ES6里有6种简单数据类型:undefined, null, Number, Boolean, String, Symbol
1种复杂数据类型:Object
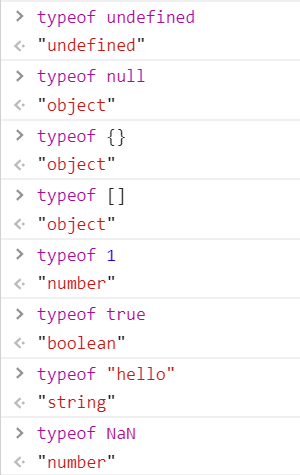
typeof 操作符
undefined
未初始化的变量为undefined,永远不要显示的指定一个变量值为undefined
undefined值用于比较
let xxxconsole.log(xxx == undefined) // true
typeof 一个未声明过的变量返回的是undefined
let xxxtypeof xxx"undefined"typeof ssssss"undefined"
null
Logically, a null value is an empty object pointer
如果要声明一个对象,但不打算赋值,就应该指定为null
let car = null;console.log(typeof car); // "object"
console.log(null == undefined); // trueconsole.log(null === undefined); // false
Boolean
Boolean()函数可以将任何值转为true或false
5个falsy值:
0,NaN, “”, null, undefined
Number
decimal number 十进制
octal (base 8) 八进制以0开头
let octalNum1 = 070; // octal for 56let octalNum2 = 079; // invalid octal - interpreted as 79let octalNum3 = 08; // invalid octal - interpreted as 8
hexadecimal (base 16) 十六进制以0x开头
let hexNum1 = 0xA; // hexadecimal for 10let hexNum2 = 0x1f; // hexadecimal for 31
positive zero (+0) and negative zero (–0)
浮点数比整数占用双倍内存,JS总是想办法把数值转为整数
浮点数计算不精确
if (0.1 + 0.2 == 0.3) { // avoid!console.log("You got 0.3.");}
数值范围
Number.MIN_VALUE5e-324Number.MAX_VALUE1.7976931348623157e+308–Infinity // (negative infinity)Infinity // (positive infinity)isFinite(-Infinity) // 判断是否介于[MIN_VALUE, MAX_VALUE]// false
NaN
// 任何不能转换为number的值,isNaN都返回trueconsole.log(isNaN(NaN)); // trueconsole.log(isNaN(10)); // false - 10 is a numberconsole.log(isNaN("10")); // false - can be converted to number 10console.log(isNaN("blue")); // true - cannot be converted to a numberconsole.log(isNaN(true)); // false - can be converted to number 1
转换为number
Number("hello") // NaNNumber("123") // 123Number(true) // 1Number(null) // 0Number(undefined) // NaN// 将字符串转换为数值parseInt("0xf") // 15parseInt("AF", 16); // 175 指定基数radixparseInt("AF"); // NaN 默认10进制// parseFloat只能转换10进制,不能指定基数parseFloat("123") // 123parseFloat("0xAF") // 0parseFloat("1.22.33") // 1.22
String
toString()
可以将除null、undefined之外的任何值转为字符串
将数字转为字符串时可指定基数
0xAF.toString()"175"0xAF.toString(16)"af"
String()可以将任何值转为字符串,有toString方法的调用toString方法
String(0xAF)String(null)String(undefined)
+””可以转换字符串
1 + ""null + ""
文字模板template literals
用反引号backticks
let myMultiLineTemplateLiteral = `first linesecond line`;
Interpolation插值替换
在``中用${}
let name = "jack"let age = 19console.log(`Hi,${name}, you're ${age} years old`)
tag function
第一个参数strings是去除了${}后分隔的片段组成的数组
剩下的参数是${}里的值
用途:可以把${ a } + ${ b } = ${ a + b }里的${}值作为参数分解出来
let a = 6;let b = 9;function simpleTag(strings, aValExpression, bValExpression, sumExpression) {console.log(strings); // 第一个参数传入的肯定是数组console.log(aValExpression);console.log(bValExpression);console.log(sumExpression);return 'foobar';}// 调用标签函数simpleTag`${ a } + ${ b } = ${ a + b }`// 结果["", " + ", " = ", "", raw: Array(4)]6915"foobar"
用spread operator改写
let a = 6;let b = 9;function simpleTag(strings, ...expressions) {console.log(strings); // 第一个参数传入的肯定是数组for(const expression of expressions){console.log(expression)}return 'foobar';}// 调用标签函数simpleTag`${ a } + ${ b } = ${ a + b }`
String.raw
console.log(`\u00A9`); // ©console.log(String.raw`\u00A9`); // \u00A9
Symbol
symbol是唯一且不可变的,用于对象属性
symbols are intended to be used as unique tokens
let genericSymbol = Symbol();console.log(genericSymbol); // Symbol()let fooSymbol = Symbol('foo');console.log(fooSymbol); // Symbol(foo);
Symbol()不能用new操作符
let myBoolean = new Boolean();console.log(typeof myBoolean); // "object"let myString = new String();console.log(typeof myString); // "object"let myNumber = new Number();console.log(typeof myNumber); // "object"let mySymbol = new Symbol(); // TypeError: Symbol is not a constructor
Object
let o = new Object();o.__proto__ === Object.prototype// 构造函数都有prototype
o.proto里的属性
- constructor —The function that was used to create the object. In the previous example, the
constructor is the Object() function.
- hasOwnProperty(propertyName) —Indicates if the given property exists on the object
instance (not on the prototype). The property name must be specified as a string (for
example, o.hasOwnProperty(“name”) ).