JPA第二天
第1章 Spring Data JPA的概述
1.1 Spring Data JPA概述

Spring Data JPA 是 Spring 基于 ORM 框架、JPA 规范的基础上封装的一套JPA应用框架,可使开发者用极简的代码即可实现对数据库的访问和操作。它提供了包括增删改查等在内的常用功能,且易于扩展!学习并使用 Spring Data JPA 可以极大提高开发效率!
Spring Data JPA 让我们解脱了DAO层的操作,基本上所有CRUD都可以依赖于它来实现,在实际的工作工程中,推荐使用Spring Data JPA + ORM(如:hibernate)完成操作,这样在切换不同的ORM框架时提供了极大的方便,同时也使数据库层操作更加简单,方便解耦
1.2 Spring Data JPA的特性

SpringData Jpa 极大简化了数据库访问层代码。 如何简化的呢? 使用了SpringDataJpa,我们的dao层中只需要写接口,就自动具有了增删改查、分页查询等方法。
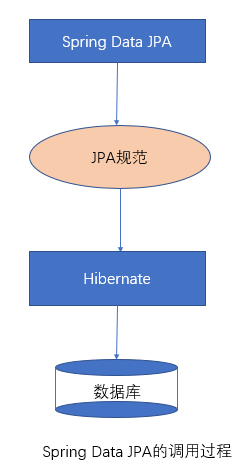
1.3 Spring Data JPA 与 JPA和hibernate之间的关系
JPA是一套规范,内部是有接口和抽象类组成的。hibernate是一套成熟的ORM框架,而且Hibernate实现了JPA规范,所以也可以称hibernate为JPA的一种实现方式,我们使用JPA的API编程,意味着站在更高的角度上看待问题(面向接口编程)
Spring Data JPA是Spring提供的一套对JPA操作更加高级的封装,是在JPA规范下的专门用来进行数据持久化的解决方案。
第2章 Spring Data JPA的快速入门
2.1 需求说明
2.2 搭建Spring Data JPA的开发环境
2.2.1 引入Spring Data JPA的坐标
使用Spring Data JPA,需要整合Spring与Spring Data JPA,并且需要提供JPA的服务提供者hibernate,所以需要导入spring相关坐标,hibernate坐标,数据库驱动坐标等
2.2.2 整合Spring Data JPA与Spring
2.2.3 使用JPA注解配置映射关系
我们使用昨天案例中的Customer实体类对象,已经配置好了映射关系
| package cn.itcast.entity; import javax.persistence.Column; import javax.persistence.Entity; import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; import javax.persistence.GenerationType; import javax.persistence.Id; import javax.persistence.Table; / 所有的注解都是使用JPA的规范提供的注解, 所以在导入注解包的时候,一定要导入javax.persistence下的 / @Entity //声明实体类 @Table(name=”cst_customer”) //建立实体类和表的映射关系 public class Customer { @Id//声明当前私有属性为主键 @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY) //配置主键的生成策略 @Column(name=”cust_id”) //指定和表中cust_id字段的映射关系 private Long custId; @Column(name=”cust_name”) //指定和表中cust_name字段的映射关系 private String custName; @Column(name=”cust_source”)//指定和表中cust_source字段的映射关系 private String custSource; @Column(name=”cust_industry”)//指定和表中cust_industry字段的映射关系 private String custIndustry; @Column(name=”cust_level”)//指定和表中cust_level字段的映射关系 private String custLevel; @Column(name=”cust_address”)//指定和表中cust_address字段的映射关系 private String custAddress; @Column(name=”cust_phone”)//指定和表中cust_phone字段的映射关系 private String custPhone; public Long getCustId() { return custId; } public void setCustId(Long custId) { this.custId = custId; } public String getCustName() { return custName; } public void setCustName(String custName) { this.custName = custName; } public String getCustSource() { return custSource; } public void setCustSource(String custSource) { this.custSource = custSource; } public String getCustIndustry() { return