概述
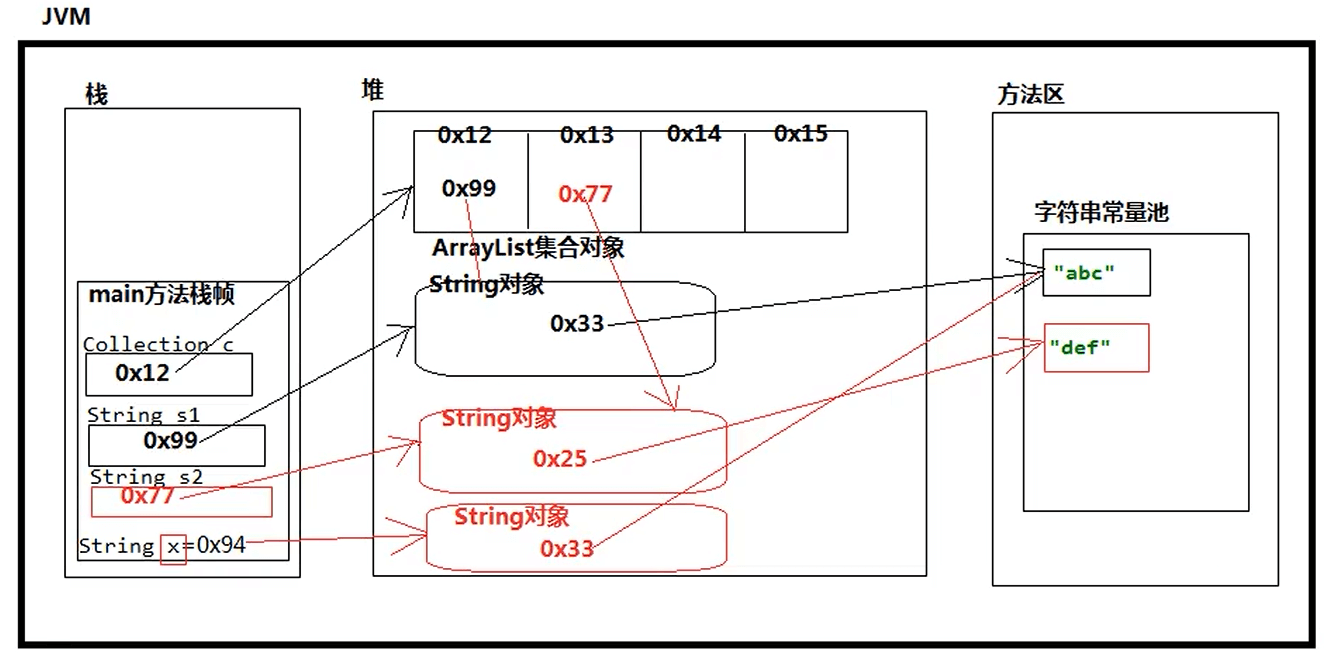
集合本质上就是一个存储数据的容器,数组就是集合的一种数据类型。集合不能直接存储基本数据类型和Java对象,只能存储Java对象的内存地址(或者叫引用),如下图所示: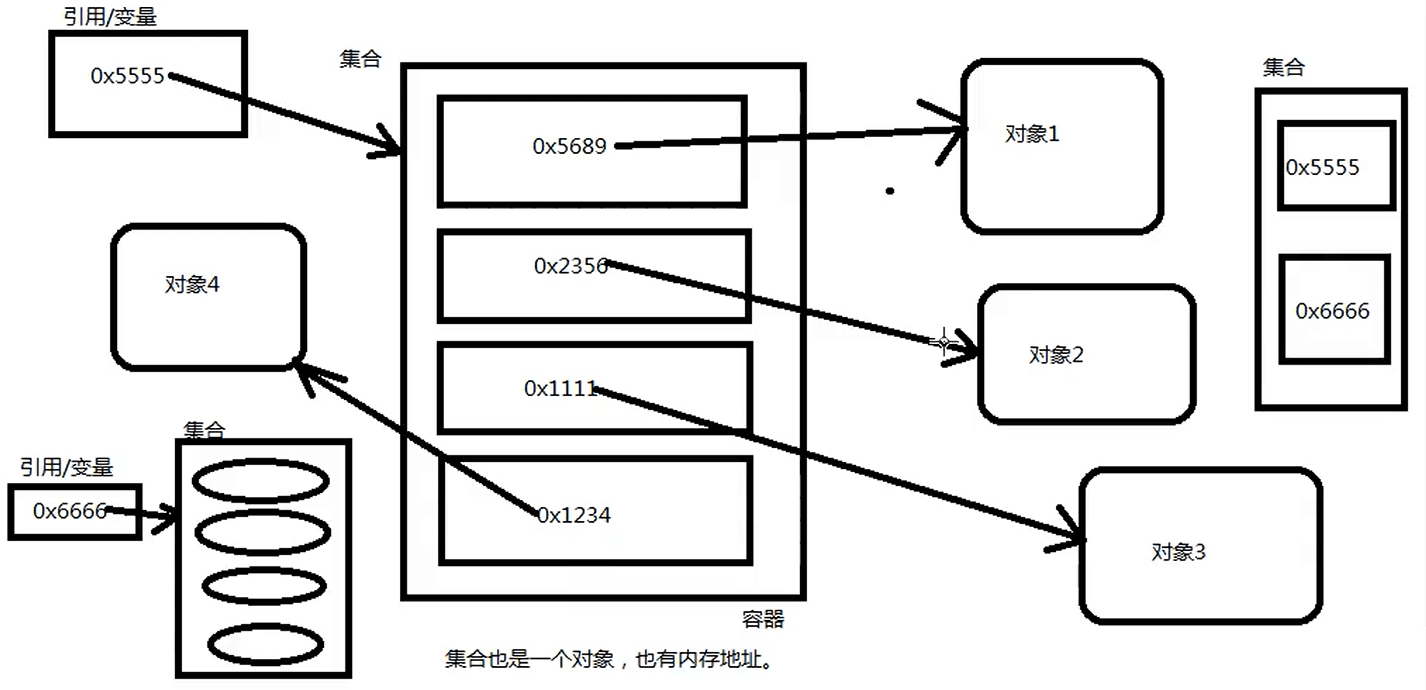
Java中不同的集合对应不同的数据结构。往不同的集合中存储元素就是往不同的数据结构中存储元素,这些数据结构包括数组、二叉树、链表、哈希表等。
集合是在java.util.*包下的,集合的整个继承体系是非常庞杂的。总的来说,根据集合体系的元素的存储方式(以单个方式存储元素、以键值对存储元素)的不同,将集合体系分成Collection集合和Map集合,分别在java.util.Collection包和java.util.Map包下。
Collection集合体系继承关系
Collection集合体系如下: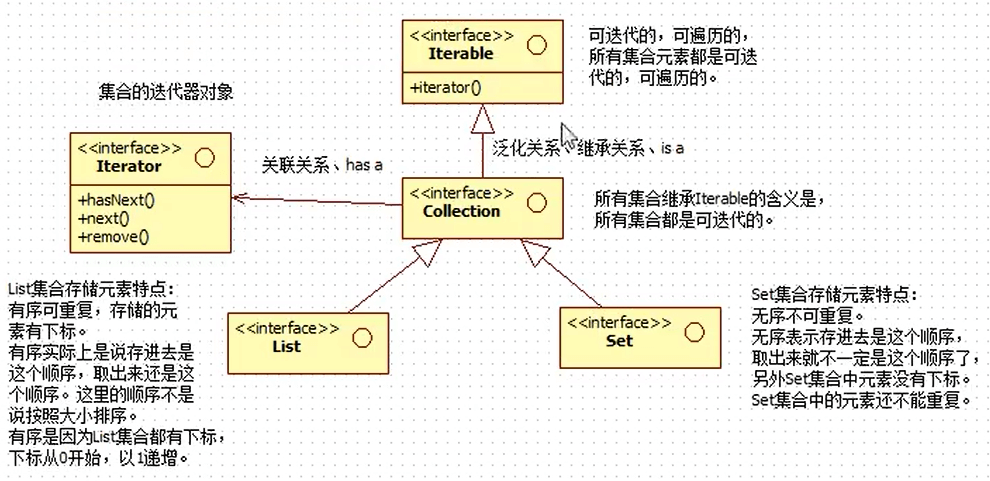
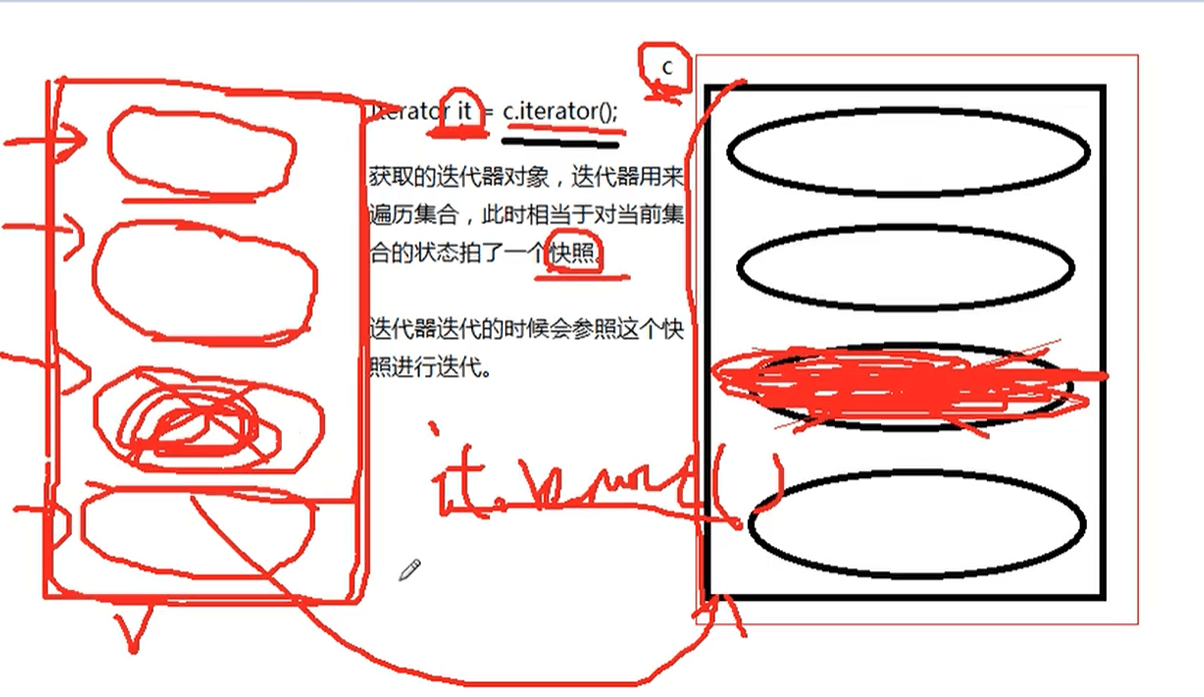
注意,Collection是个接口,它继承了Iterator接口,用法如下:
Iterator it = “Collection对象”.iterator();
it是迭代器对象
Map集合体系的继承关系
Map集合体系的继承关系如下: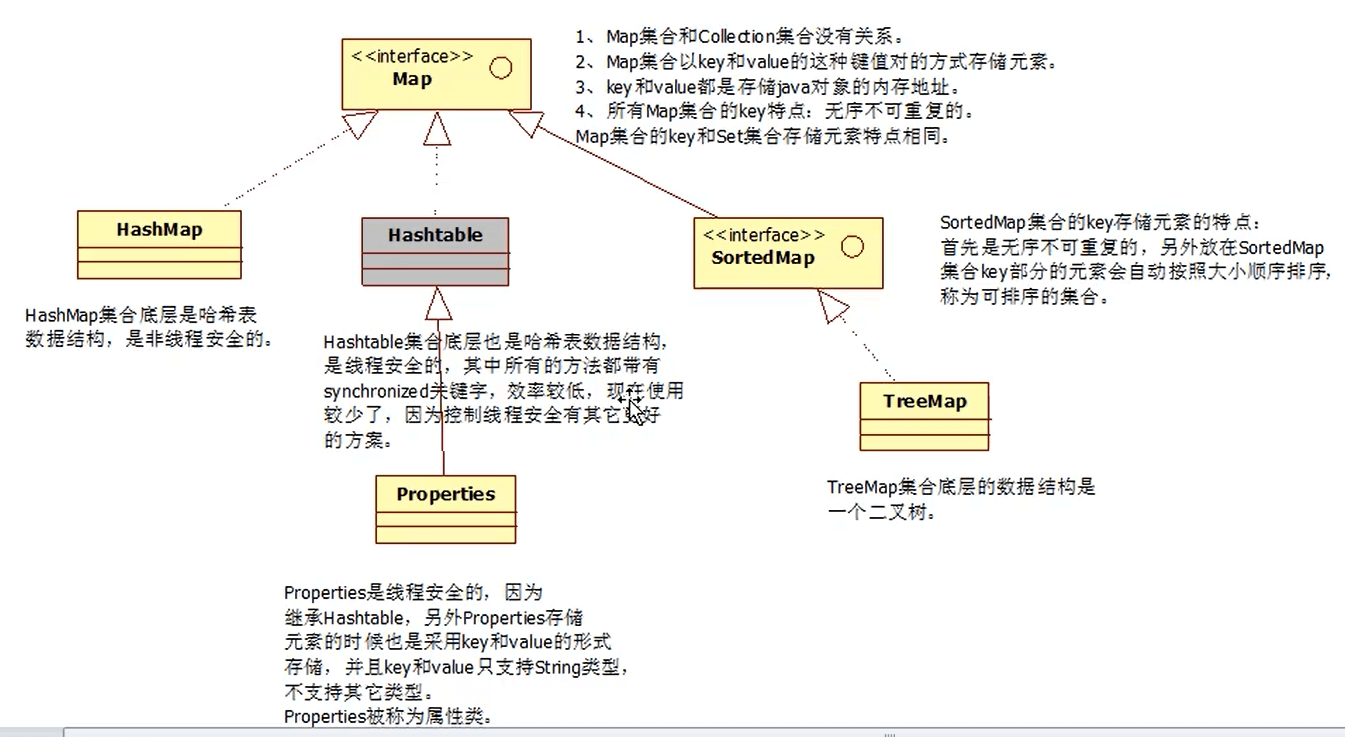
/*** The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon* shrinkage.*/static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;/*** The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.*/static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;/*** The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts* between resizing and treeification thresholds.*/static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
Collection接口
普通常用方法

package javase.collection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;/*1、Collection中能存放什么元素?未使用泛型之前,Collection可以存储Object类的所有子类型使用泛型之后,Collection中只能存放某个具体的数据类型。2、Collection的常用方法:add();clear();size();contain();remove();toCharArray();iterator();*/public class ClooectionTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection c = new ArrayList(); //多态c.add("zs");c.add(125); //就算是这里,其实集合存储的还是引用c.add(new Student());c.add(129);System.out.println(c.size()); //3System.out.println(c.contains("zs"));//trueSystem.out.println(c.remove(125));//trueObject[] objects = c.toArray();for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++) {//zs javase.collection.Student@1b6d3586 129System.out.print(objects[i]+"\t");}}}class Student{}
重点常用方法(亟待加强)
iterator方法(其一)
package javase.collection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Iterator;/*** 迭代专题:Collection及其子实现能用,Map接口不行*/public class CollectionTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection c = new ArrayList();c.add("zs");c.add("ls");c.add(123); //存进去是什么类型,取出来还是什么类型,只是输出时会转成字符串c.add(123);Iterator it = c.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){System.out.print(it.next()+"\t"); //zs ls 123 123}Collection c2 = new HashSet();c2.add(1);c2.add(20);c2.add(5);c2.add(99);c2.add(90);c2.add(99);Iterator it2 = c2.iterator();while (it2.hasNext()){//1 99 20 5 90,无序且不可重复System.out.print(it2.next()+"\t");}}}
