Spark 运行时架构
经过近几年的高速发展,分布式计算框架的架构逐渐趋同。资源管理模块作为其中最通用的模块逐渐与框架解耦,独立成通用的组件。目前大部分分布式计算框架都支持接入多款不同的资源管理器。资源管理器负责集群资源的管理和调度,为计算任务分配资源容器并保证资源隔离。Apache Spark 作为通用分布式计算平台,目前同时支持多款资源管理器,包括:
- YARN
- Mesos
- Kubernetes
- Spark Standalone
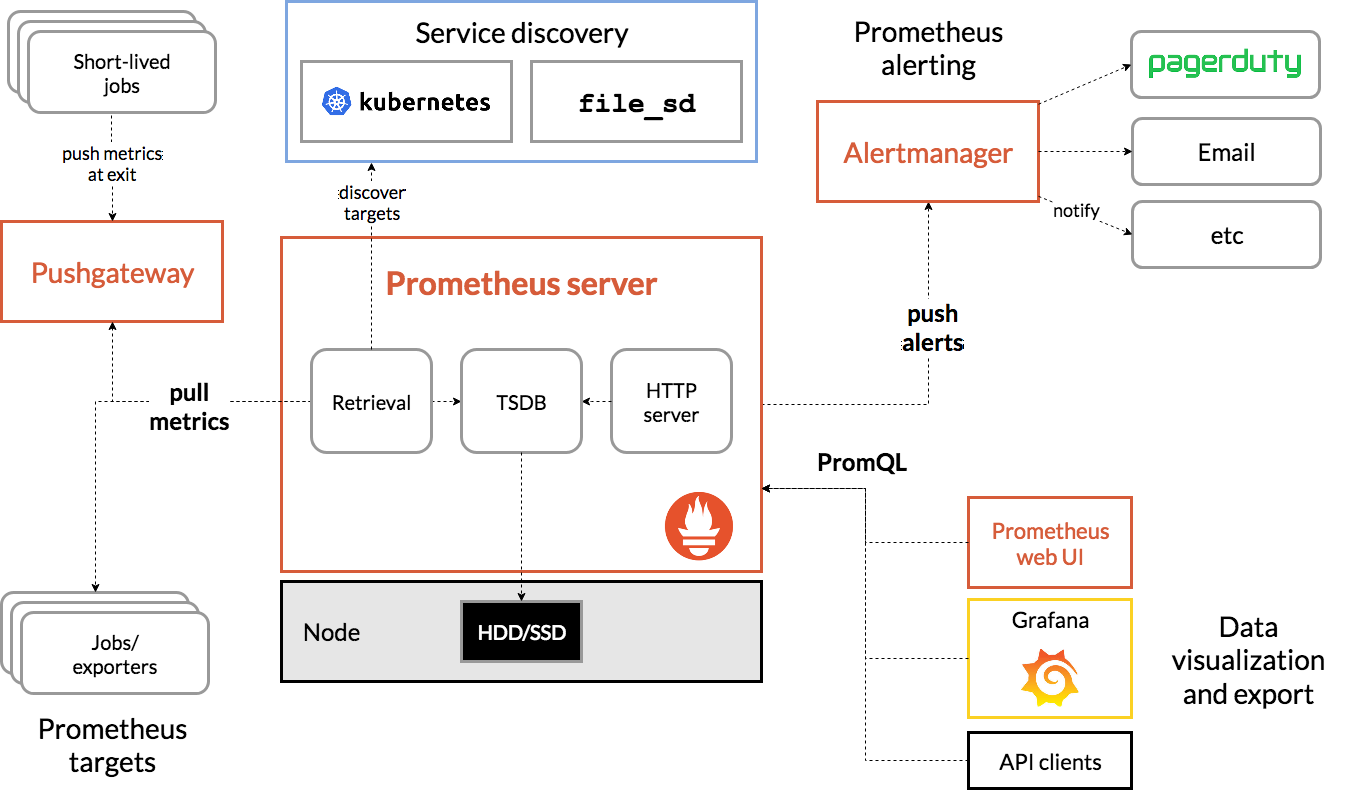
Apache Spark 的运行时框架如下图所示,其与各类资源调度器的交互流程比较类似:
其中,Driver 负责作业逻辑的调度和任务的监控,资源管理器负责资源分配和监控。Driver 根据部署模式的不同,启动和运行的物理位置有所不同。其中,Client 模式下,Driver 模块运行在 Spark-Submit 进程中,Cluster 模式下,Driver 的启动过程和Executor 类似,运行在资源调度器分配的资源容器内。
K8s 是 Spark 在 2.3 开始支持资源管理器,而相关讨论早在2016年就已经开始展开。Spark对 K8s 的支持随着版本的迭代也逐步深入,在发布的 3.0 中,Spark on K8s 提供了更好的 Kerberos 支持和资源动态支持的特性。
Spark on Kubernetes
Kubernetes 是由 Google 开源的一款面向应用的容器集群部署和管理系统,近年来发展十分迅猛,相关生态已经日趋完善。在 Spark 官方接入 K8s 前,社区通常通过在 K8s 集群上部署一个 Spark Standalone 集群的方式来实现在 K8s 集群上运行 Spark 任务的目的。方案架构如下图所示:
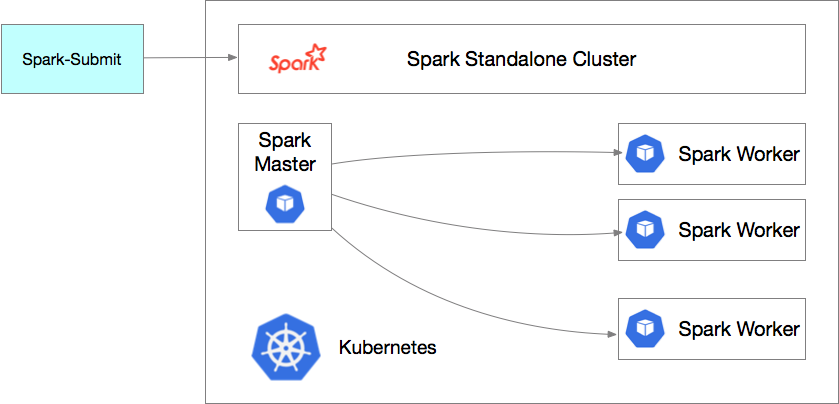
这个模式简单易用,但存在相当大的缺陷:
- 无法按需扩展,Spark Standalone 部署后集群规模固定,无法根据作业需求自动扩展集群;
- 无法利用K8s原生能力,Spark Standalone 内建的资源调度器不支持扩展,难以接入K8s 调度,无法利用 K8s 提供的云原生特性;
- Spark Standalone 集群在多租户资源隔离上天生存在短板。
Spark on Kubernetes 方案架构如下图所示,设计细节可以参考:SPARK-18278
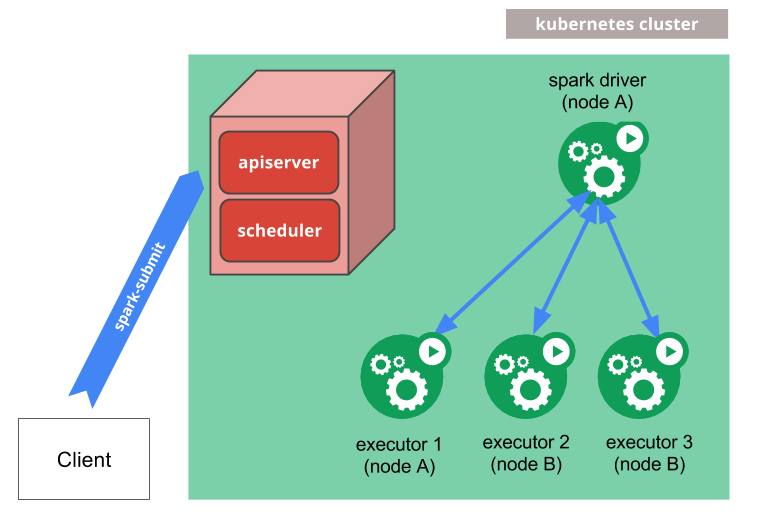
在这个方案中,
- Spark-Submit 通过调用 K8s API 在 K8s 集群中启动一个 Spark Driver Pod;
- Driver 通过调用 K8s API 启动相应的 Executor Pod,组成一个 Spark Application 集群,并指派作业任务到这些 Executor 中执行;
- 作业结束后,Executor Pod 会被销毁,而 Driver Pod 会持久化相关日志,并保持在
completed状态,直到用户手清理或被 K8s 集群的垃圾回收机制回收。
当前的方案已经解决了 Spark Standalone on K8s 方案的部分缺陷,然而,Spark Application 的生命周期管理方式和调度方式与 K8s 内置的工作负载(如 Deployments、DaemonSets、StatefulSets等)存在较大差异,在 K8s 上执行作业仍然存在不少问题:
- Spark-submit 在 K8s 集群之外,使用非声明式的提交接口;
- Spark Application 之间没有协同调度,在小集群中很容易出现调度饿死的情况;
- 需要手动配置网络,来访问 WebUI;
- 任务监控比较麻烦,没有接入 Prometheus 集群监控。
当然Spark on Kubernetes 方案目前还在快速开发中,更多特性不久会发布出来,相信未来和 K8s 的集成会更加紧密和 Native,这些特性包括:
- 动态资源分配和外部 Shuffle 服务
- 本地文件依赖管理器
