$mount
首先看一下mount的代码
/*把原本不带编译的$mount方法保存下来,在最后会调用。*/const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount/*挂载组件,带模板编译*/Vue.prototype.$mount = function (el?: string | Element,hydrating?: boolean): Component {el = el && query(el)/* istanbul ignore if */if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`)return this}const options = this.$options// resolve template/el and convert to render function/*处理模板templete,编译成render函数,render不存在的时候才会编译template,否则优先使用render*/if (!options.render) {let template = options.template/*template存在的时候取template,不存在的时候取el的outerHTML*/if (template) {/*当template是字符串的时候*/if (typeof template === 'string') {if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {template = idToTemplate(template)/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {warn(`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`,this)}}} else if (template.nodeType) {/*当template为DOM节点的时候*/template = template.innerHTML} else {/*报错*/if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {warn('invalid template option:' + template, this)}return this}} else if (el) {/*获取element的outerHTML*/template = getOuterHTML(el)}if (template) {/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {mark('compile')}/*将template编译成render函数,这里会有render以及staticRenderFns两个返回,这是vue的编译时优化,static静态不需要在VNode更新时进行patch,优化性能*/const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {shouldDecodeNewlines,delimiters: options.delimiters}, this)options.render = renderoptions.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {mark('compile end')measure(`${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end')}}}/*Github:https://github.com/answershuto*//*调用const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount保存下来的不带编译的mount*/return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)}
通过mount代码我们可以看到,在mount的过程中,如果render函数不存在(render函数存在会优先使用render)会将template进行compileToFunctions得到render以及staticRenderFns。譬如说手写组件时加入了template的情况都会在运行时进行编译。而render function在运行后会返回VNode节点,供页面的渲染以及在update的时候patch。接下来我们来看一下template是如何编译的。
一些基础
首先,template会被编译成AST,那么AST是什么?
在计算机科学中,抽象语法树(abstract syntax tree或者缩写为AST),或者语法树(syntax tree),是源代码的抽象语法结构的树状表现形式,这里特指编程语言的源代码。具体可以查看抽象语法树。
AST会经过generate得到render函数,render的返回值是VNode,VNode是Vue的虚拟DOM节点,具体定义如下:
export default class VNode {tag: string | void;data: VNodeData | void;children: ?Array<VNode>;text: string | void;elm: Node | void;ns: string | void;context: Component | void; // rendered in this component's scopefunctionalContext: Component | void; // only for functional component root nodeskey: string | number | void;componentOptions: VNodeComponentOptions | void;componentInstance: Component | void; // component instanceparent: VNode | void; // component placeholder noderaw: boolean; // contains raw HTML? (server only)isStatic: boolean; // hoisted static nodeisRootInsert: boolean; // necessary for enter transition checkisComment: boolean; // empty comment placeholder?isCloned: boolean; // is a cloned node?isOnce: boolean; // is a v-once node?/*Github:https://github.com/answershuto*/constructor (tag?: string,data?: VNodeData,children?: ?Array<VNode>,text?: string,elm?: Node,context?: Component,componentOptions?: VNodeComponentOptions) {/*当前节点的标签名*/this.tag = tag/*当前节点对应的对象,包含了具体的一些数据信息,是一个VNodeData类型,可以参考VNodeData类型中的数据信息*/this.data = data/*当前节点的子节点,是一个数组*/this.children = children/*当前节点的文本*/this.text = text/*当前虚拟节点对应的真实dom节点*/this.elm = elm/*当前节点的名字空间*/this.ns = undefined/*编译作用域*/this.context = context/*函数化组件作用域*/this.functionalContext = undefined/*节点的key属性,被当作节点的标志,用以优化*/this.key = data && data.key/*组件的option选项*/this.componentOptions = componentOptions/*当前节点对应的组件的实例*/this.componentInstance = undefined/*当前节点的父节点*/this.parent = undefined/*简而言之就是是否为原生HTML或只是普通文本,innerHTML的时候为true,textContent的时候为false*/this.raw = false/*静态节点标志*/this.isStatic = false/*是否作为跟节点插入*/this.isRootInsert = true/*是否为注释节点*/this.isComment = false/*是否为克隆节点*/this.isCloned = false/*是否有v-once指令*/this.isOnce = false}// DEPRECATED: alias for componentInstance for backwards compat./* istanbul ignore next */get child (): Component | void {return this.componentInstance}}
关于VNode的一些细节,请参考VNode节点。
createCompiler
createCompiler用以创建编译器,返回值是compile以及compileToFunctions。compile是一个编译器,它会将传入的template转换成对应的AST、render函数以及staticRenderFns函数。而compileToFunctions则是带缓存的编译器,同时staticRenderFns以及render函数会被转换成Funtion对象。
因为不同平台有一些不同的options,所以createCompiler会根据平台区分传入一个baseOptions,会与compile本身传入的options合并得到最终的finalOptions。
compileToFunctions
首先还是贴一下compileToFunctions的代码。
/*带缓存的编译器,同时staticRenderFns以及render函数会被转换成Funtion对象*/function compileToFunctions (template: string,options?: CompilerOptions,vm?: Component): CompiledFunctionResult {options = options || {}/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {// detect possible CSP restrictiontry {new Function('return 1')} catch (e) {if (e.toString().match(/unsafe-eval|CSP/)) {warn('It seems you are using the standalone build of Vue.js in an ' +'environment with Content Security Policy that prohibits unsafe-eval. ' +'The template compiler cannot work in this environment. Consider ' +'relaxing the policy to allow unsafe-eval or pre-compiling your ' +'templates into render functions.')}}}/*Github:https://github.com/answershuto*/// check cache/*有缓存的时候直接取出缓存中的结果即可*/const key = options.delimiters? String(options.delimiters) + template: templateif (functionCompileCache[key]) {return functionCompileCache[key]}// compile/*编译*/const compiled = compile(template, options)// check compilation errors/tipsif (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {if (compiled.errors && compiled.errors.length) {warn(`Error compiling template:\n\n${template}\n\n` +compiled.errors.map(e => `- ${e}`).join('\n') + '\n',vm)}if (compiled.tips && compiled.tips.length) {compiled.tips.forEach(msg => tip(msg, vm))}}// turn code into functionsconst res = {}const fnGenErrors = []/*将render转换成Funtion对象*/res.render = makeFunction(compiled.render, fnGenErrors)/*将staticRenderFns全部转化成Funtion对象 */const l = compiled.staticRenderFns.lengthres.staticRenderFns = new Array(l)for (let i = 0; i < l; i++) {res.staticRenderFns[i] = makeFunction(compiled.staticRenderFns[i], fnGenErrors)}// check function generation errors.// this should only happen if there is a bug in the compiler itself.// mostly for codegen development use/* istanbul ignore if */if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {if ((!compiled.errors || !compiled.errors.length) && fnGenErrors.length) {warn(`Failed to generate render function:\n\n` +fnGenErrors.map(({ err, code }) => `${err.toString()} in\n\n${code}\n`).join('\n'),vm)}}/*存放在缓存中,以免每次都重新编译*/return (functionCompileCache[key] = res)}
我们可以发现,在闭包中,会有一个functionCompileCache对象作为缓存器。
/*作为缓存,防止每次都重新编译*/const functionCompileCache: {[key: string]: CompiledFunctionResult;} = Object.create(null)
在进入compileToFunctions以后,会先检查缓存中是否有已经编译好的结果,如果有结果则直接从缓存中读取。这样做防止每次同样的模板都要进行重复的编译工作。
// check cache/*有缓存的时候直接取出缓存中的结果即可*/const key = options.delimiters? String(options.delimiters) + template: templateif (functionCompileCache[key]) {return functionCompileCache[key]}
在compileToFunctions的末尾会将编译结果进行缓存
/*存放在缓存中,以免每次都重新编译*/return (functionCompileCache[key] = res)
compile
/*编译,将模板template编译成AST、render函数以及staticRenderFns函数*/function compile (template: string,options?: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {const finalOptions = Object.create(baseOptions)const errors = []const tips = []finalOptions.warn = (msg, tip) => {(tip ? tips : errors).push(msg)}/*做下面这些merge的目的因为不同平台可以提供自己本身平台的一个baseOptions,内部封装了平台自己的实现,然后把共同的部分抽离开来放在这层compiler中,所以在这里需要merge一下*/if (options) {// merge custom modules/*合并modules*/if (options.modules) {finalOptions.modules = (baseOptions.modules || []).concat(options.modules)}// merge custom directivesif (options.directives) {/*合并directives*/finalOptions.directives = extend(Object.create(baseOptions.directives),options.directives)}// copy other optionsfor (const key in options) {/*合并其余的options,modules与directives已经在上面做了特殊处理了*/if (key !== 'modules' && key !== 'directives') {finalOptions[key] = options[key]}}}/*基础模板编译,得到编译结果*/const compiled = baseCompile(template, finalOptions)if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {errors.push.apply(errors, detectErrors(compiled.ast))}compiled.errors = errorscompiled.tips = tipsreturn compiled}
compile主要做了两件事,一件是合并option(前面说的将平台自有的option与传入的option进行合并),另一件是baseCompile,进行模板template的编译。
来看一下baseCompile
baseCompile