iterator方法(其二)
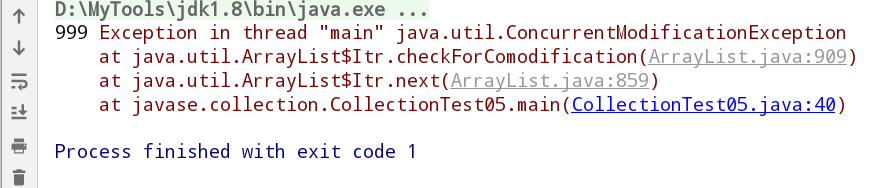
package javase.collection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Iterator;/*关于集合元素的remove方法重点:当集合的结构发生改变时,迭代器必须重新获取,如果还是用以前老的迭代器,会出现并发修改异常java.util.ConcurrentModificationException。在迭代集合元素的过程中,不能调用集合对象的remove方法删除元素。*/public class CollectionTest05 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*Collection c = new ArrayList();*//*** 注意:此时获取的迭代器,指向的是集合中没有元素状态下的迭代器* 集合结构一旦发生改变,迭代器必须重新获取*//*Iterator it = c.iterator();c.add(1);c.add(2);c.add(3);while (it.hasNext()){//Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationExceptionObject obj = it.next();System.out.print(obj+" ");}*/Collection c2 = new ArrayList();c2.add(999);c2.add("zs");c2.add(new Object());Iterator it2 = c2.iterator();while (it2.hasNext()){//未做任何修改之前输出://999 zs java.lang.Object@1b6d3586Object obj2 = it2.next();//添加一行删除元素的代码后输出://999 Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException// c2.remove(obj2); //直接通过集合去删除元素,没有通知迭代器,//导致快照和原集合状态不同,产生并发修改异常System.out.print(obj2+" ");}//使用迭代器可以删除,删除的一定是迭代器指向的当前元素it2.remove();System.out.println(c2.size()); //2}}
contains方法
package javase.collection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;//总结,放在Collection集合的类型一定要重写equals方法public class CollectionTest03 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection c = new ArrayList();String s1 = new String("123");String s2 = new String("234");String s3 = new String("123");c.add(s1);c.add(s2);//之所以输出为true,是因为存储元素时会比较内容,// contains方法先调用indexof方法,然后indexof方法调用indexOfRange方法// 最后indexOfRange调用equals方法System.out.println(c.contains(s3)); //trueCollection c2 = new ArrayList();User user1 = new User("zs");User user2 = new User("zs");c2.add(user1);//输出结果为false,因为User类没有重写equals方法,比较的是地址System.out.println(c2.contains(user2)); //false}}class User{private String name;public User() {}public User(String name) {this.name = name;}}
remove方法