- Spark Application 管理器
- 作业队列和资源管理器
Spark Operator 浅析
在分析 Spark Operator 的实现之前,先简单梳理下 Kubernetes Operator 的基本概念。Kubernetes Operator 是由 CoreOS 开发的 Kubernetes 扩展特性,目标是通过定义一系列 CRD 和实现控制器,将特定领域的应用程序运维技术和知识(如部署方法、监控、故障恢复等)通过代码的方式固化下来。Spark Operator 是 Google 基于 Operator 模式开发的一款的工具(https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/spark-on-k8s-operator),用于通过声明式的方式向 K8s 集群提交 Spark 作业。使用 Spark Operator 管理 Spark 应用,能更好的利用 K8s 原生能力控制和管理 Spark 应用的生命周期,包括应用状态监控、日志获取、应用运行控制等,弥补 Spark on K8s 方案在集成 K8s 上与其他类型的负载之间存在的差距。
系统架构
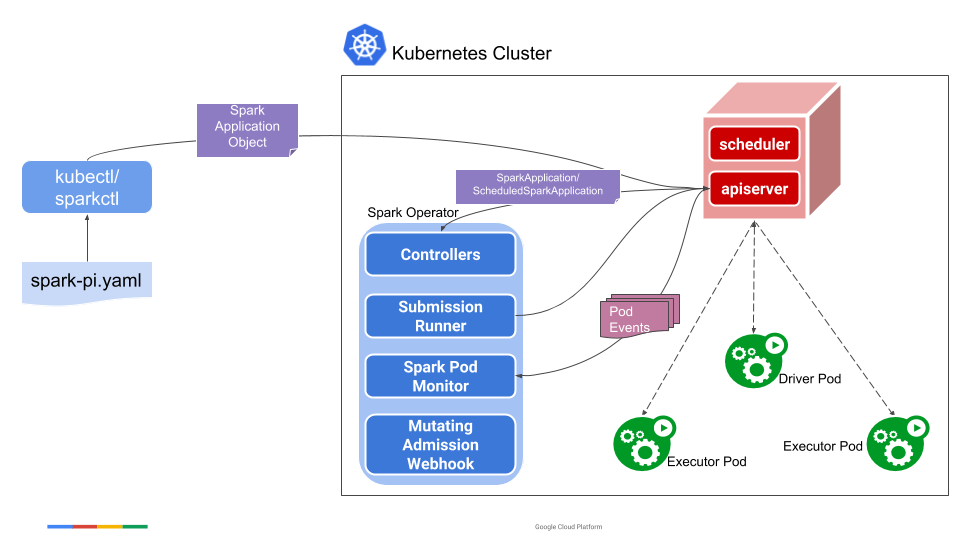
可以看出,Spark Operator 相比 Spark on K8s,架构上要复杂一些,实际上 Spark Operator 集成了 Spark on K8s 的方案,提供了更全面管控特性。通过 Spark Operator,用户可以使用更加符合 K8s 理念的方式来控制 Spark 应用的生命周期。Spark Operator 包括如下几个组件:
- SparkApplication 控制器:该控制器用于创建、更新、删除SparkApplication对象,同时控制器还会监控相应的事件,执行相应的动作;
- Submission Runner:负责调用 spark-submit 提交 Spark 作业,作业提交的流程完全复用 Spark on K8s 的模式;
- Spark Pod Monitor:监控 Spark 作业相关 Pod 的状态,并同步到控制器中;
- Mutating Admission Webhook:可选模块,基于注解来实现 Driver/Executor Pod 的一些定制化需求;
- SparkCtl:用于和 Spark Operator 交互的命令行工具。
Spark Operator 除了实现基本的作业提交外,还支持如下特性:
- 声明式的作业管理;
- 支持更新 SparkApplication 对象后自动重新提交作业;
- 支持可配置的重启策略;
- 支持失败重试;
- 集成 Prometheus,可以收集和转发 Spark 应用级别的度量和 Driver/Executor 的度量到 Prometheus 中。
工程结构
Spark Operator 的项目是标准的 K8s Operator 结构,其中最重要的包括:
- manifest:定义了 Spark 相关的 CRD,包括:
- ScheduledSparkApplication:表示一个定时执行的 Spark 作业
- SparkApplication:表示一个 Spark 作业
- pkg:具体的 Operator 逻辑实现
- api:定义了 Operator 的多个版本的 API
- client:用于对接的 client-go SDK
- controller:自定义控制器的实现,包括:
- ScheduledSparkApplication 控制器
- SparkApplication 控制器
- batchscheduler: 批处理调度器集成模块, 目前已经集成了 K8s volcano 调度器
- spark-docker:spark docker 镜像
- sparkctl:spark operator 命令行工具
Spark Application 控制器
控制器的代码主要位于pkg/controller/sparkapplication/controller.go中。
提交作业