function baseCompile (template: string,options: CompilerOptions): CompiledResult {/*parse解析得到AST*/const ast = parse(template.trim(), options)/*将AST进行优化优化的目标:生成模板AST,检测不需要进行DOM改变的静态子树。一旦检测到这些静态树,我们就能做以下这些事情:1.把它们变成常数,这样我们就再也不需要每次重新渲染时创建新的节点了。2.在patch的过程中直接跳过。*/optimize(ast, options)/*根据AST生成所需的code(内部包含render与staticRenderFns)*/const code = generate(ast, options)return {ast,render: code.render,staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns}}
baseCompile首先会将模板template进行parse得到一个AST,再通过optimize做一些优化,最后通过generate得到render以及staticRenderFns。
parse
parse的源码可以参见https://github.com/answershuto/learnVue/blob/master/vue-src/compiler/parser/index.js#L53。
parse会用正则等方式解析template模板中的指令、class、style等数据,形成AST。
optimize
optimize的主要作用是标记static静态节点,这是Vue在编译过程中的一处优化,后面当update更新界面时,会有一个patch的过程,diff算法会直接跳过静态节点,从而减少了比较的过程,优化了patch的性能。
generate
generate是将AST转化成render funtion字符串的过程,得到结果是render的字符串以及staticRenderFns字符串。
至此,我们的template模板已经被转化成了我们所需的AST、render function字符串以及staticRenderFns字符串。
举个例子
来看一下这段代码的编译结果
<div class="main" :class="bindClass"><div>{{text}}</div><div>hello world</div><div v-for="(item, index) in arr"><p>{{item.name}}</p><p>{{item.value}}</p><p>{{index}}</p><p>---</p></div><div v-if="text">{{text}}</div><div v-else></div></div>
转化后得到AST,如下图:
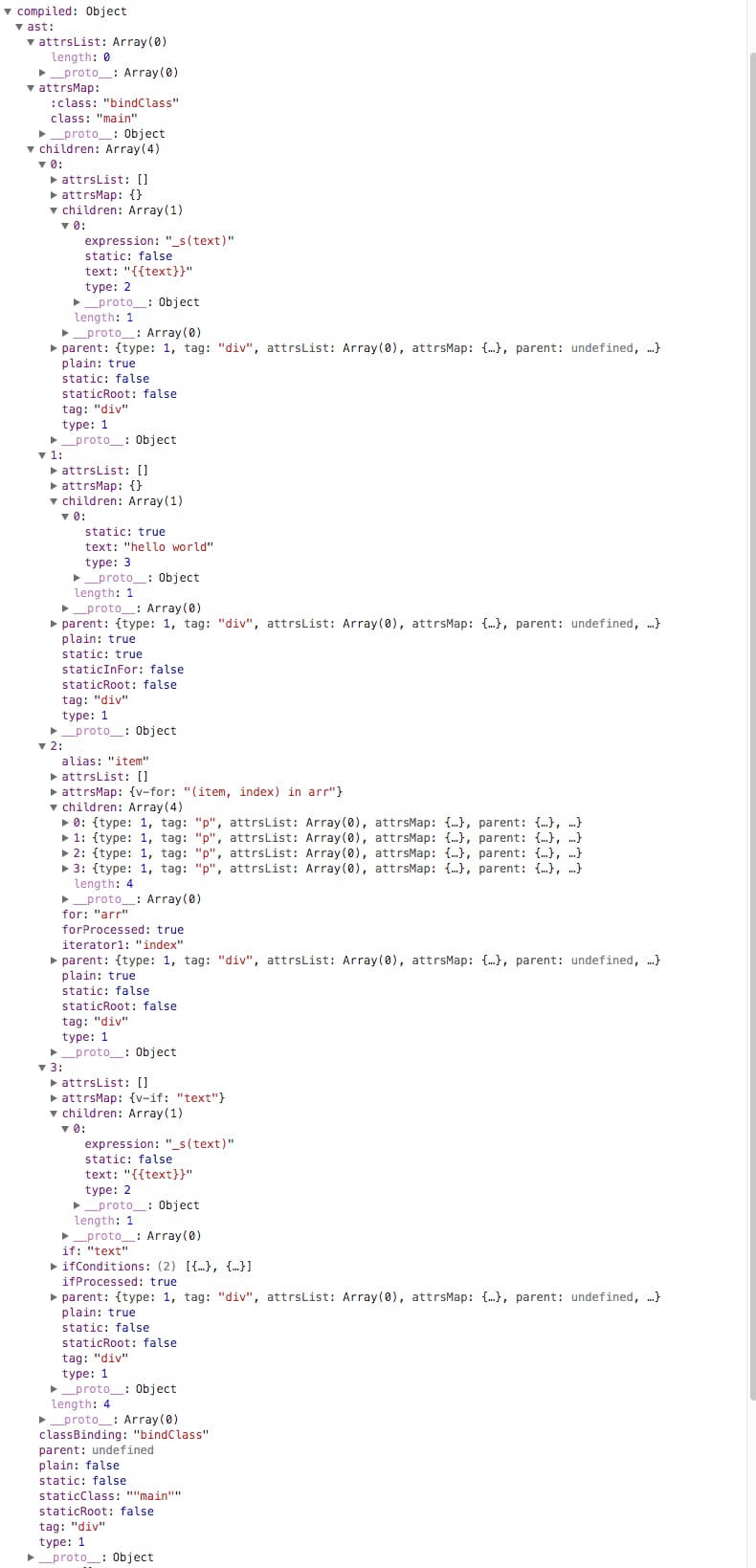
我们可以看到最外层的div是这颗AST的根节点,节点上有许多数据代表这个节点的形态,比如static表示是否是静态节点,staticClass表示静态class属性(非bind:class)。children代表该节点的子节点,可以看到children是一个长度为4的数组,里面包含的是该节点下的四个div子节点。children里面的节点与父节点的结构类似,层层往下形成一棵AST。
再来看看由AST得到的render函数
with(this){return _c( 'div',{/*static class*/staticClass:"main",/*bind class*/class:bindClass},[_c( 'div', [_v(_s(text))]),_c('div',[_v("hello world")]),/*这是一个v-for循环*/_l((arr),function(item,index){return _c( 'div',[_c('p',[_v(_s(item.name))]),_c('p',[_v(_s(item.value))]),_c('p',[_v(_s(index))]),_c('p',[_v("---")])])}),/*这是v-if*/(text)?_c('div',[_v(_s(text))]):_c('div',[_v("no text")])],2)}
_c,_v,_s,_q
看了render function字符串,发现有大量的_c,_v,_s,_q,这些函数究竟是什么?
带着问题,我们来看一下core/instance/render。
/*处理v-once的渲染函数*/Vue.prototype._o = markOnce/*将字符串转化为数字,如果转换失败会返回原字符串*/Vue.prototype._n = toNumber/*将val转化成字符串*/Vue.prototype._s = toString/*处理v-for列表渲染*/Vue.prototype._l = renderList/*处理slot的渲染*/Vue.prototype._t = renderSlot/*检测两个变量是否相等*/Vue.prototype._q = looseEqual/*检测arr数组中是否包含与val变量相等的项*/Vue.prototype._i = looseIndexOf/*处理static树的渲染*/Vue.prototype._m = renderStatic/*处理filters*/Vue.prototype._f = resolveFilter/*从config配置中检查eventKeyCode是否存在*/Vue.prototype._k = checkKeyCodes/*合并v-bind指令到VNode中*/Vue.prototype._b = bindObjectProps/*创建一个文本节点*/Vue.prototype._v = createTextVNode/*创建一个空VNode节点*/Vue.prototype._e = createEmptyVNode/*处理ScopedSlots*/Vue.prototype._u = resolveScopedSlots/*创建VNode节点*/vm._c = (a, b, c, d) => createElement(vm, a, b, c, d, false)
通过这些函数,render函数最后会返回一个VNode节点,在_update的时候,经过patch与之前的VNode节点进行比较,得出差异后将这些差异渲染到真实的DOM上。