package javase.collection;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;//测试remove()方法有没有重写equals方法public class CollectionTest04 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection c = new ArrayList();String s1 = new String("hello");String s2 = new String("hello");c.add(s1);System.out.println(c.contains(s2));//trueSystem.out.println(c.remove(s2));//trueSystem.out.println(c.size());//0}}
总结
加入Collection集合的对象需要重写equals方法,除非像String那种已经重写了equals()方法的就不必了,一般自定义的类都要重写。
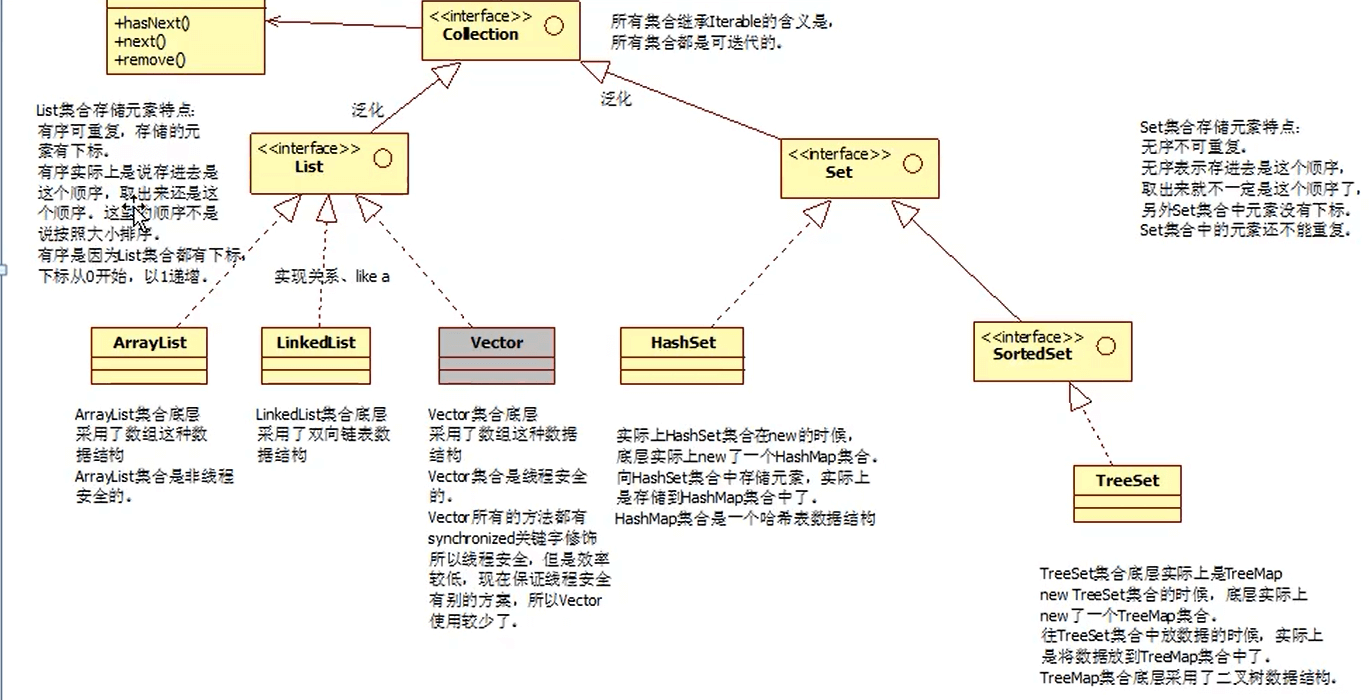
List接口
自身特色方法
package javase.list;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.List;/*测试List接口的常用方法:1、存储特点:有序可重复2、自身特色方法:①void add(int index, E element)在列表的指定位置插入指定元素(可选操作)。②E get(int index)返回列表中指定位置的元素。③int hashCode()返回列表的哈希码值。④int indexOf(Object o)返回此列表中第一次出现的指定元素的索引;如果此列表不包含该元素,则返回 -1。⑤E set(int index, E element)用指定元素替换列表中指定位置的元素(可选操作)。*/public class ListTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {List myList = new ArrayList();myList.add("1");myList.add(2);myList.add("999");//向指定位置添加元素,用得不多myList.add(1,777);Iterator mle = myList.iterator();while (mle.hasNext()){Object obj = mle.next();//1 777 2 999System.out.print(obj+" ");}//获取下标元素Object obj2 = myList.get(1);System.out.println(obj2); //777//获取下标元素,改进for (int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) {//1 777 2 999System.out.print(myList.get(i)+" ");}//获取元素第一次、最后一次出现处的索引System.out.println(myList.indexOf(777)); //1System.out.println(myList.lastIndexOf(777)); //1//根据下标删除元素Object obj3 = myList.remove(1);System.out.println(myList.size()); //3//修改元素myList.set(1,"这就是中国");System.out.println(myList.get(1)); //这就是中国//查看整体for (int i = 0; i < myList.size(); i++) {//1 这就是中国 999System.out.print(myList.get(i)+" ");}}}
子实现之ArrayList
特点
/*** Default initial capacity.*///初始容量是10//底层先创建一个长度为0的数组,当添加第一个元素的时候初始化容量为10private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;//底层是个Object类型的数组transient Object[] elementData;//扩容机制,是原来的1.5倍/*** Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.** @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity*/private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}//带一个整型参数的构造器:可以自定义初始容量public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);}}//带一个集合类型参数的构造器/*** Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's* iterator.