custIndustry; } public void setCustIndustry(String custIndustry) { this.custIndustry = custIndustry; } public String getCustLevel() { return custLevel; } public void setCustLevel(String custLevel) { this.custLevel = custLevel; } public String getCustAddress() { return custAddress; } public void setCustAddress(String custAddress) { this.custAddress = custAddress; } public String getCustPhone() { return custPhone; } public void setCustPhone(String custPhone) { this**.custPhone = custPhone; } } |
|---|
2.3 使用Spring Data JPA完成需求
2.3.1 编写符合Spring Data JPA规范的Dao层接口
Spring Data JPA是spring提供的一款对于数据访问层(Dao层)的框架,使用Spring Data JPA,只需要按照框架的规范提供dao接口,不需要实现类就可以完成数据库的增删改查、分页查询等方法的定义,极大的简化了我们的开发过程。
在Spring Data JPA中,对于定义符合规范的Dao层接口,我们只需要遵循以下几点就可以了:
1.创建一个Dao层接口,并实现JpaRepository和JpaSpecificationExecutor
2.提供相应的泛型
| package cn.itcast.dao; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor; import cn.itcast.entity.Customer; / JpaRepository<实体类类型,主键类型>:用来完成基本CRUD操作 JpaSpecificationExecutor<实体类类型>:用于复杂查询(分页等查询操作) */ public interface CustomerDao extends** JpaRepository } |
|---|
这样我们就定义好了一个符合Spring Data JPA规范的Dao层接口
2.3.2 完成基本CRUD操作
完成了Spring Data JPA的环境搭建,并且编写了符合Spring Data JPA 规范的Dao层接口之后,就可以使用定义好的Dao层接口进行客户的基本CRUD操作
| @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations=”classpath:applicationContext.xml”) public class CustomerDaoTest { @Autowired private CustomerDao customerDao; / 保存客户:调用save(obj)方法 / @Test public void testSave() { Customer c = new Customer(); c.setCustName(“传智播客”); customerDao.save(c); } / 修改客户:调用save(obj)方法 对于save方法的解释:如果执行此方法是对象中存在id属性,即为更新操作会先根据id查询,再更新 如果执行此方法中对象中不存在id属性,即为保存操作 / @Test public void testUpdate() { //根据id查询id为1的客户 Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(1l); //修改客户名称 customer.setCustName(“传智播客顺义校区”); //更新 customerDao.save(customer); } /** 根据id删除:调用delete(id)方法 / @Test public void testDelete() { customerDao.delete(1l); } /** 根据id查询:调用findOne(id)方法 / @Test public void testFindById() { Customer customer = customerDao.findOne(2l); System.*out.println(customer); } } |
|---|
第3章 Spring Data JPA的内部原理剖析
3.1 Spring Data JPA的常用接口分析
在客户的案例中,我们发现在自定义的CustomerDao中,并没有提供任何方法就可以使用其中的很多方法,那么这些方法究竟是怎么来的呢?答案很简单,对于我们自定义的Dao接口,由于继承了JpaRepository和JpaSpecificationExecutor,所以我们可以使用这两个接口的所有方法。
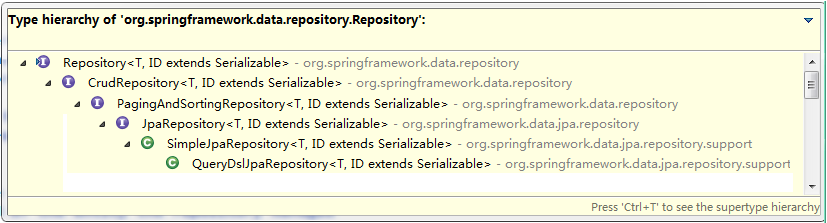
在使用Spring Data JPA时,一般实现JpaRepository和JpaSpecificationExecutor接口,这样就可以使用这些接口中定义的方法,但是这些方法都只是一些声明,没有具体的实现方式,那么在 Spring Data JPA中它又是怎么实现的呢?
