前置知识
先来理解DOM元素的三个属性
- scrollTop: 元素顶部到元素可视区域顶部的像素距离(可读写)
- clientHeight: 元素的像素高度,包括盒子内容content和内边距padding, 不包括边框外边距和水平滚动条(只读)
- scrollHeight: 类似于clientHeight,但包括由于overflow属性不可见内容的高度。
三者的关系如下图所示:绿色部分是滚动元素能看到的部分,假设红色框区域是元素的总高度,部分被隐藏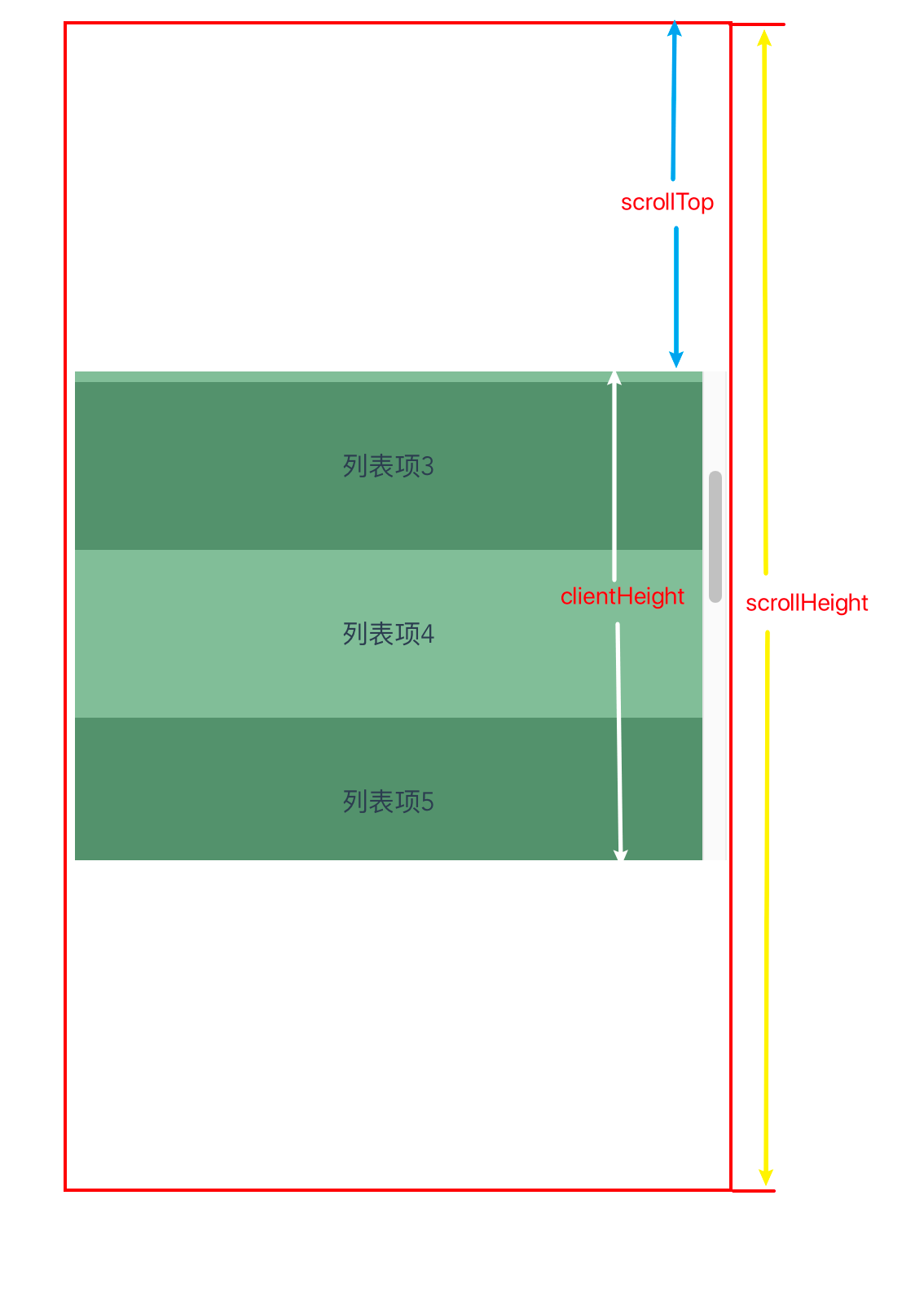
如何判断
MDN上有一条公式,用于判断元素是否滚动到底部
结合前面的示意图可知,元素滚动到底部的条件是scrollTop + clientHeight === scrollHeight
Vue写法
以Vue举例,只需监听scroll事件获取到scrollTop, clientHeight 和 scrollHeight的值再进行判断,就能知道元素是否滚动到底部。
<template><div id="app"><div class="scroll-view"ref="scrollView"id="scroll-view"@scroll="handleScroll"><divv-for="(item, index) in list":key="index"class="list-item">列表项{{item}}</div></div></div></template><script>export default {name: 'HelloWorld',data() {return {list: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]};},mounted() {this.$nextTick(() => {console.log('clientHeight', this.$refs.scrollView.clientHeight)})},methods: {handleScroll(e) {const {scrollTop, clientHeight, scrollHeight} = e.target// console.log(scrollTop, clientHeight, scrollHeight)if (scrollTop + clientHeight === scrollHeight){alert('滚动到底部啦')}}}}</script><style scoped>.scroll-view {width: 400px;height: 300px;overflow-y: scroll;background-color: #68b687;}.list-item {padding: 40px 0;}.list-item:nth-child(2n + 1){background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .2);}.list-item:nth-child(2n + 2){background-color: rgba(222, 221, 221, 0.2);}</style>
效果演示
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/weiyf/p/8718051.html
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Element/scrollHeight
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Element/scrollTop
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Element/clientHeight