** @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null*/public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {elementData = c.toArray();if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);} else {// replace with empty array.this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}}//无参构造器/*** Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.*/public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}
ArrayList集合类3个构造方法
package javase.list.arraylist;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.List;import java.util.Set;public class ArrayListTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//默认数组初始容量为10List c1 = new ArrayList();//指定数组初始容量为100List c2 = new ArrayList(100);//将一个集合作为参数传到ArrayList集合类中Set set = new HashSet();set.add(11);set.add(22);set.add(33);set.add(44);List c3 = new ArrayList(set);for (int i = 0; i < set.size(); i++) {System.out.print(c3.get(i)+" "); //33 22 11 44}}}
子实现之LinkedList
package javase.list;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.List;/*** 链表的优点:* 由于链表上的元素在空间存储上内存地址不连续* 所以随机增删的时候不会有大量元素位移,因此随机增删效率较高* 链表的缺点:* 不能通过数学表达式计算被查找元素的内存地址,每一次查找都是从头开始遍历,* 直到找到为止,所以LinkedList集合检索效率较低** ArrayList:把检索发挥到极致* LinkedList:本质上是双向链表,把随机增删发挥到极致* 由于添加元素都是往末尾添加的,而ArrayList末尾添加元素效率还是很高的,* 所以ArrayList用得比LinkedList多*/public class LinkedListTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {List c = new LinkedList();c.add(100);c.add(200);c.add(300);c.add(400);for (int i = 0; i < c.size(); i++) {//100 200 300 400System.out.print(c.get(i)+" ");/*同ArrayList一样,LinkedList也是有下标的注意:ArrayList之所以检索效率比较高,不是单纯因为下标的原因,而是因为底层数组发挥了作用LinkedList集合照样有下标,只是检索某个元素的时候效率比较低,因为只能从头结点开始一个一个遍历*/}}}
子实现之Vector
//初始容量是10/*** Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is* zero.*/public Vector() {this(10);}//扩容机制是原来的2倍/*** The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically* incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If* the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity* of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow.** @serial*/protected int capacityIncrement;//随便列举一个方法,证明Vector是线程安全的/*** Returns the number of components in this vector.** @return the number of components in this vector*/public synchronized int size() {return elementCount;}
如何将ArrayList类转成线程安全的?
package javase.list;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;public class ListTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//非线程安全的List myList = new ArrayList();//如何将其变成线程安全的?这行的代码Collections.synchronizedList(myList);myList.add(10);myList.add(20);myList.add(30);}}
泛型
普通泛型
package javase.generic;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.List;/*jdk5.0推出的泛型机制1、泛型这种语法机制,只在程序编译阶段起作用,只是给编译器参考的,运行阶段泛型没用2、优点:①集合存储的元素统一了②从集合中取出的元素类型是泛型指定的类型,不需要进行大量的向下转型3、缺点:①导致集合中存储的元素缺乏多样性②大多数业务中,集合中的元素还是统一的,所以泛型的这种特性还是被大家认可的*/public class GenericTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*List myList = new ArrayList();Cat c = new Cat();Bird b = new Bird();myList.add(c);myList.add(b);Iterator it = myList.iterator();//遍历集合,取出每个Animal,让它movewhile (it.hasNext()){Object obj = it.next();if (obj instanceof Animal){Animal a = (Animal) obj;a.move();}}}*///使用泛型List<Animal>之后,表示List集合中只允许存储Animal类型的数据//用泛型来指定集合中存储的数据元素List<Animal> myList2 = new ArrayList<>();//指定List集合中只能存储Animal,那么,存储String就编译报错了//这样使用泛型之后,集合中元素的数据类型就更加统一了Cat c = new Cat();Bird b = new Bird();myList2.add(c);myList2.add(b);//获取迭代器,这个表示迭代器迭代的是Animal类型Iterator<Animal> it2 = myList2.iterator();while (it2.hasNext()){//使用泛型之后,每一次迭代返回的都是Animal类型Animal a2 = it2.next();//这里不需要进行强制类型转换了,直接调用//但是调用子类特有的方法还是需要向下转型的a2.move();}}}class Animal{public void move(){System.out.println("动物在移动");}}class Cat extends Animal{public void catchMouse(){System.out.println("猫抓老鼠");}}class Bird extends Animal{public void fly(){System.out.println("鸟儿在飞翔");}}//2种方式都输出:// 动物在移动//动物在移动
自定义泛型
package javase.generic;//自定义泛型//定义时先是以某种格式,而后使用时是指定类型格式public class GenericTest03<MyType> {public void doSome(MyType mt){System.out.println(mt);}public static void main(String[] args) {GenericTest03<String> gt = new GenericTest03<>();//类型不匹配// gt.doSome(100);//类型匹配gt.doSome("abc"); //abc}}
增强for循环
定义
package javase.forcycle;public class StrongerForCycleTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5,232,43,434,2135,65};//普通for循环for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");}//增强for循环(语法格式如下:)/*for(元素类型 变量名:数组或集合){变量名.sout;}*/System.out.println("\n"+"===================================");//i就是数组中的每一个元素,foreach缺点是没有下标,//这里建议没有下标时采用增强for循环//同时建议采用:arr.iter格式快速生成增强for循环语法格式for (int i : arr) {System.out.print(i+" ");}}}/*输出如下:1 2 3 4 5 232 43 434 2135 65===================================1 2 3 4 5 232 43 434 2135 65*/
集合三类循环的比较
package javase.forcycle;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.List;//三种方式遍历集合public class StrongerForCycleTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> mylist = new ArrayList<>();mylist.add("my test01");mylist.add("my test02");mylist.add("my test03");//方式一:迭代器遍历Iterator<String> it1 = mylist.iterator();while (it1.hasNext()){String s1 = it1.next();System.out.print(s1+" ");}System.out.println();//方式二:普通for循环for (int i = 0; i < mylist.size(); i++) {System.out.print(mylist.get(i)+" ");}System.out.println();//方式三:增强for循环for (String s : mylist) {System.out.print(s+" ");}}}/*结果输出:my test01 my test02 my test03my test01 my test02 my test03my test01 my test02 my test03*/
Set接口
HashSet集合类
HashSet类效果演示
package javase.hashset;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Set;public class HashSetTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> strs = new HashSet<>();strs.add("hello1");strs.add("hello2");strs.add("hello3");strs.add("hello4");strs.add("hello5");strs.add("hello1");strs.add("hello1");for (String str : strs) {//hello1 hello4 hello5 hello2 hello3System.out.print(str+" ");//存储时顺序和取出的顺序不同,不可重复,// 且放到HashSet集合中的元素实际上是放到HashMap集合的key部分了}}}
TreeSet集合类
TreeSet类效果演示
package javase.set.treeset;import java.util.Set;import java.util.TreeSet;//验证TreeSet的特性:①无序 ②不可重复//但存储的元素可以自动按照大小排序,称为可排序集合//这里的无序是指存入和取出的顺序不一样,没有下标public class TreeSetTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Set<String> strs = new TreeSet<>();strs.add("A");strs.add("B");strs.add("Z");strs.add("X");strs.add("Y");strs.add("Z");for (String str : strs) {//从小到大自动排序System.out.print(str+" ");//A B X Y Z}}}
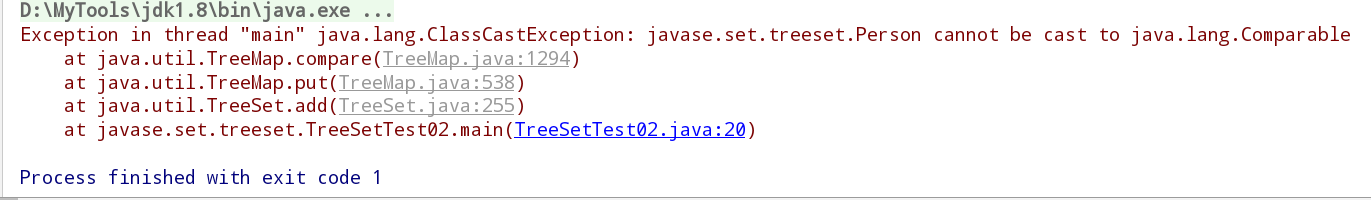
TreeSet无法对自定义类型进行排序★★
package javase.set.treeset;import java.util.TreeSet;/*1、TreeSet集合底层实际上是一个TreeMap2、TreeMap集合底层是一个二叉树3、放到TreeSet集合中的元素,等同于放到TreeMap集合key部分4、TreeSet集合中的元素:无序不可重复,但是可以按照元素的大小顺序自动排序,被称为:可排序集合*/public class TreeSetTest02 {//对于自定义的类型来说,TreeSet不可以排序public static void main(String[] args) {Person p1 = new Person(20);Person p2 = new Person(30);Person p3 = new Person(25);Person p4 = new Person(35);TreeSet<Person> persons = new TreeSet<>();persons.add(p1);persons.add(p2);persons.add(p3);persons.add(p4);for (Person person : persons) {System.out.println(person.toString());}}}class Person{int age;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"age=" + age +'}';}public Person(int age) {this.age = age;}}
探究原因
要在TreeMap的put方法中去找:
