简介
XOR (异或)逻辑回归
预测概率
操作步骤
1、引入数据集
引自 playground 源码
会生成 [{x:-1, y: -2, label: 0}, {x:1, y: 2, label: 1}] 这样的数据结构
export function getData(numSamples) {let points = [];function genGauss(cx, cy, label) {for (let i = 0; i < numSamples / 2; i++) {let x = normalRandom(cx);let y = normalRandom(cy);points.push({ x, y, label });}}genGauss(2, 2, 0);genGauss(-2, -2, 0);genGauss(-2, 2, 1);genGauss(2, -2, 1);return points;}/*** Samples from a normal distribution. Uses the seedrandom library as the* random generator.** @param mean The mean. Default is 0.* @param variance The variance. Default is 1.*/function normalRandom(mean = 0, variance = 1) {let v1, v2, s;do {v1 = 2 * Math.random() - 1;v2 = 2 * Math.random() - 1;s = v1 * v1 + v2 * v2;} while (s > 1);let result = Math.sqrt(-2 * Math.log(s) / s) * v1;return mean + Math.sqrt(variance) * result;}
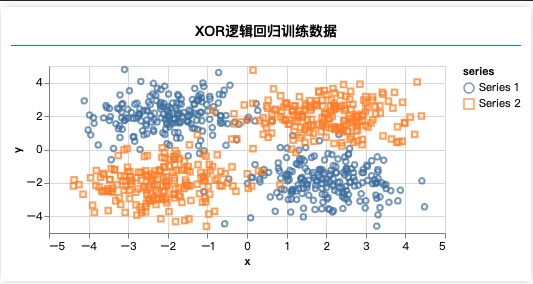
2、可视化数据集
3、创建模型、添加层、训练、训练结果
import * as tf from '@tensorflow/tfjs'import * as tfvis from '@tensorflow/tfjs-vis'import { getData } from './data'window.onload = async () => {const data = getData(400)// 可视化数据集tfvis.render.scatterplot({name: 'XOR逻辑回归训练数据'},{values: [data.filter(p => p.label === 1), // 分类为1 的数组data.filter(p => p.label === 0) // 分类为0 的数组] // 这里是嵌套数组,来渲染不同颜色的点})// 定义多层神经网络const model = tf.sequential()// 添加第一层model.add(tf.layers.dense({units: 4, // 神经元个数inputShape: [2], // 数据特征是[x,y]activation: 'relu'}))// 添加第二层 (第二层会继承第一层的入参)model.add(tf.layers.dense({units: 1, // 这里是一个,因为只需要输出一个概率activation: 'sigmoid' // 输出0-1的概率}))model.compile({loss: tf.losses.logLoss,optimizer: tf.train.adam(0.1)})const inputs = tf.tensor(data.map(p => [p.x,p.y]))const label = tf.tensor(data.map(p => p.label))await model.fit(inputs, label, {epochs: 10,callbacks: tfvis.show.fitCallbacks({name: '训练效果'}, ['loss'])})window.predict = (form) => {const pred = model.predict(tf.tensor([[form.x.value*1, form.y.value*1]])) // * 1转化成数字alert(`预测结果${pred.dataSync()[0]}`)}}
总结: 与此前单一神经元不同的是,多层神经元要添加多层,以来解决复杂的问题