线程安全的类—方法加入了synchronized关键字
- StringBuffer
- Vector(不常用) —- synchronizedList
Hashtable(不常用) —- synchronizedMap
------ synchronizedSet
线程不安全的类
StringBuilder
- ArrayList
HashMap ```java
new StringBuffer();new StringBuilder();new Hashtable<>();new HashMap<>();new Vector<>();new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());Map<Integer,String> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>());Set<Integer> set = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>());
<a name="ovsgy"></a>### Lock锁```javapublic class MyThread implements Runnable {private int tickets = 100; //总票数private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();public MyThread() {}@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {//解决线程同步安全问题try {lock.lock(); //加锁if (tickets > 0) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + tickets-- + "张票");}} finally {lock.unlock();//释放锁}}}}
生产者消费者模式

public class Customer implements Runnable{private Box b;public Customer(Box b) {this.b = b;}@Overridepublic void run() {while (true){b.get();}}}
public class Producer implements Runnable {private Box b;public Producer(Box b) {this.b = b;}@Overridepublic void run() {int i = 1;while (i<6){b.put(i++);}}}
public class Box {private int milk;private boolean state = false; //默认状态-->表示奶箱中没有奶public synchronized void put(int milk){if (state){try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}this.milk = milk;System.out.println("送来了第"+this.milk+"瓶奶");//修改状态state = true;//唤醒其他等待线程notifyAll();}public synchronized void get(){if (!state){try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("消费者消费了第"+this.milk+"瓶奶");state = false;notifyAll();}}
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {Box b = new Box();Producer p = new Producer(b);Customer c = new Customer(b);Thread t1 = new Thread(p);Thread t2 = new Thread(c);t1.start();t2.start();}}
送来了第1瓶奶 消费者消费了第1瓶奶 送来了第2瓶奶 消费者消费了第2瓶奶 送来了第3瓶奶 消费者消费了第3瓶奶 送来了第4瓶奶 消费者消费了第4瓶奶 送来了第5瓶奶 消费者消费了第5瓶奶
网络编程
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {//获取ip地址与主机名InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("117.154.105.233");String name = address.getHostName();String ip = address.getHostAddress();System.out.println(name);System.out.println(ip);}
UDP协议
优点:消耗少
缺点:不太可靠,数据可能会丢失
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();byte[] bys = "Hello UDP协议".getBytes();int len = bys.length;InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("117.154.105.233");int port = 10086;//创建数据包DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, len, address, port);//发送数据ds.send(dp);//关闭ds.close();}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//接收数据DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10086);byte[] bys = new byte[1024];int len = bys.length;//创建数据包DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, len);ds.receive(dp);//解析数据包byte[] datas = dp.getData();int lenth = dp.getLength();String dataString = new String(datas,0,lenth);System.out.println(dataString);//关闭ds.close();}
TCP协议
聊天示列
发送用户端
输入886结束退出
可多开SendDemo窗口
import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.InputStreamReader;import java.net.DatagramPacket;import java.net.DatagramSocket;import java.net.InetAddress;public class SendDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));String line;while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){if ("886".equals(line)){break;}byte[] bys = line.getBytes();DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length, InetAddress.getByName("192.168.115.249"),12345);ds.send(dp);}ds.close();}}
接收数据
import java.io.IOException;import java.net.DatagramPacket;import java.net.DatagramSocket;public class ReceiveDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(12345);while (true) {byte[] bys = new byte[1024];DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bys, bys.length);ds.receive(dp);byte[] datas = dp.getData();int len = dp.getLength();String dataString = new String(datas, 0, len);System.out.println("数据为:"+dataString);}}}
TCP协议
先启动服务器端
public class ServerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);Socket s = ss.accept();InputStream is = s.getInputStream();byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len = is.read(bytes);String data = new String(bytes,0,len);System.out.println("接受的数据是:"+data);ss.close();}}
再启动客户端程序
public class ClientDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Socket s = new Socket("192.168.217.249", 10000);OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();os.write("hello 你好 java".getBytes());s.close();}}
接受的数据是:hello 你好 java
注意启动顺序,否则将报错
Exception in thread “main” java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused: connect at java.net.DualStackPlainSocketImpl.connect0(Native Method) at java.net.DualStackPlainSocketImpl.socketConnect(DualStackPlainSocketImpl.java:79) at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.doConnect(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:350) at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.connectToAddress(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:206) at java.net.AbstractPlainSocketImpl.connect(AbstractPlainSocketImpl.java:188) at java.net.PlainSocketImpl.connect(PlainSocketImpl.java:172) at java.net.SocksSocketImpl.connect(SocksSocketImpl.java:392) at java.net.Socket.connect(Socket.java:589) at java.net.Socket.connect(Socket.java:538) at java.net.Socket.