/*** Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the* natural ordering of its elements. All elements inserted into* the set must implement the {@link Comparable} interface.* Furthermore, all such elements must be <i>mutually* comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and* {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add an element* to the set that violates this constraint (for example, the user* attempts to add a string element to a set whose elements are* integers), the {@code add} call will throw a* {@code ClassCastException}.*/public TreeSet() {this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());}/*** Constructs a new, empty tree map, using the natural ordering of its* keys. All keys inserted into the map must implement the {@link* Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such keys must be* <em>mutually comparable</em>: {@code k1.compareTo(k2)} must not throw* a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys {@code k1} and* {@code k2} in the map. If the user attempts to put a key into the* map that violates this constraint (for example, the user attempts to* put a string key into a map whose keys are integers), the* {@code put(Object key, Object value)} call will throw a* {@code ClassCastException}.*/public TreeMap() {comparator = null;}/*** Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if* the set contains no element {@code e2} such that* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set* unchanged and returns {@code false}.** @param e element to be added to this set* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified* element* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared* with the elements currently in this set* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator* does not permit null elements*/public boolean add(E e) {return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}/*** Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old* value is replaced.** @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated* @param value value to be associated with the specified key** @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or* {@code null} if there was no mapping for {@code key}.* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared* with the keys currently in the map* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null* and this map uses natural ordering, or its comparator* does not permit null keys*/public V put(K key, V value) {Entry<K,V> t = root;if (t == null) {compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) checkroot = new Entry<>(key, value, null);size = 1;modCount++;return null;}int cmp;Entry<K,V> parent;// split comparator and comparable pathsComparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;if (cpr != null) {do {parent = t;cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);if (cmp < 0)t = t.left;else if (cmp > 0)t = t.right;elsereturn t.setValue(value);} while (t != null);}else {if (key == null)throw new NullPointerException();@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")//这行就极有可能出现问题//给人的启示就是,要实现Comparable接口,才能比较大小,才好转型,不会出现类型转换异常//怎么做?实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo()方法,自定义规则Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;do {parent = t;cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);if (cmp < 0)t = t.left;else if (cmp > 0)t = t.right;elsereturn t.setValue(value);} while (t != null);}Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);if (cmp < 0)parent.left = e;elseparent.right = e;fixAfterInsertion(e);size++;modCount++;return null;}
解决措施
1.bean类实现Comparable接口,重写compareTo()方法
package javase.set.treeset;import java.util.TreeSet;//先按照年龄升序,如果年龄一样再按照姓名升序public class TreeSetTest05 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Vip> vips = new TreeSet<>();vips.add(new Vip("zs",20));vips.add(new Vip("ls",30));vips.add(new Vip("ww",60));vips.add(new Vip("zl",27));for (Vip vip : vips) {//Vip{name='zs', age=20} Vip{name='zl', age=27} Vip{name='ls', age=30} Vip{name='ww', age=60}System.out.print(vip+" ");}}}class Vip implements Comparable<Vip>{String name;int age;public Vip(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Vip{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Vip v) {if (this.age == v.age){//姓名是String类型,可以直接比,调用compareTo()来完成return this.name.compareTo(v.name);}else {return this.age - v.age;}}}
2.使用比较器的方式
package javase.set.treeset;import java.util.Comparator;import java.util.TreeSet;/*** 放到TreeSet或者TreeMap集合key部分的元素想要做到排序,包括以下2种方式:* 第一种:放在集合中的元素实现java.lang.Comparable接口* 第二种:在构造TreeSet或者TreeMap集合的时候给它传一个比较器对象* Comparable和Comparator怎么选择呢?* 当比较规则不会发生改变的时候,或者说当比较规则只有1个的时候,建议实现Comparable接口* 当比较规则有多个,并且需要多个比较规则之间频繁切换,建议使用Comparator接口* Comparator接口的设计符合OCP原则*/public class TreeSetTest06 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建TreeSet集合的时候,需要使用这个比较器//注意:这样是不行的,没有通过构造器传递一个比较器进去// TreeSet<Wugui> wuguis = new TreeSet<>();TreeSet<Wugui> wuguis = new TreeSet<>(new WuguiComparator());wuguis.add(new Wugui(1000));wuguis.add(new Wugui(800));wuguis.add(new Wugui(789));wuguis.add(new Wugui(606));for (Wugui wugui : wuguis) {//小乌龟【age=606】 小乌龟【age=789】 小乌龟【age=800】 小乌龟【age=1000】System.out.print(wugui+" ");}}}class Wugui{int age;public Wugui(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "小乌龟【" +"age=" + age +'】';}}//单独在这里编写一个比较器//比较器实现java.util.Comparator接口(Comparable是java.lang包下的,Comparator是java.util包下的)class WuguiComparator implements Comparator<Wugui>{@Overridepublic int compare(Wugui o1, Wugui o2) {//指定比较规则:按年龄排序return o1.age - o2.age;}}
Map接口
Map接口的普通常用方法
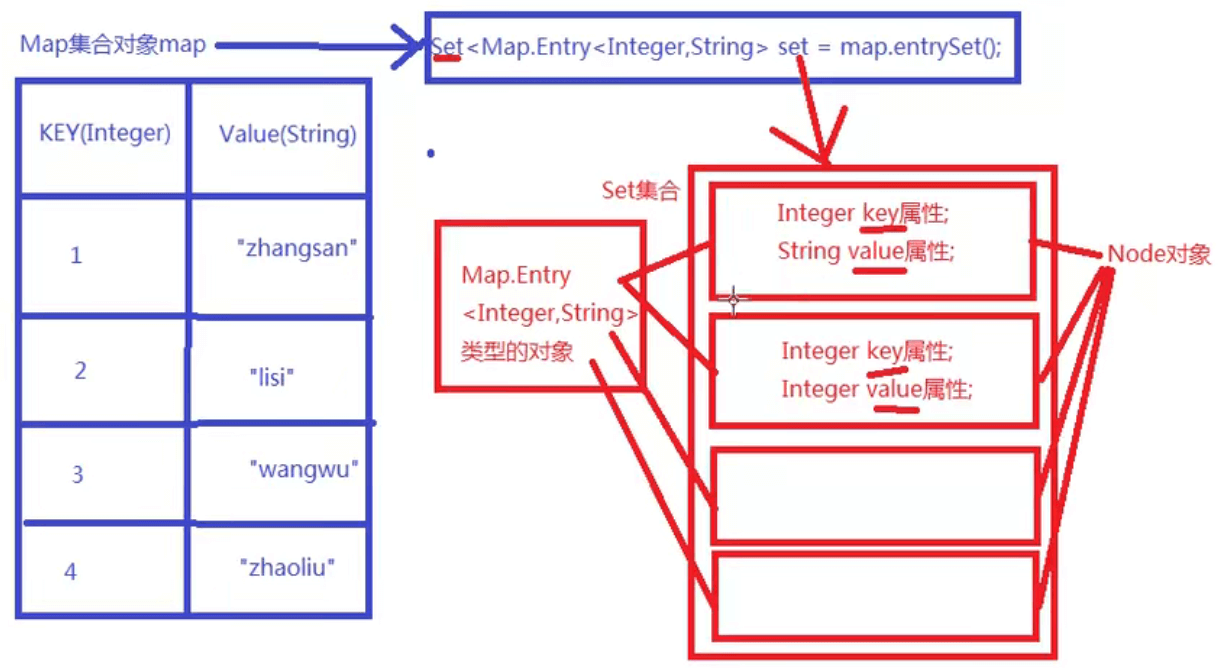
package javase.map;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;/*java.util.Map接口中常用的方法:1、Map集合以key和value的方式存储数据:键值对key和value是引用数据类型;key和value都是存储对象的内存地址key起到主导的地位,value是key的一个附属品2、Map接口常用方法:void clear() 清空Map集合boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合是否包含某个keyboolean containsValue(Object value) 判断集合是否包含某个valueV get(Object key) 通过key获取对应的value值boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空Set<K> keySet() 获取所有的key(所有的key组成自己的set集合)V put(K key, V value) 添加一组键值对V remove(Object key) 根据key删除所在的键值对int size() 获取Map集合中元素的个数Collection<V> values() 获取所有的value,返回一个CollectionSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 将Map集合转成Set集合假设现在有一个Map集合,如下所示:map1集合对象:key value-----------------------1 zhangsan2 lisi3 wangwu4 zhaoliuSet set = map1.entrySet();set集合对象:1=zhangsan【注意:Map集合通过entrySet()方法转换成的这个Set集合,Set集合中元素的类型是Map.EntrySet】2=lisi 【Map.Entry和String一样,都是一种类型的名字,只不过Map.Entry是静态内部类,是Map中的】3=wangwu4=zhaoliu*/public class MapTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(1,"zs");map.put(2,"ls");map.put(3,"ww");map.put(4,"zl");//V get(Object key) 通过key获取对应的value值String val = map.get(2);System.out.println(val); //ls//int size() 获取Map集合中元素的个数System.out.println("键值对的数量" + map.size());//键值对的数量4//V remove(Object key) 根据key删除所在的键值对map.remove(1);System.out.println("键值对的数量" + map.size());//键值对的数量3//boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合是否包含某个key//contains方法底层调用的都是equals进行比对的,所以自定义的类型需要重写equals方法System.out.println(map.containsKey(new Integer(2)));//true//boolean containsValue(Object value) 判断集合是否包含某个valueSystem.out.println(map.containsValue("zs"));//false//Collection<V> values() 获取所有的value,返回一个CollectionCollection<String> values = map.values();for (String value : values) {System.out.print(" "+value);//ls ww zl}//void clear() 清空Map集合map.clear();System.out.println("键值对的数量" + map.size());//键值对的数量0//boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//true}}
Map接口的遍历三种方式
package javase.map;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;//Map集合的遍历public class MapTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();map.put(1,"zs");map.put(2,"ls");map.put(3,"ww");map.put(4,"zl");Set<Integer> keys = map.keySet();//前2种方式遍历:迭代器和foreachIterator<Integer> it = keys.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){//1:zs 2:ls 3:ww 4:zlInteger key = it.next();String value = map.get(key);System.out.print(key+":"+value+" ");}System.out.println();for (Integer key : keys) {//1:zs 2:ls 3:ww 4:zlSystem.out.print(key+":"+map.get(key)+" ");}System.out.println();//第三种方式遍历:Set集合中元素的类型是:Map.Entry// Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() 将Map集合转成Set集合Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> set = map.entrySet();//遍历Set集合,每次取出一个Node//这种效率其实更高,因为key和value都是直接从node对象获取的Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> it2 = set.iterator();while (it2.hasNext()){Map.Entry<Integer, String> node = it2.next();Integer key = node.getKey();String value = node.getValue();//1:zs 2:ls 3:ww 4:zlSystem.out.print(key + ":" + value+"\t");}System.out.println();for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> node : set) {//1-->zs 2-->ls 3-->ww 4-->zlSystem.out.print(node.getKey() + "-->" + node.getValue()+"\t");}}}
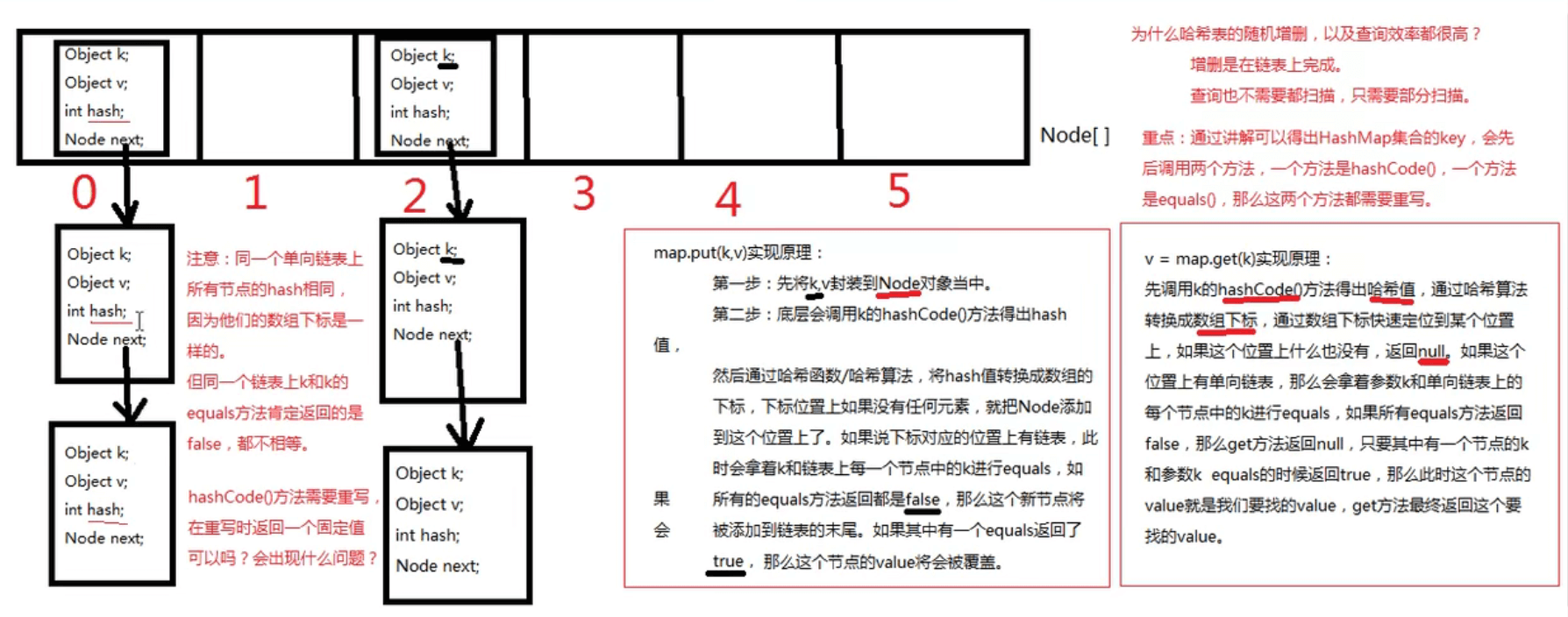
HashMap集合类★★
重点方法:put和get
hashCode()方法和equals()方法重写的问题
package javase.hashmap.bean;public class Student {private String name;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public Student(String name) {this.name = name;}public Student() {}//重写equalspublic boolean equals(Object obj){if (obj == null||!(obj instanceof Student)) return false;if (obj == this) return true;Student s = (Student) obj;if (this.name.equals(s.name)) return true;return false;}}
package javase.hashmap;import javase.hashmap.bean.Student;import java.util.HashSet;/*1、向Map集合中存,以及从Map集合中取,都是先调用key的hashCode方法,然后再调用equals方法。equals方法有可能调,也可能不调。2、拿put(k,v)和get(k)举例,什么时候不会调用?k.hashCode()方法返回哈希值,哈希值经过哈希算法转换成数组下标;如果数组下标为null,equals不需要执行。3、hashCode方法和equals方法不用研究了,直接用IDEA工具生成,但这两个方法需要同时生成4、终极结论:放在HashMap集合key部分的,以及放在HashSet集合中的元素,需要同时重写hashCode方法和equals方法*/public class HashMapTest02 {public static void main(String[] args) {Student s1 = new Student("zs");Student s2 = new Student("zs");//重写equals方法之前是false,重写之后是trueSystem.out.println(s1.equals(s2));System.out.println(s1.hashCode());System.out.println(s2.hashCode());//s1.equals(s2)结果已经是true了,表示s1和s2是一样的,同样地,那么往HashSet集合的话,//按说只能放进去一个HashSet<Student> students = new HashSet<>();students.add(s1);students.add(s2);//按理说是1,实际上是2。所以一个类的equals方法重写了,那么hashCode()方法也必须重写//并且equals方法返回如果是true,hashCode()方法返回的值必须一样System.out.println(students.size());}}
JDK8中HashMap新特性
HashMap集合底层是哈希表,这种数据结构是非线程安全的。JDK8以后,如果哈希表单向链表中元素超过8个,单向链表这种数据结构会变成红黑树。当红黑树的节点数量小于6时,会重新把红黑树变成单向链表数据结构。这种方式也是为了提高检索效率,二叉树的检索会再次缩小扫描范围,提高效率。源码如下:
/*** The bin count threshold for using a tree rather than list for a* bin. Bins are converted to trees when adding an element to a* bin with at least this many nodes. The value must be greater* than 2 and should be at least 8 to mesh with assumptions in* tree removal about conversion back to plain bins upon* shrinkage.*/static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;/*** The bin count threshold for untreeifying a (split) bin during a* resize operation. Should be less than TREEIFY_THRESHOLD, and at* most 6 to mesh with shrinkage detection under removal.*/static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;/*** The smallest table capacity for which bins may be treeified.* (Otherwise the table is resized if too many nodes in a bin.)* Should be at least 4 * TREEIFY_THRESHOLD to avoid conflicts* between resizing and treeification thresholds.*/static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;
HashMap集合类存放空值元素的问题
package javase.hashmap;import java.util.HashMap;//HashMap集合key部分允许为null吗?允许,但只能有1个public class HashMapTest03 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap map = new HashMap();map.put(null,null);System.out.println(map.size()); //1System.out.println(map.get(null));//null}}
HashTable集合类
HashTable类的基本信息
初始容量、负载因子、扩容机制
/*** Constructs a new, empty hashtable with a default initial capacity (11)* and load factor (0.75).*///初始容量为11,负载因子为0.75public Hashtable() {this(11, 0.75f);}/*** Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this* hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more* efficiently. This method is called automatically when the* number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity* and load factor.*///扩容机制是原来的2倍+1@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")protected void rehash() {int oldCapacity = table.length;Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;// overflow-conscious codeint newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE bucketsreturn;newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];modCount++;threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);table = newMap;for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {Entry<K,V> e = old;old = old.next;int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];newMap[index] = e;}}}
HashTable集合类存放空值元素的问题
package javase.hashtable;import java.util.Hashtable;//HashTable类的k-v都不能为空,否则空指针异常//HashTable方法都带有Synchronized关键字,因此是线程安全的,线程安全有其他解决方案,//因此HashTable对线程的处理导致效率较低,使用较少//public class HashTableTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Hashtable<Integer, String> ht = new Hashtable<>();ht.put(null,"zs"); //本行代码出现空指针异常ht.put(12,null); //本行代码也出现了空指针异常System.out.println(ht);}}
究其原因,是源代码有以下规则:
/*** Maps the specified <code>key</code> to the specified* <code>value</code> in this hashtable. Neither the key nor the* value can be <code>null</code>. <p>** The value can be retrieved by calling the <code>get</code> method* with a key that is equal to the original key.** @param key the hashtable key* @param value the value* @return the previous value of the specified key in this hashtable,* or <code>null</code> if it did not have one* @exception NullPointerException if the key or value is* <code>null</code>* @see Object#equals(Object)* @see #get(Object)*/public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {// Make sure the value is not nullif (value == null) {throw new NullPointerException();}// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;int hash = key.hashCode();int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {V old = entry.value;entry.value = value;return old;}}addEntry(hash, key, value, index);return null;}
Properties类
package javase.hashtable.properties;/*Properties是一个Map集合,继承自Hashtable,Properties的key和value都是String类型,Properties被称为属性类对象*/import java.util.Properties;/*** Properties类的常用方法:* String getProperty(String key) 用指定的键在此属性列表中搜索属性。* String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue) 用指定的键在属性列表中搜索属性。* void load(InputStream inStream) 从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)。* void load(Reader reader) 按简单的面向行的格式从输入字符流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)。* Object setProperty(String key, String value) 调用 Hashtable 的方法 put。*/public class PropertiesTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//需要掌握Properties的2个方法,一个存,一个取Properties pro = new Properties();pro.setProperty("username","root");pro.setProperty("password","admin123");String username = pro.getProperty("username");System.out.println(username); //root}}
Collections工具类常用方法
package javase;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;//java.util.Collection 集合接口//java.util.Collections 集合工具类,方便集合的操作public class CollectionsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {//ArrayList集合不是线程安全的ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();//变成线程安全的Collections.synchronizedList(list);//排序//注意:对List集合中元素排序(限list),需要保证List集合中的元素实现了Comparable接口list.add("abc");list.add("abf");list.add("ahj");list.add("bcx");Collections.sort(list);for (String s : list) {//abc abf ahj bcxSystem.out.print(s+" ");}}}