零碎知识点
- 栈的大小:
答:1MB,大概10^6字节,可以存25W个int
实现memcpy函数
void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n)
从存储区src复制n个字符到dest
考虑步长对齐和内存重叠问题
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>void *my_memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, int n){if (dst == NULL || src == NULL || n <= 0)return NULL;char * pdst = (char *)dst;char * psrc = (char *)src;if (pdst > psrc && pdst < psrc + n){pdst = pdst + n - 1;psrc = psrc + n - 1;while (n--)*pdst-- = *psrc--;}else{while (n--)*pdst++ = *psrc++;}return dst;}int main(){char src[] = "Helloaaaaaa";char dest[] = "My lady";my_memcpy(dest, src, 20);printf("%s\n", dest);return 0;}
如何在main函数之前让函数执行?
1.全局类的构造函数
2.将函数返回值赋值
#include<iostream>using namespace std;class Test {public:Test();int test2();};Test::Test() {cout << "Test" << endl;}int Test::test2() {cout << "Test2" << endl;return 0;}Test ts;int a = ts.test2();int main() {cout << "main" << endl;//ts.test2();return 0;}
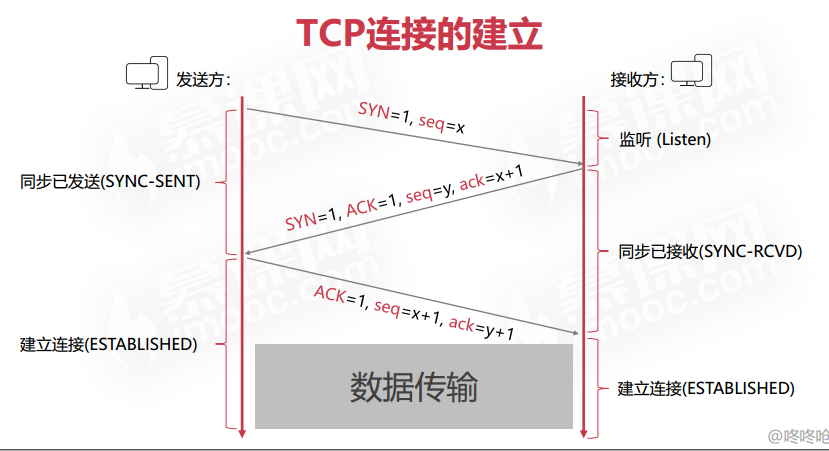
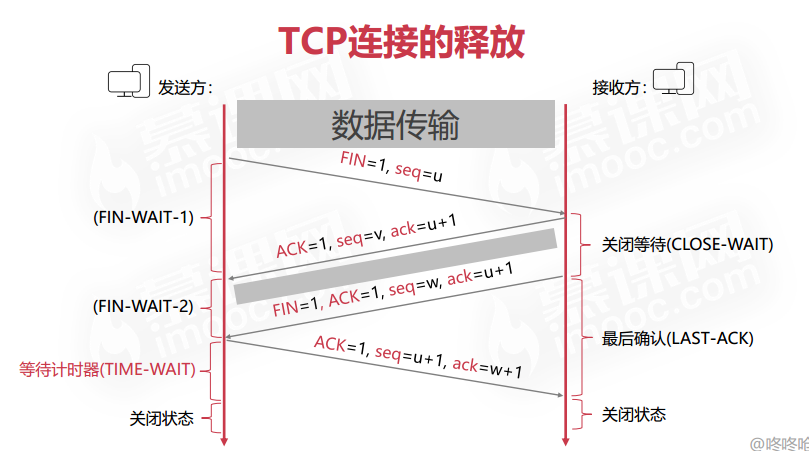
三次握手和四次挥手
生产者消费者问题-互斥锁-线程同步
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <vector>pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;int num = 0;void *producer(void*){int times = 10000000;while(times --){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);num += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}}void *comsumer(void*){int times = 10000000;while(times --){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);num -= 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}}int main(){printf("Start in main function.");pthread_t thread1, thread2;pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, &producer, NULL);pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, &comsumer, NULL);pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);printf("Print in main function: num = %d\n", num);return 0;}
编译:一定要加-lpthread参数
g++ mutex_lock_demo.cpp -o lock -lpthread
结果分析
不加锁:每次的结果都不同 加锁:结果为0
条件变量-线程同步
通常与互斥锁配合使用
#include <iostream>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <vector>#include <queue>#include <unistd.h>#include <pthread.h>int MAX_BUF = 100;int num = 0;pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;void* producer(void*){while(true){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);while (num >= MAX_BUF){// 等待printf("缓冲区满了, 等待消费者消费...\n");pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); //休眠并解锁,等待}num += 1;printf("生产一个产品,当前产品数量为:%d\n", num);sleep(1);pthread_cond_signal(&cond);printf("通知消费者...\n");pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);sleep(1);}}void* consumer(void*){while(true){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);while (num <= 0){// 等待printf("缓冲区空了, 等待生产者生产...\n");pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); //休眠并解锁,等待}num -= 1;printf("消费一个产品,当前产品数量为:%d\n", num);sleep(1);pthread_cond_signal(&cond);printf("通知生产者...\n");pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}}int main(){pthread_t thread1, thread2;pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, &consumer, NULL);pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, &producer, NULL);pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);return 0;}
父进程子进程
#include <iostream>#include <cstring>#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;int main(){pid_t pid;int num = 888;pid = fork();if(pid == 0){cout << "这是一个子进程." << endl;cout << "num in son process: " << num << endl;while(true){num += 1;cout << "num in son process: " << num << endl;sleep(1);}}else if(pid > 0){cout << "这是一个父进程." << endl;cout << "子进程id: " << pid << endl;cout << "num in father process: " << num << endl;while(true){num -= 1;cout << "num in father process: " << num << endl;sleep(1);}}else if (pid < 0){cout << "创建进程失败." << endl;}return 0;}
读写锁-线程同步