(Socket.java:434) at java.net.Socket. (Socket.java:211) at icu.itheima_02.ClientDemo.main(ClientDemo.java:9)
增添反馈
public class ServerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);Socket s = ss.accept();InputStream is = s.getInputStream();byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len = is.read(bytes);String data = new String(bytes,0,len);System.out.println("服务器接受的数据是:"+data);OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();os.write("数据已收到".getBytes());ss.close();}}
public class ClientDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Socket s = new Socket("192.168.217.249", 10000);OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();os.write("hello 你好 java".getBytes());InputStream is = s.getInputStream();byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len = is.read(bytes);String data = new String(bytes,0,len);System.out.println("提示:"+data);s.close();}}
键盘录入实现
public class ServerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);//监听客户端连接,返回一个Socket对象Socket s = ss.accept();BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));String line;while ((line = br.readLine())!=null) {System.out.println(line);}ss.close();}}
public class ClientDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Socket s = new Socket("192.168.217.249", 10000);BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));String line;while ((line = br.readLine())!=null){if ("886".equals(line)){break;}bw.write(line);bw.newLine();bw.flush();}s.close();}}
写入到文本文件
….
public class ServerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);//监听客户端连接,返回一个Socket对象Socket s = ss.accept();BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\copy.txt"));String line;while ((line = br.readLine())!=null) {System.out.println(line);bw.write(line);bw.newLine();bw.flush();}bw.close();ss.close();}}
public class ClientDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Socket s = new Socket("192.168.217.249", 10000);BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\owx.txt"));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));String line;while ((line = br.readLine())!=null){if ("886".equals(line)){break;}bw.write(line);bw.newLine();bw.flush();}br.close();s.close();}}
多线程上传文件
lambda 表达式
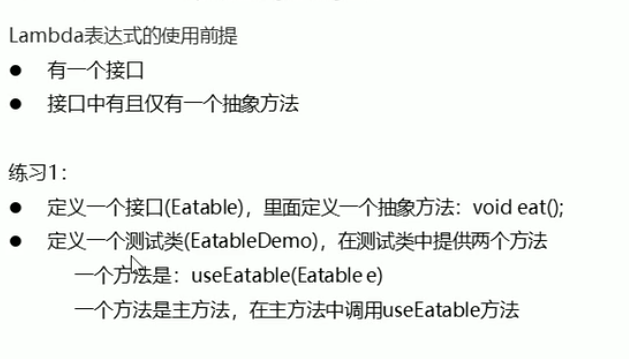
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("多线程程序启动了");}}
public class Demo {public static void main(String[] args) {MyRunnable m = new MyRunnable();//普通调用m.run();//多线程方式调用Thread thread = new Thread(m);thread.start();//匿名内部类方式new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("匿名内部类实现多线程启动了");}}).start();//Lambda表达式的方式new Thread( () ->{System.out.println("Lambda表达式调用");}).start();}}

public interface Eatable {void eat();}
public class EatableImpl implements Eatable {@Overridepublic void eat() {System.out.println("一天一苹果,就会没钱钱");}}
public class EatableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Eatable e = new EatableImpl();useEatable(e);useEatable(new Eatable() {@Overridepublic void eat() {System.out.println("匿名内部类吃苹果");}});useEatable(()->{System.out.println("Lambda吃苹果");});}private static void useEatable(Eatable e) {e.eat();}}
练习2 — 带参lambda
public interface Flyable {void fly(String s);}
public class FlyableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {useFlyable(new Flyable() {@Overridepublic void fly(String s) {System.out.println("猜猜s是啥?-->"+s);System.out.println("恭喜你猜对啦!");}});useFlyable((String s)->{System.out.print("输出s:");System.out.println(s);});}public static void useFlyable(Flyable f){f.fly("我想要飞得更高!");}}