3.2 Spring Data JPA的实现过程
通过对客户案例,以debug断点调试的方式,通过分析Spring Data JPA的原来来分析程序的执行过程
我们以findOne方法为例进行分析
l 代理子类的实现过程
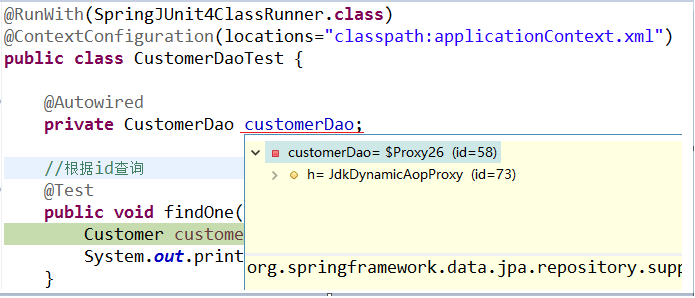
断点执行到方法上时,我们可以发现注入的customerDao对象,本质上是通过JdkDynamicAopProxy生成的一个代理对象
l 代理对象中方法调用的分析
当程序执行的时候,会通过JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法,对customerDao对象生成动态代理对象。根据对Spring Data JPA介绍而知,要想进行findOne查询方法,最终还是会出现JPA规范的API完成操作,那么这些底层代码存在于何处呢?答案很简单,都隐藏在通过JdkDynamicAopProxy生成的动态代理对象当中,而这个动态代理对象就是SimpleJpaRepository
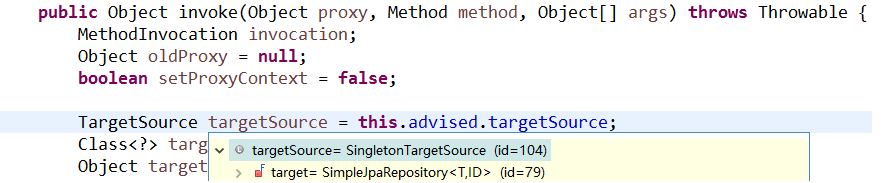
通过SimpleJpaRepository的源码分析,定位到了findOne方法,在此方法中,返回em.find()的返回结果,那么em又是什么呢?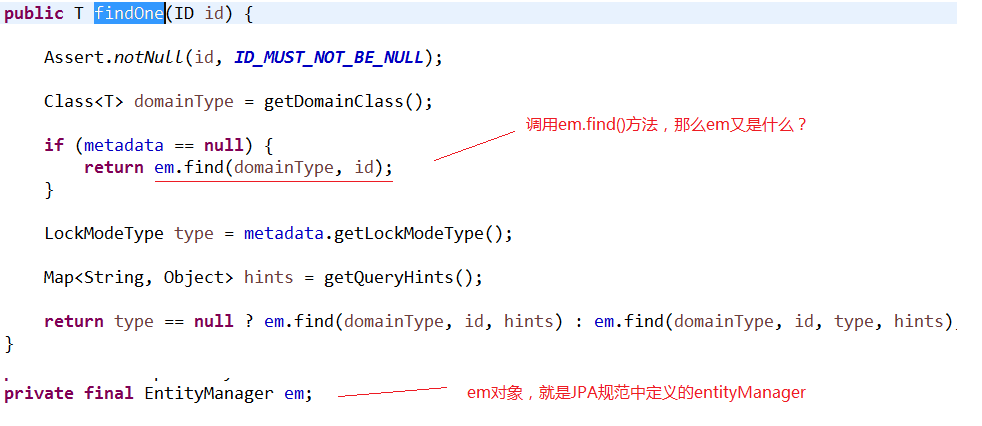
带着问题继续查找em对象,我们发现em就是EntityManager对象,而他是JPA原生的实现方式,所以我们得到结论Spring Data JPA只是对标准JPA操作进行了进一步封装,简化了Dao层代码的开发
3.3 Spring Data JPA完整的调用过程分析
第4章 Spring Data JPA的查询方式
4.1 使用Spring Data JPA中接口定义的方法进行查询
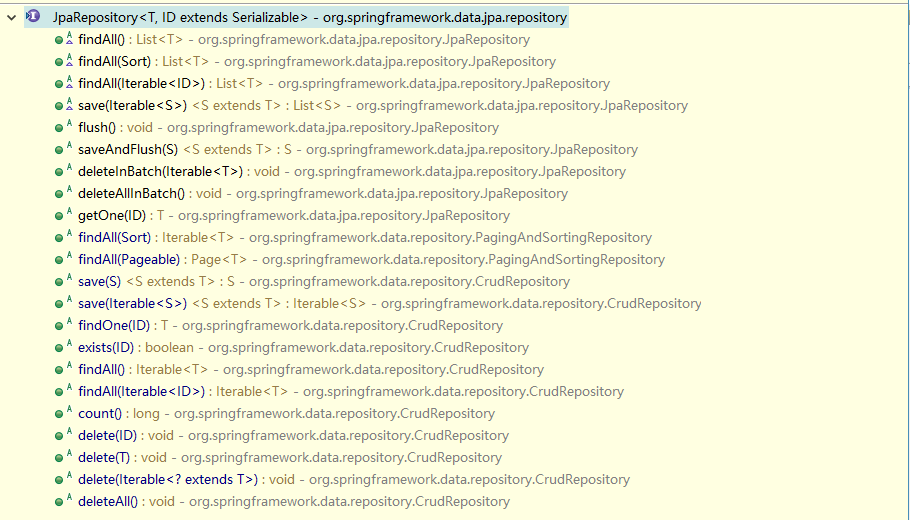
在继承JpaRepository,和JpaRepository接口后,我们就可以使用接口中定义的方法进行查询
l 继承JpaRepository后的方法列表
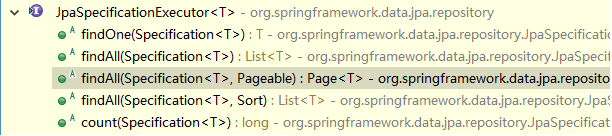
l 继承JpaSpecificationExecutor的方法列表
4.2 使用JPQL的方式查询
使用Spring Data JPA提供的查询方法已经可以解决大部分的应用场景,但是对于某些业务来说,我们还需要灵活的构造查询条件,这时就可以使用@Query注解,结合JPQL的语句方式完成查询
@Query 注解的使用非常简单,只需在方法上面标注该注解,同时提供一个JPQL查询语句即可
| public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository //@Query 使用jpql的方式查询。 @Query(value=”from Customer”) public List //@Query 使用jpql的方式查询。?1代表参数的占位符,其中1对应方法中的参数索引 @Query(value=”from Customer where custName = ?1”) public Customer findCustomer(String custName); } |
|---|
此外,也可以通过使用 @Query 来执行一个更新操作,为此,我们需要在使用 @Query 的同时,用 @Modifying 来将该操作标识为修改查询,这样框架最终会生成一个更新的操作,而非查询
| @Query(value=”update Customer set custName = ?1 where custId = ?2”) @Modifying public void updateCustomer(String custName,Long custId); |
|---|
4.3 使用SQL语句查询
Spring Data JPA同样也支持sql语句的查询,如下:
| / nativeQuery : 使用本地sql的方式查询 / @Query(value=”select * from cst_customer”,nativeQuery=true) public void** findSql(); |
|---|
4.4 方法命名规则查询
顾名思义,方法命名规则查询就是根据方法的名字,就能创建查询。只需要按照Spring Data JPA提供的方法命名规则定义方法的名称,就可以完成查询工作。Spring Data JPA在程序执行的时候会根据方法名称进行解析,并自动生成查询语句进行查询
按照Spring Data JPA 定义的规则,查询方法以findBy开头,涉及条件查询时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是:条件属性首字母需大写。框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,然后对剩下部分进行解析。