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <vector>int num = 0;pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;pthread_rwlock_t rwlock = PTHREAD_RWLOCK_INITIALIZER;void *reader(void*){int times = 10000000;while(times --){// pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);if (times % 1000 == 0){// printf("print num in reader: num = %d\n", num);// sleep(1);usleep(10);}pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);// pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);}}void *writer(void*){int times = 10000000;while(times --){pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);// pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);num += 1;// pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}}int main(){printf("Start in main function.\n");pthread_t thread1, thread2, thread3;pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, &reader, NULL);pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, &reader, NULL);pthread_create(&thread3, NULL, &writer, NULL);pthread_join(thread1, NULL);pthread_join(thread2, NULL);pthread_join(thread3, NULL);printf("Print in main function: num = %d\n", num);return 0;}
共享内存-进程间通信
common.h
#ifndef __COMMON_H__
#define __COMMON_H__
#define TEXT_LEN 2048
// 共享内存的数据结构
struct ShmEntry{
// 是否可以读取共享内存,用于进程间同步
bool can_read;
// 共享内存信息
char msg[2048];
};
#endif
server.cpp
#include "common.h"
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// 共享内存的结构体
struct ShmEntry *entry;
// 1. 申请共享内存
int shmid = shmget((key_t)1111, sizeof(struct ShmEntry), 0666|IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1){
std::cout << "Create share memory error!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 2. 连接到当前进程空间/使用共享内存
entry = (ShmEntry*)shmat(shmid, 0, 0);
entry->can_read = 0;
while (true){
if (entry->can_read == 1){
std::cout << "Received message: " << entry->msg << std::endl;
entry->can_read = 0;
}else{
std::cout << "Entry can not read. Sleep 1s." << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
}
// 3. 脱离进程空间
shmdt(entry);
// 4. 删除共享内存
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0);
return 0;
}
client.cpp
#include "common.h"
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
struct ShmEntry *entry;
// 1. 申请共享内存
int shmid = shmget((key_t)1111, sizeof(struct ShmEntry), 0666|IPC_CREAT);
if (shmid == -1){
std::cout << "Create share memory error!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 2. 连接到当前进程空间/使用共享内存
entry = (ShmEntry*)shmat(shmid, 0, 0);
entry->can_read = 0;
char buffer[TEXT_LEN];
while (true){
if (entry->can_read == 0){
std::cout << "Input message>>> ";
fgets(buffer, TEXT_LEN, stdin);
strncpy(entry->msg, buffer, TEXT_LEN);
std::cout << "Send message: " << entry->msg << std::endl;
entry->can_read = 1;
}
}
// 3. 脱离进程空间
shmdt(entry);
// 4. 删除共享内存
shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0);
return 0;
}
socket套接字-进程间通信
server.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
// 域套接字
#define SOCKET_PATH "./domainsocket"
#define MSG_SIZE 2048
int main()
{
int socket_fd, accept_fd;
int ret = 0;
socklen_t addr_len;
char msg[MSG_SIZE];
struct sockaddr_un server_addr;
// 1. 创建域套接字
socket_fd = socket(PF_UNIX,SOCK_STREAM,0); //本地套接字
if(-1 == socket_fd){
std::cout << "Socket create failed!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 移除已有域套接字路径
remove(SOCKET_PATH);
// 内存区域置0
bzero(&server_addr,sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sun_family = PF_UNIX;
strcpy(server_addr.sun_path, SOCKET_PATH);
// 2. 绑定域套接字
std::cout << "Binding socket..." << std::endl;
ret = bind(socket_fd,(sockaddr *)&server_addr,sizeof(server_addr));
if(0 > ret){
std::cout << "Bind socket failed." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 3. 监听套接字
std::cout << "Listening socket..." << std::endl;
ret = listen(socket_fd, 10);
if(-1 == ret){
std::cout << "Listen failed" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
std::cout << "Waiting for new requests." << std::endl;
accept_fd = accept(socket_fd, NULL, NULL);
bzero(msg,MSG_SIZE);
while(true){
// 4. 接收&处理信息
recv(accept_fd, msg, MSG_SIZE, 0);
std::cout << "Received message from remote: " << msg <<std::endl;
}
close(accept_fd);
close(socket_fd);
return 0;
}
client.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
#define SOCKET_PATH "./domainsocket"
#define MSG_SIZE 2048
int main()
{
int socket_fd;
int ret = 0;
char msg[MSG_SIZE];
struct sockaddr_un server_addr;
// 1. 创建域套接字
socket_fd = socket(PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(-1 == socket_fd){
std::cout << "Socket create failed!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 内存区域置0