带参带返回值的Lambda
Variable used in lambda expression should be final or effectively final
在lambda表达式中使用的变量应该是最终的或有效的最终的。
public interface Addable {int add(int x,int y);}
public class AddableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {/*匿名内部类定义的sum与外部定义的sum互不干扰*/int aa =1;int sum = useAddable(new Addable() {@Overridepublic int add(int x, int y) {int aa = 3; //不会显示已定义,不会报错int sum = x + y;return sum;}});System.out.println(sum);/*而Lambda中定义的,只能在内部使用但是外部定义的,两者内部都可以直接使用*/int mul1 = useAddable((int x, int y) -> {int aa = 5; //报错提示:Variable 'aa' is already defined in the scopeint mul = x * y;return mul;});System.out.println(mul1);}private static int useAddable(Addable a) {int sum = a.add(12345, 54321);return sum;}}
Lambda表达式的省略模式
public class AddableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {useAddable(new Addable() {@Overridepublic int add(int x, int y) {return x + y;}// @Override// public void _print(String s) {// System.out.println(s);// }});//参数类型可省,多个参数不可只省一个,全部省略或全部不//当执行语句只有一条且带有return,return也可以省略useAddable((x, y) -> x + y);//当参数只有一个,可以省略括号//当执行语句只有一条,可省略大括号{}useFlyable(s -> System.out.println(s));}private static void useAddable(Addable a) {int sum = a.add(12345, 54321);System.out.println(sum);}public static void useFlyable(Flyable f) {f.fly("我想要飞得更高!");}}
Lambda使用注意事项
public class LambdaDemo {/*Lambda使用注意事项*/public static void main(String[] args) {useInner(() -> System.out.println("使用Lambda必须要有接口,且接口有且仅有一个方法"));// 必须有上下文环境,才能推导出Lambda对应的接口Runnable r = () -> System.out.println("接口1111");new Thread(r).start();new Thread(() -> System.out.println("接口22222")).start();}private static void useInner(Inner i) {i.show();}}
Lambda表达式与匿名内部类的区别
实现原理不同:
//匿名内部类会产生一个新的字节码 .class文件
//而 Lambda不会产生
public class LambdaDemo {/*Lambda与匿名内部类区别*/public static void main(String[] args) {//只能实现接口useInner(() -> System.out.println("使用Lambda必须要有接口,且接口有且仅有一个方法"));//useAnimal(()-> System.out.println("实现抽象类调用")); //报错//useStudent(()-> System.out.println("实现具体类调用")); //报错//匿名内部类会产生一个新的字节码 .class文件//而 Lambda不会产生useInner(new Inner() {@Overridepublic void show() {System.out.println("匿名内部类实现接口");}});useAnimal(new Animal() {@Overridepublic void method() {System.out.println("匿名内部类实现抽象类");}});useStudent(new Student() {@Overridepublic void study() {System.out.println("匿名内部类实现具体类");}});}private static void useInner(Inner i) {i.show();}private static void useAnimal(Animal a) {a.method();}private static void useStudent(Student s) {s.study();}}
接口更新

public interface MyInterface {void show1();void show2();//默认方法: 使用 default 关键字修饰,可以含有方法体,可以被重写default void show3(){System.out.println("俺是默认方法");}//静态方法: 也可以拥有方法体static void show4(){System.out.println("俺是静态方法");}//java 9 新增私有方法/* 注意:默认方法可以调用静态方法和费静态方法而静态方法只能调用私有的静态方法*/private void show5(){}}
public class MyInterfaceImplOne implements MyInterface {@Overridepublic void show1() {System.out.println("ImplOne -->show1方法");}@Overridepublic void show2() {System.out.println("ImplOne -->show2方法");}@Overridepublic void show3() {System.out.println("默认方法被重写了哎");}//静态方法不可被重写/*@Overridepublic void show4() {System.out.println("默认方法被重写了哎");}*/}
public class MyInterfaceImplTwo implements MyInterface{@Overridepublic void show1() {System.out.println("ImplTwo -->show1方法");}@Overridepublic void show2() {System.out.println("ImplTwo -->show2方法");}}