| //方法命名方式查询(根据客户名称查询客户) public Customer findByCustName(String custName); |
|---|
具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成SQL如下表所示
| Keyword | Sample | JPQL | ||
| And | findByLastnameAndFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 | ||
| Or | findByLastnameOrFirstname | … where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 | ||
| Is,Equals | findByFirstnameIs, findByFirstnameEquals |
… where x.firstname = ?1 | ||
| Between | findByStartDateBetween | … where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 | ||
| LessThan | findByAgeLessThan | … where x.age < ?1 | ||
| LessThanEqual | findByAgeLessThanEqual | … where x.age ⇐ ?1 | ||
| GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan | … where x.age > ?1 | ||
| GreaterThanEqual | findByAgeGreaterThanEqual | … where x.age >= ?1 | ||
| After | findByStartDateAfter | … where x.startDate > ?1 | ||
| Before | findByStartDateBefore | … where x.startDate < ?1 | ||
| IsNull | findByAgeIsNull | … where x.age is null | ||
| IsNotNull,NotNull | findByAge(Is)NotNull | … where x.age not null | ||
| Like | findByFirstnameLike | … where x.firstname like ?1 | ||
| NotLike | findByFirstnameNotLike | … where x.firstname not like ?1 | ||
| StartingWith | findByFirstnameStartingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) | ||
| EndingWith | findByFirstnameEndingWith | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) | ||
| Containing | findByFirstnameContaining | … where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) | ||
| OrderBy | findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc | … where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc | ||
| Not | findByLastnameNot | … where x.lastname <> ?1 | ||
| In | findByAgeIn(Collection ages) | … where x.age in ?1 | ||
| NotIn | findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) | … where x.age not in ?1 | ||
| TRUE | findByActiveTrue() | … where x.active = true | ||
| FALSE | findByActiveFalse() | … where x.active = false | ||
| IgnoreCase | findByFirstnameIgnoreCase | … where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |