- 1. MyBatis入门
- {} 是 sql 中的参数占位符,预编译处理,#{} 传入参数是以字符串传入,MyBatis 在处理 #{} 时,会将 SQL 中的 #{} 替换为 ?号,调用 PreparedStatement 的 set 方法来赋值。变量替换后,#{} 对应的变量自动加上单引号,并且使用 #{} 可以有效的防止 SQL 注入,提高系统安全性。
- 2. MyBatis全局配置文件
- 2.1 properties标签(引入外部文件)
- 2.2 settings标签(常用设置)
- 2.3 typeAliases标签(别名)
- 2.4 environments标签(环境配置)
- 2.5 mappers映射器
- 3.2 参数传递
- 3.3 结果映射
- 3.4 模糊查询
- 6.5 简述Mybatis的Xml映射文件和Mybatis内部数据结构之间的映射关系?
- 6.6 Mybatis是如何将sql执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
- 6.7 Mybatis映射文件中,如果A标签通过include引用了B标签的内容,请问,B标签能否定义在A标签的后面,还是说必须定义在A标签的前面?
- 6.8 MyBatis实现一对一,一对多有几种方式,怎么操作的?
- 6.9 Mybatis是否可以映射Enum枚举类?
- 6.10 MyBatis 嵌套查询和嵌套结果有什么区别?
1. MyBatis入门
1.1 MyBatis是什么?
MyBatis 是一款的持久层框架,支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射,免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作,可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口 和 Java POJO 为数据库中的记录。
为什么说 MyBatis 是半自动 ORM 映射工作?它与全自动的区别在哪里?
MyBatis 在查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,需要手动编写 sql 来完成,所以它是半自动的。而 Hibernate 查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取,所以它是全自动的。
1.2 MyBatis接口开发规范
- 对应的 Mapper 配置文件的 namespace 属性值必须是 Mapper 接口的全类名。比如,com.xuwei.mapper.UserMapper
- Mapper 接口的方法名必须与 mapper 配置文件对应的 id 值相同。
- Mapper 接口的方法参数类型必须与 mapper 配置文件中的 parameterType 类型匹配上。
- Mapper接口的方法返回值类型必须与mapper配置文件中配置的 resultType 类型匹配上。
1.3 #{}和${}
{} 是 sql 中的参数占位符,预编译处理,#{} 传入参数是以字符串传入,MyBatis 在处理 #{} 时,会将 SQL 中的 #{} 替换为 ?号,调用 PreparedStatement 的 set 方法来赋值。变量替换后,#{} 对应的变量自动加上单引号,并且使用 #{} 可以有效的防止 SQL 注入,提高系统安全性。
${} 没有预编译处理。MyBatis 在处理 ${} 时,就是把 ${} 替换成变量的值,相当于 JDBC 的 Statement 编译。不能防止 SQL 注入。
1.4 快速上手
mybatis依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.mybatis</groupId><artifactId>mybatis</artifactId><version>3.4.5</version></dependency>
mapper接口
public interface EmployeeMapper {Employee getEmployeeById(Integer id);}
sql 映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><!--namespace属性:设置为接口的全类名--><mapper namespace="com.xuwei.dao.EmployeeMapper"><!--id属性:设置为接口中的方法名resultType属性:设置为方法的返回值的类型的全类名--><select id="getEmployeeById" resultType="com.xuwei.entity.Employee">select id,last_name lastName,email,salary,dept_id deptIdfrom employeeswhere id = #{id}</select></mapper>
全局配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"><configuration><environments default="development"><environment id="development"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/><property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/><property name="username" value="root"/><property name="password" value="123"/></dataSource></environment></environments><!--设置Mapper映射文件(sql映射文件)--><mappers><mapper resource="com/xuwei/dao/EmployeeMapper.xml"/></mappers></configuration>
测试文件
@Testpublic void testEmployee() throws IOException {//mybatis全局配置文件路径String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";//读取类路径下的配置文件得到输入流InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);//创建sqlSessionFactory对象SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);//获取sqlSession对象SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try {//获取mapper对象EmployeeMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);//调用方法Employee employee = mapper.getEmployeeById(1);System.out.println(employee);} finally {sqlSession.close();}}
查看结果
2. MyBatis全局配置文件
2.1 properties标签(引入外部文件)
<!--resource属性:引入类路径下的属性文件url属性:引入网络或磁盘路径下的属性文件--><properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties><environments default="development"><environment id="development"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments>
2.2 settings标签(常用设置)
settings 标签必须放在其他标签的上面。
| 设置名 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| cacheEnabled | 缓存的全局开关 | true |
| lazyLoadingEnabled | 延迟加载的全局开关 | false |
| aggressiveLazyLoading | 开启时,任一方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有延迟加载属性。 否则,每个延迟加载属性会按需加载 | false (在 3.4.1 及之前的版本中默认为 true) |
| useGeneratedKeys | 允许 JDBC 支持自动生成主键,需要数据库驱动支持。如果设置为 true,将强制使用自动生成主键。尽管一些数据库驱动不支持此特性,但仍可正常工作(如 Derby)。 | false |
| autoMappingBehavior | 指定 MyBatis 应如何自动映射列到字段或属性。 NONE 表示关闭自动映射;PARTIAL 只会自动映射没有定义嵌套结果映射的字段。 FULL 会自动映射任何复杂的结果集(无论是否嵌套)。 | partial |
| mapUnderscoreToCamelCase | 是否开启驼峰命名自动映射,即从经典数据库列名 A_COLUMN 映射到经典 Java 属性名 aColumn | false |
2.3 typeAliases标签(别名)
注意:typeAliases 只能写在 environments 标签上面。
<!-- 第一种子标签typeAlias:用来给某些类指定别名type属性:指定起别名的类的全类名alias属性:指定别名,如果没有指定则是类命的首字母小写,但是别名大小写不敏感--><typeAlias type="com.atguigu.mybatis.entities.Employee" alias="employee"></typeAlias><!-- 第二种 --><typeAliases><!--子标签package:通过指定包名给包下所有的类起别名--><package name="com.atguigu.mybatis.entities"/></typeAliases>
2.4 environments标签(环境配置)
- id 为每个环境的标识;
- transactionManager:为事务管理器,具体有三种 JDBC、MANAGED 和自定义。
- JDBC 表示使用了 JDBC 的提交和回滚设置,依赖于从数据源得到的连接来管理事务范 围,常用类 JdbcTransactionFactory;
- MANAGED 表示不提交或回滚一个连接、让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期(比如 JEE 应用服务器的上下文),常用类 ManagedTransactionFactory;
- 如果需要自定义的话,需实现 TransactionFactory 接口,type=全类名/别名。
dataSource:数据源,具体分为4种,实际开发中我们使用 Spring 管理数据源。
- UNPOOLED:不使用连接池, UnpooledDataSourceFactory;
- POOLED:使用连接池, PooledDataSourceFactory;
- JNDI: 在EJB 或应用服务器这类容器中查找指定的数据源;
自定义:实现DataSourceFactory接口,定义数据源的获取方式。
<environments default="development"><!--开发环境 id为标识--><environment id="development"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/></dataSource></environment><!--生产环境--><environment id="online"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments>
2.5 mappers映射器
用来在 mybatis 初始化的时候,告诉 mybatis 需要引入哪些 Mapper 映射文件,只能写在 envirements 下边。具体有两种。 ```xml
---<a name="PQKDR"></a># 3. MyBatis映射CRUD<a name="lEmha"></a>## 3.1 主键生成1、若数据库支持自动生成主键的字段(比如 MySQL 和 SQL Server),则可以设置 useGeneratedKeys=”true”,然后再把 keyProperty 设置到目标属性上。> 主键必须不为空,且自动递增。```xml<insert id="insertTeacher" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id" parameterType="teacher">insert into mybatis_test.teacher(name) values (#{name})</insert>
2、而对于不支持自增型主键的数据库(例如 Oracle),可以使用 selectKey 子标签。比如我们可以在 insert 标签里的 sql 语句上加上 selectKey 子标签,将子标签里的 sql 语句执行结果作为主键 id,然后再调用 insert 语句。
<insert id="addEmployee" databaseId="oracle"><selectKey order="BEFORE" keyProperty="id" resultType="integer">select employee_seq.nextval from dual</selectKey>insert into oracle_employees(id,last_name,email,salary,dept_id)values(#{id},#{lastName},#{email},#{salary},#{deptId})</insert>或者是<insert id="addEmployee" databaseId="oracle"><selectKey order="AFTER" keyProperty="id" resultType="integer">select employee_seq.currval from dual</selectKey>insert into oracle_employees(id,last_name,email,salary,dept_id)values(employee_seq.nextval,#{lastName},#{email},#{salary},#{deptId})</insert>
3.2 参数传递
1、顺序传参法:#{} 里面的数字代表传入参数的顺序,不建议使用。
public User selectUser(String name, int deptId);<select id="selectUser" resultMap="UserResultMap">select * from userwhere user_name = #{0} and dept_id = #{1}</select>
2、@Param注解传参法:#{} 里面的名称对应的是注解 @Param括号里面修饰的名称,推荐使用。
public User selectUser(@Param("userName") String name, int @Param("deptId") deptId);<select id="selectUser" resultMap="UserResultMap">select * from userwhere user_name = #{userName} and dept_id = #{deptId}</select>
3、Map 传参法:#{} 里面的名称对应的是 Map 里面的 key 名称。这种方法适合传递多个参数,且参数易变能灵活传递的情况。
public User selectUser(Map<String, Object> params);<select id="selectUser" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultMap="UserResultMap">select * from userwhere user_name = #{userName} and dept_id = #{deptId}</select>
4、Java Bean 传参法:#{} 里面的名称对应的是 User 类里面的成员属性。
public User selectUser(User user);<select id="selectUser" parameterType="com.jourwon.pojo.User" resultMap="UserResultMap">select * from userwhere user_name = #{userName} and dept_id = #{deptId}</select>
3.3 结果映射
3.3.1 映射相关
MyBatis 中我们经常使用 resultType 完成普通列的映射,比如查询学生的详细信息,定义就是resultType='student',如果我们想要完成复杂查询,比如一对多或者多对一查询,就需要用到 resultMap 实现高级结果集映射。
resultMap 标签里有两个重要的子标签:collection 标签用于一对多处理,association 用于多对一处理。
举例说明:
数据表定义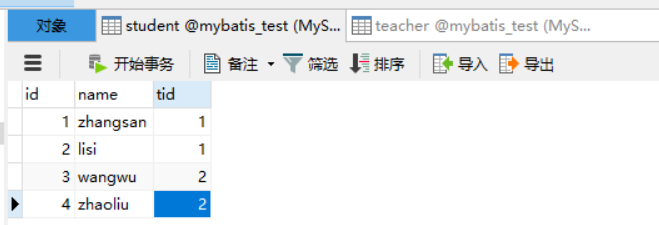
实体类定义
@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class Teacher {private Integer id;private String name;private List<Student> students;}@Data@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructorpublic class Student {private Integer id;private String name;}
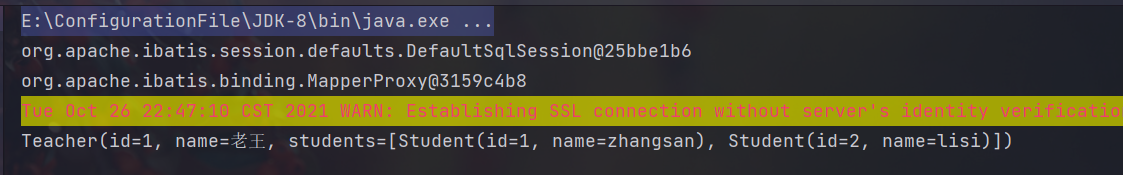
3.2 一对多处理(collection )
mapper 文件
<!-- yxw写,一对多查询,面向对象方式 --><select id="getTeacherById3" resultMap="getTeacherById3Map">select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.name tname,t.id tidfrom mybatis_test.student s, mybatis_test.teacher twhere s.tid = t.id and t.id = #{id}</select><resultMap id="getTeacherById3Map" type="teacher"><id property="id" column="tid"/><result property="name" column="tname"/><!-- 此处students代表的是Teacher类中定义的 List<Student> students --><collection property="students" ofType="student"><id property="id" column="sid"/><result property="name" column="sname"/></collection></resultMap><!--数据库思想--><select id="getTeacherById2" resultMap="TeacherStudent2">select t.id,t.name from mybatis_test.teacher t where t.id = #{id}</select><resultMap id="TeacherStudent2" type="Teacher"><collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="Student" column="id" select="T2"/></resultMap><select id="T2" resultType="Student">select * from mybatis_test.student where tid = #{id}</select>
测试代码
public class TeacherDaoTest {private static InputStream is;private static SqlSession sqlSession;private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;@Testpublic void getTeacherById() throws IOException {try {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();System.out.println(sqlSession);TeacherDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);System.out.println(mapper);Teacher teacher = mapper.getTeacherById(1);System.out.println(teacher);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {sqlSession.close();is.close();}}@Testpublic void getTeacherTwoById() throws IOException {try {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";is = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();System.out.println(sqlSession);TeacherDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(TeacherDao.class);System.out.println(mapper);Teacher teacher = mapper.getTeacherById(1);System.out.println(teacher);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {sqlSession.close();is.close();}}}
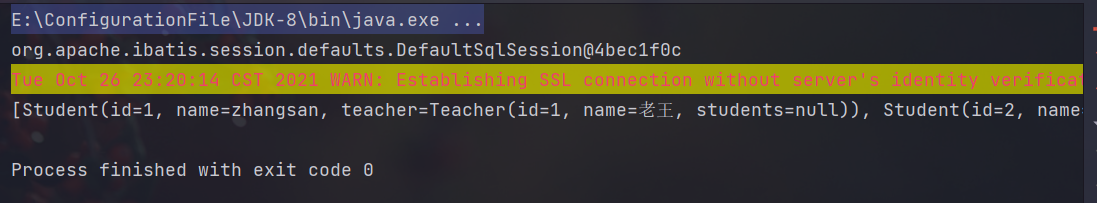
3.3 多对一处理(association)
mapper文件
<!--属性和字段对应 , 类和表对应 , 对象和记录关联一个字段需求:拿到老师这个类的属性association : 关联,多对一column : 数据库对应的列名property : 对应属性名javaType : 多对一字段对应的Java类型select : 关联一个语句--><!-- 按结果嵌套处理,模拟数据库思想 --><select id="getStudents" resultMap="StudentTeacher">select s.id sid,s.name sname,s.tid from mybatis_test.student s</select><resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="Student"><id column="sid" property="id"/><result column="sname" property="name"/><!-- column指向的字段是表里的字段,property指的是类的属性值 --><association column="tid" property="teacher" javaType="teacher" select="getTeacher"/></resultMap><select id="getTeacher" resultType="Teacher">select * from mybatis_test.teacher where id = #{id}</select><!-- 模拟面向对象的思想 --><select id="getStudents2" resultMap="getStudents2Map">select s.id sid,s.name sname,t.id tid,t.name tnamefrom mybatis_test.student s,mybatis_test.teacher twhere s.tid = t.id</select><resultMap id="getStudents2Map" type="student"><id property="id" column="sid"/><result property="name" column="sname"/><association property="teacher" javaType="teacher"><id property="id" column="tid"/><result property="name" column="tname"/></association></resultMap>
3.4 模糊查询
思考一个问题,在 MyBatis 中使用 like语句,应该怎么写?
’%${question}%’:可能引起SQL注入,不推荐。"%"#{question}"%":注意:因为 #{…} 解析成 sql 语句时候,会在变量外侧自动加单引号 ’ ‘,所以这里 % 需要使用双引号 “ “,不能使用单引号 ’ ‘,不然会查不到任何结果。CONCAT(’%’,#{question},’%’):使用 CONCAT() 函数,推荐。- 使用
bind子标签。 ```xml
---
<a name="TJToN"></a>
# 4. 动态SQL
<a name="oQSdb"></a>
## 4.1 什么是动态SQL
比如说,在 jdbc 方法中,我们写复杂 sql 语句时,经常会需要拼接 sql 语句,稍不注意就是少写一个空格或者 "" 然后导致报错。这个 MyBatis 动态 sql 的功能,就能有效解决这个问题,可以让我们像使用标签那样对 sql 进行拼接和判断。
**常用的动态 SQL 有**:
- if && where
- trim
- set
- choose && when
- foreach
<a name="V6sQB"></a>
## 4.2 if && where
where 标签用于解决 SQL 语句中 where 关键字以及条件中第一个 and 或者 or 的问题,if 标签用于简单的判断。xml
<a name="dE69N"></a>
## 4.3 trim
trim 标签可以在条件判断完的 SQL 语句前后添加或者去掉指定的字符。
- prefix:添加前缀。
- prefixOverrides:去掉前缀。
- suffix:添加后缀。
- suffixOverrides:去掉后缀。xml
select id,last_name,email,salary
from employees
<a name="AoGjt"></a>
## 4.6 foreach
foreach 标签主要用在构建 in 条件中,它可以在SQL语句中进行迭代一个集合。常用的属性有:item,index,collection,open,separator,close。
- collection:要迭代的集合。
- item:当前从集合中迭代出的元素。
- open:开始字符。
- close:结束字符。
- separator:元素与元素之间的分隔符。
- index:
- 迭代的是 List 集合: index 表示的当前元素的下标。
- 迭代的 Map 集合: index 表示的当前元素的 key。
**mapper接口**java
List**映射文件**xml
//推荐使用
---<a name="jhuhT"></a># 5. 缓存机制**一级缓存**:1. 一级缓存(local cache),即本地缓存, 作用域默认为 sqlSession。当 Session flush 或 close 后, 该 Session 中的所有 Cache 将被清空。本地缓存不能被关闭,但可以调用 clearCache() 来清空本地缓存, 或者改变缓存的作用域。1. 一级缓存的工作机制:同一次会话期间只要查询过的数据都会保存在当前 SqlSession 的一个 Map 中 key:hashCode+ 查询的 SqlId+ 编写的 sql 查询语句+参数。1. 一级缓存失效的几种情况:1. 不在同一个 SqlSession 对象中。1. 执行语句的参数不同,缓存中也不存在数据。1. 执行增,删,改,语句,会清空掉缓存。1. 手动清空缓存数据。**二级缓存:**<br />1、二级缓存(second level cache),全局作用域缓存,默认不开启,需要手动配置。- 我们需要在 mybatis 的核心配置文件中配置 setting 选项:`cacheEnabled`- 在 Mapper 的配置文件中加入 cache 标签:- 并且需要被二级缓存的对象必须要实现 java 的序列化接口,即实现 Serializable 接口。2、二级缓存在 SqlSession 关闭或提交之后才会生效。<br />**缓存的使用顺序** :1. 当我们执行一个查询语句的时候。mybatis 会先去二级缓存中查询数据。如果二级缓存中没有。就到一级缓存中查找。1. 如果二级缓存和一级缓存都没有。就发 sql 语句到数据库中去查询。1. 查询出来之后马上把数据保存到一级缓存中。1. 当 SqlSession 关闭的时候,会把一级缓存中的数据保存到二级缓存中。---<a name="iCMxd"></a># 6. MyBatis进阶<a name="zGmhD"></a>## 6.1 通常一个Xml映射文件,都会写一个Dao接口与之对应,请问,这个Dao接口的工作原理是什么?Dao接口里的方法,参数不同时,方法能重载吗?Dao 接口,就是我们常说的 Mapper 接口;接口的全限名,就是映射文件中的 namespace 值;接口的方法名,就是映射文件中标签中的 id 值;接口方法内的参数,就是传递给 sql 的参数。Mapper 接口是没有实现类的,当调用接口方法时,接口的全限名+方法名拼接字符串会作为 key 值,可唯一定位一个 MappedStatement ,即定位唯一一个标签对象。举例:com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentDao.findStudentById,可以唯一找到 namespace 为com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentDao 下面 id = findStudentById 的 MappedStatement。在 Mybatis 中,每一个这样的标签,都会被解析为一个 MappedStatement 对象。所以说,Dao 接口里的方法,是不能重载的,因为是接口全限名+方法名的保存和寻找策略。Dao 接口的工作原理是 JDK 动态代理,MyBatis 运行时会使用 JDK 动态代理为 Dao 接口生成 proxy 代理对象,代理对象 proxy 会拦截接口方法,转而执行 MappedStatement 所代表的 sql,并将 sql 执行结果返回。<a name="aGzAr"></a>## 6.2 MyBatis是如何进行分页的?分页插件的原理是什么?插件运行原理?如何编写一个插件?MyBatis 内部使用 RowBounds 对象进行分页,需要注意的是,它是针对 ResultSet 结果集执行的内存分页,而非数据库分页。所以,在生产环境下,不适合直接使用 RowBounds 对象进行分页,有以下两种方案。<br />1、在 SQL 内书写数据库的分页参数来实现分页功能。代码如右:`select * from t_user limit#{start}, #{pageSize}`。<br />2、可以使用开源的分页插件来完成数据库分页。- Mybatis-PageHelper。- MyBatis-Plus。分页插件的基本原理是使用 MyBatis 提供的插件接口,实现自定义插件,在插件的拦截方法内拦截待执行的 sql,然后重写 sql,根据 dialect 方言,添加对应的物理分页语句和物理分页参数。比如:`select * from student;`,拦截 sql 后重写为:`select t.* from (select \* from student) t limit 0,10;`。插件运行原理:MyBatis 仅可以编写针对 ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler、Executor 这 4 种接口的插件,MyBatis 使用 JDK 动态代理,为需要拦截的接口生成代理对象来实现接口方法拦截功能,每当执行这 4 种接口对象的方法时,就会进入拦截方法,具体就是 InvocationHandler 的 invoke() 方法。编写插件:实现 MyBatis 的 Interceptor 接口并重写 intercept() 方法,然后在给插件编写注解,指定要拦截哪⼀个接口的哪些方法即可,最后在配置⽂件中配置你编写的插件。<a name="mwaZn"></a>## 6.3 Mybatis是否支持延迟加载?如果支持,它的实现原理是什么?延迟加载:在真正使用数据的时候才发起查询,不用的时候不查询关联的数据,延迟加载又叫按需查询。MyBatis 仅支持 association 关联对象和 collectioin 关联对象的延迟加载,association 指的是一对一和多对一查询,collection 指的是一对多查询。在 MyBatis 配置文件中,可以使用 settings 标签,配置使用启用延迟加载 `lazyLoadingEnabled=true|false`。实现原理是,使用 CGLIB 创建目标对象的代理对象,当调用目标方法时,进入拦截器方法,比如调用a.getB().getName(),拦截器 invoke() 方法发现 a.getB() 是 null 值,那么就会单独发送事先保存好的查询关联 B 对象的 sql,把 B 查询上来,然后调用 a.setB(b),于是 a 的对象 b 属性就有值了,接着完成a.getB().getName() 方法的调用,这就是延迟加载的基本原理。当然了,不光是 Mybatis,几乎所有的包括 Hibernate,支持延迟加载的原理都是一样的。<a name="kgO4m"></a>## 6.4 当实体类中的属性名和表中的字段名不一样 ,怎么办?1、通过在查询的 SQL 语句中定义字段名的别名,让字段名的别名和实体类的属性名一致。```xml<select id="getOrder" parameterType="int" resultType="com.jourwon.pojo.Order">select order_id id, order_no orderno ,order_price price form orders where order_id=#{id};</select>
2、通过 resultMap 标签来映射字段名和实体类属性名的一一对应的关系。
<select id="getOrder" parameterType="int" resultMap="orderResultMap">select * from orders where order_id=#{id}</select><resultMap type="com.jourwon.pojo.Order" id="orderResultMap"><!–用id属性来映射主键字段–><id property="id" column="order_id"><!–用result属性来映射非主键字段,property为实体类属性名,column为数据库表中的属性–><result property ="orderno" column ="order_no"/><result property="price" column="order_price" /></reslutMap>
6.5 简述Mybatis的Xml映射文件和Mybatis内部数据结构之间的映射关系?
Mybatis 将所有 Xml 配置信息都封装到 All-In-One 重量级对象 Configuration 内部。在 Xml 映射文件中,