public class MyInterfaceDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {MyInterface mi1 = new MyInterfaceImplOne();mi1.show1();mi1.show2();MyInterface mi2 = new MyInterfaceImplTwo();mi2.show1();mi2.show2();mi2.show3(); //默认方法//>>> 默认方法被重写了哎mi1.show3(); //被重写后的默认方法//>>> 俺是默认方法//mi1.show4(); //报错//>>> 静态方法不可通过接口实现类调用MyInterface.show4(); //只能通过接口调用//>>> 俺是静态方法}}
方法引用
方法引用符 ::
public interface Printable {void _print(String s);}
public class PrintableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {usePrintable(s -> System.out.println("憨憨要"+s));//>>> 憨憨要开心-的life//可推导则可省,可根据上下文推导//方法引用符 ::System.out.println("开心-的life--区别");//>>> 开心-的life--区别usePrintable(System.out::println);//>>> 开心-的life}private static void usePrintable(Printable p) {p._print("开心-的life");}}
Lambda表达式支持的引用方法
引用类方法
类名::静态方法
public interface Converter {int covert(String s);}
public class ConverterDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {useConverter(s -> Integer.parseInt(s));//类方法引用useConverter(Integer::parseInt);}private static void useConverter(Converter c) {int a = c.covert("666");System.out.println(a);}}
引用对象的实例方法
对象::成员方法
public interface Printer {void printUpperCase(String s);}
public class PrintString {public static void static_print(String s){System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()); //转换为大写}public void _print(String s){System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());}}
public class printerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//Lambda表达式usePrinter(s -> System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()));//>>> A//引用对象的实例方法usePrinter(PrintString::static_print);//>>> APrintString ps = new PrintString();usePrinter(ps::_print);//>>> A}private static void usePrinter(Printer p) {p.printUpperCase("a");}}
引用类的实例方法
public interface MyString {String mySubString(String s,int x,int y);}
public class MyStringDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//截取输出 "Hello" 的[2,5)之间的字符useMyString((s, x, y) -> s.substring(x, y));//>>> llouseMyString(String::substring);//>>> llo}private static void useMyString(MyString ms) {String s = ms.mySubString("Hello", 2, 5);System.out.println(s);}}
构造器引用
public interface StudentBuilder {Student build(String name,int age);}
import lombok.Data;@Datapublic class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}}
public class StudentDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {useStudentBuilder((n,a)-> new Student(n,a));//>>> Student(name=张飞, age=33)// Student(name=关羽, age=40)//构造器引用useStudentBuilder(Student::new);//>>> Student(name=张飞, age=33)// Student(name=关羽, age=40)}private static void useStudentBuilder(StudentBuilder sb) {Student sz = sb.build("张飞",33);System.out.println(sz);Student sg = sb.build("关羽",40);System.out.println(sg);}}
函数式接口

//函数式接口注解标记@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface MyInterface {void show();//void show1(); 新增方法 注解将提示报错}
public class MyInterfaceDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {MyInterface mi = ()-> System.out.println("函数式接口");mi.show();}}
函数式接口作为方法的参数
public class RunnableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {startThread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"多线程启动了");//>>> main多线程启动了}});startThread(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"Lambda多线程启动了"));//>>> mainLambda多线程启动了}private static void startThread(Runnable r) {r.run();}}