bzero(&server_addr,sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sun_family = PF_UNIX;
strcpy(server_addr.sun_path, SOCKET_PATH);
// 2. 连接域套接字
ret = connect(socket_fd, (sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
if(-1 == ret){
std::cout << "Connect socket failed" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
while(true){
std::cout << "Input message>>> ";
fgets(msg, MSG_SIZE, stdin);
// 3. 发送信息
ret = send(socket_fd, msg, MSG_SIZE, 0);
}
close(socket_fd);
return 0;
}
自旋锁-线程同步
自旋锁会导致阻塞,cpu占用100
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <vector>
pthread_spinlock_t spin_lock;
int num = 0;
void *producer(void*){
int times = 10000000;
while(times --){
pthread_spin_lock(&spin_lock);
num += 1;
pthread_spin_unlock(&spin_lock);
}
}
void *comsumer(void*){
int times = 10000000;
while(times --){
pthread_spin_lock(&spin_lock);
num -= 1;
sleep(10);
pthread_spin_unlock(&spin_lock);
}
}
int main(){
printf("Start in main function.\n");
pthread_spin_init(&spin_lock, 0);
pthread_t thread1, thread2;
pthread_create(&thread1, NULL, &producer, NULL);
pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, &comsumer, NULL);
pthread_join(thread1, NULL);
pthread_join(thread2, NULL);
printf("Print in main function: num = %d\n", num);
return 0;
}
线程间共享哪些资源?
| 独立的资源 | 栈 |
|---|---|
| 共享的资源 | 堆、全局变量、静态变量 |
六大排序算法:快排、归并、插入、希尔、堆排序、冒泡。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void bubble_sort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
bool flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j <= n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
flag = true;
}
}
if (!flag) break;
}
}
void insert_sort(int arr[], int n) {
//空位最多到i
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
void shell_sort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int step = n / 2; step > 0; step /= 2) {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i += step) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - step;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + step] = arr[j];
j -= step;
}
arr[j + step] = key;
}
}
}
/*
堆排序
递归和非递归写法
*/
void heapify(int arr[], int root, int n) {
int left = root * 2;
int right = root * 2 + 1;
if (right <= n && arr[right] > arr[left] ) {
left = right;
}
if (left <= n && arr[left] > arr[root]) {
swap(arr[left], arr[root]);
heapify(arr, left, n);
}
}
void heapify2(int arr[], int root, int n) {
int left = root * 2;
while (left <= n) {
int right = left + 1;
if (right <= n && arr[right] > arr[left]) left = right;
if (left <= n && arr[left] > arr[root]) {
swap(arr[left], arr[root]);
root = left;
left = root * 2;
}
else break;
}
}
void build_heap(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = n / 2; i >= 1; i--) {
heapify2(arr, i, n);
}
}
void heap_sort(int arr[], int n) {
build_heap(arr, n);
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
swap(arr[i], arr[1]);
heapify2(arr, 1, i-1);
}
}
/*
快排
两个函数:quick_sort和partition
*/
int partition(int arr[], int l, int r) {
int temp = arr[l];
while (l < r) {
while (l < r && arr[r] >= temp) r--;
arr[l] = arr[r];
while (l < r && arr[l] < temp) l++;
arr[r] = arr[l];
}
arr[l] = temp;
return l;
}
void quick_sort(int arr[], int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return;
int p = partition(arr, l, r);
quick_sort(arr, l, p - 1);
quick_sort(arr, p + 1, r);
}
void merge_sort(int arr[], int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return;
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
merge_sort(arr, l, mid); //返回的一定是一个有序的数组
merge_sort(arr, mid + 1, r);
int* tmp = new int[r - l + 1];
int left_idx = l, r_idx = mid + 1;
int k = 0;
while (left_idx <= mid && r_idx <= r) {
if (arr[left_idx] < arr[r_idx]) tmp[k++] = arr[left_idx++];
else tmp[k++] = arr[r_idx++];
}
while (left_idx <= mid) tmp[k++] = arr[left_idx++];
while (r_idx <= r) tmp[k++] = arr[r_idx++];
for (int i = l, j = 0;i<=r; i++, j++) {
arr[i] = tmp[j];
}
delete[]tmp;
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {688,-1,5,100,10 ,999 ,3, 5, 7 };
//heap_sort(arr, 8);
//quick_sort(arr, 0, 8);
//bubble_sort(arr, 8);
//insert_sort(arr, 8);
//shell_sort(arr, 8);
merge_sort(arr,0, 8);
for (int i = 0; i <= 8; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
}