提交作业的提交作业的主流程在 submitSparkApplication 方法中。
// controller.go// submitSparkApplication creates a new submission for the given SparkApplication and submits it using spark-submit.func (c *Controller) submitSparkApplication(app *v1beta2.SparkApplication) *v1beta2.SparkApplication {if app.PrometheusMonitoringEnabled() {...configPrometheusMonitoring(app, c.kubeClient)}// Use batch scheduler to perform scheduling task before submitting (before build command arguments).if needScheduling, scheduler := c.shouldDoBatchScheduling(app); needScheduling {newApp, err := scheduler.DoBatchSchedulingOnSubmission(app)...//Spark submit will use the updated app to submit tasks(Spec will not be updated into API server)app = newApp}driverPodName := getDriverPodName(app)submissionID := uuid.New().String()submissionCmdArgs, err := buildSubmissionCommandArgs(app, driverPodName, submissionID)...// Try submitting the application by running spark-submit.submitted, err := runSparkSubmit(newSubmission(submissionCmdArgs, app))...app.Status = v1beta2.SparkApplicationStatus{SubmissionID: submissionID,AppState: v1beta2.ApplicationState{State: v1beta2.SubmittedState,},DriverInfo: v1beta2.DriverInfo{PodName: driverPodName,},SubmissionAttempts: app.Status.SubmissionAttempts + 1,ExecutionAttempts: app.Status.ExecutionAttempts + 1,LastSubmissionAttemptTime: metav1.Now(),}c.recordSparkApplicationEvent(app)service, err := createSparkUIService(app, c.kubeClient)...ingress, err := createSparkUIIngress(app, *service, c.ingressURLFormat, c.kubeClient)return app}
提交作业的核心逻辑在 submission.go 这个模块中:
// submission.gofunc runSparkSubmit(submission *submission) (bool, error) {sparkHome, present := os.LookupEnv(sparkHomeEnvVar)if !present {glog.Error("SPARK_HOME is not specified")}var command = filepath.Join(sparkHome, "/bin/spark-submit")cmd := execCommand(command, submission.args...)glog.V(2).Infof("spark-submit arguments: %v", cmd.Args)output, err := cmd.Output()glog.V(3).Infof("spark-submit output: %s", string(output))if err != nil {var errorMsg stringif exitErr, ok := err.(*exec.ExitError); ok {errorMsg = string(exitErr.Stderr)}// The driver pod of the application already exists.if strings.Contains(errorMsg, podAlreadyExistsErrorCode) {glog.Warningf("trying to resubmit an already submitted SparkApplication %s/%s", submission.namespace, submission.name)return false, nil}if errorMsg != "" {return false, fmt.Errorf("failed to run spark-submit for SparkApplication %s/%s: %s", submission.namespace, submission.name, errorMsg)}return false, fmt.Errorf("failed to run spark-submit for SparkApplication %s/%s: %v", submission.namespace, submission.name, err)}return true, nil}func buildSubmissionCommandArgs(app *v1beta2.SparkApplication, driverPodName string, submissionID string) ([]string, error) {...options, err := addDriverConfOptions(app, submissionID)...options, err = addExecutorConfOptions(app, submissionID)...}func getMasterURL() (string, error) {kubernetesServiceHost := os.Getenv(kubernetesServiceHostEnvVar)...kubernetesServicePort := os.Getenv(kubernetesServicePortEnvVar)...return fmt.Sprintf("k8s://https://%s:%s", kubernetesServiceHost, kubernetesServicePort), nil}
可以看出,
- 可以配置控制器启用 Prometheus 进行度量收集;
- Spark Operator 通过拼装一个 spark-submit 命令并执行,实现提交 Spark 作业到 K8s 集群中的目的;
- 在每次提交前,Spark Operator 都会生成一个 UUID 作为 Session ID,并通过 Spark 相关配置对 Driver/Executor 的 Pod 进行标记。我们可以使用这个 ID 来跟踪和控制这个 Spark 作业;
- Controller 通过监控相关作业的 Pod 的状态来更新 SparkApplication 的状态,同时驱动 SparkApplication 对象的状态流转;
- 提交成功后,还会做如下几件事情:
- 更新作业的状态;
- 启动一个Service,并配置好Ingress,方便用户访问Spark WebUI。
状态流转控制
在 Spark Operator 中,Controller 使用状态机来维护 Spark Application 的状态信息,状态流转和 Action 的关系如下图所示: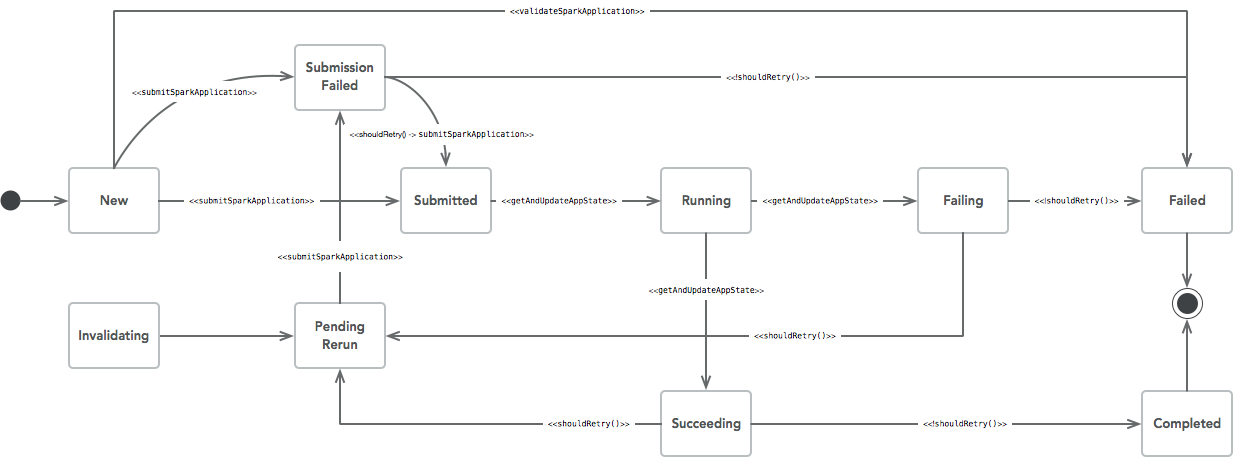
作业提交后,Spark Application 的状态更新都是通过 getAndUpdateAppState() 方法来实现的。
// controller.gofunc (c *Controller) getAndUpdateAppState(app *v1beta2.SparkApplication) error {if err := c.getAndUpdateDriverState(app); err != nil {return err}if err := c.getAndUpdateExecutorState(app); err != nil {return err}return nil}// getAndUpdateDriverState finds the driver pod of the application// and updates the driver state based on the current phase of the pod.func (c *Controller) getAndUpdateDriverState(app *v1beta2.SparkApplication) error {// Either the driver pod doesn't exist yet or its name has not been updated....driverPod, err := c.getDriverPod(app)...if driverPod == nil {app.Status.AppState.ErrorMessage = "Driver Pod not found"app.Status.AppState.State = v1beta2.FailingStateapp.Status.TerminationTime = metav1.Now()return nil}app.Status.SparkApplicationID = getSparkApplicationID(driverPod)...newState := driverStateToApplicationState(driverPod.Status)// Only record a driver event if the application state (derived from the driver pod phase) has changed.if newState != app.Status.AppState.State {c.recordDriverEvent(app, driverPod.Status.Phase, driverPod.Name)}app.Status.AppState.State = newStatereturn nil}// getAndUpdateExecutorState lists the executor pods of the application// and updates the executor state based on the current phase of the pods.func (c *Controller) getAndUpdateExecutorState(app *v1beta2.SparkApplication) error {pods, err := c.getExecutorPods(app)...executorStateMap := make(map[string]v1beta2.ExecutorState)var executorApplicationID stringfor _, pod := range pods {if util.IsExecutorPod(pod) {newState := podPhaseToExecutorState(pod.Status.Phase)oldState, exists := app.Status.ExecutorState[pod.Name]// Only record an executor event if the executor state is new or it has changed.if !exists || newState != oldState {c.recordExecutorEvent(app, newState, pod.Name)}executorStateMap[pod.Name] = newStateif executorApplicationID == "" {executorApplicationID = getSparkApplicationID(pod)}}}// ApplicationID label can be different on driver/executors. Prefer executor ApplicationID if set.// Refer https://issues.apache.org/jira/projects/SPARK/issues/SPARK-25922 for details....if app.Status.ExecutorState == nil {app.Status.ExecutorState = make(map[string]v1beta2.ExecutorState)}for name, execStatus := range executorStateMap {app.Status.ExecutorState[name] = execStatus}// Handle missing/deleted executors.for name, oldStatus := range app.Status.ExecutorState {_, exists := executorStateMap[name]if !isExecutorTerminated(oldStatus) && !exists {// If ApplicationState is SUCCEEDING, in other words, the driver pod has been completed// successfully. The executor pods terminate and are cleaned up, so we could not found// the executor pod, under this circumstances, we assume the executor pod are completed.if app.Status.AppState.State == v1beta2.SucceedingState {app.Status.ExecutorState[name] = v1beta2.ExecutorCompletedState} else {glog.Infof("Executor pod %s not found, assuming it was deleted.", name)app.Status.ExecutorState[name] = v1beta2.ExecutorFailedState}}}return nil}
从这段代码可以看到,Spark Application 提交后,Controller 会通过监听 Driver Pod 和Executor Pod 状态来计算 Spark Application 的状态,推动状态机的流转。
度量监控
如果一个 SparkApplication 示例配置了开启度量监控特性,那么 Spark Operator 会在Spark-Submit 提交参数中向 Driver 和 Executor 的 JVM 参数中添加类似-javaagent:/prometheus/jmx_prometheus_javaagent-0.11.0.jar=8090:/etc/metrics/conf/prometheus.yaml的 JavaAgent 参数来开启 SparkApplication 度量监控,实现通过 JmxExporter 向 Prometheus 发送度量数据。