个学生可以选择多门课程、一个课程也可以被多个学生所选择。
- 代码实现
- 步骤一: sql语句准备 ```sql CREATE TABLE course( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, NAME VARCHAR(20) ); INSERT INTO course VALUES (NULL,’语文’); INSERT INTO course VALUES (NULL,’数学’);
CREATE TABLE stu_cr( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, sid INT, cid INT, CONSTRAINT sc_fk1 FOREIGN KEY (sid) REFERENCES student(id), CONSTRAINT sc_fk2 FOREIGN KEY (cid) REFERENCES course(id) ); INSERT INTO stu_cr VALUES (NULL,1,1); INSERT INTO stu_cr VALUES (NULL,1,2); INSERT INTO stu_cr VALUES (NULL,2,1); INSERT INTO stu_cr VALUES (NULL,2,2);
- 步骤二:配置文件```xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.itheima.table03.ManyToManyMapper"><resultMap id="manyToMany" type="student"><id column="sid" property="id"/><result column="sname" property="name"/><result column="sage" property="age"/><collection property="courses" ofType="course"><id column="cid" property="id"/><result column="cname" property="name"/></collection></resultMap><select id="selectAll" resultMap="manyToMany">SELECT sc.sid,s.name sname,s.age sage,sc.cid,c.name cname FROM student s,course c,stu_cr sc WHERE sc.sid=s.id AND sc.cid=c.id</select></mapper>
步骤三:测试类
@Testpublic void selectAll() throws Exception{//1.加载核心配置文件InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("MyBatisConfig.xml");//2.获取SqlSession工厂对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//3.通过工厂对象获取SqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);//4.获取ManyToManyMapper接口的实现类对象ManyToManyMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(ManyToManyMapper.class);//5.调用实现类的方法,接收结果List<Student> students = mapper.selectAll();//6.处理结果for (Student student : students) {System.out.println(student.getId() + "," + student.getName() + "," + student.getAge());List<Course> courses = student.getCourses();for (Course cours : courses) {System.out.println("\t" + cours);}}//7.释放资源sqlSession.close();is.close();}
3.多对多配置文件总结:
<resultMap>:配置字段和对象属性的映射关系标签。id 属性:唯一标识type 属性:实体对象类型<id>:配置主键映射关系标签。<result>:配置非主键映射关系标签。column 属性:表中字段名称property 属性: 实体对象变量名称<collection>:配置被包含集合对象的映射关系标签。property 属性:被包含集合对象的变量名ofType 属性:集合中保存的对象数据类型
4.5 多表模型操作总结
<resultMap>:配置字段和对象属性的映射关系标签。id 属性:唯一标识type 属性:实体对象类型<id>:配置主键映射关系标签。<result>:配置非主键映射关系标签。column 属性:表中字段名称property 属性: 实体对象变量名称<association>:配置被包含对象的映射关系标签。property 属性:被包含对象的变量名javaType 属性:被包含对象的数据类型<collection>:配置被包含集合对象的映射关系标签。property 属性:被包含集合对象的变量名ofType 属性:集合中保存的对象数据类型