这里还是更新了一下服务端和客户端的版本保持一致…
之前的文章版本不一致 所以看源码和在debug客户端 jar 的时候有点费劲~
当前版本:
Nacos 2.0.3
spring-cloud-alibaba 2.2.7.RELEASE
(这也是官方建议的版本)
客户端
自动配置 NacosConfigAutoConfiguration
这个是Nacos配置的自动注入类,看看在启动容器的时候做了什么
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)@ConditionalOnProperty(name = {"spring.cloud.nacos.config.enabled"},matchIfMissing = true)public class NacosConfigAutoConfiguration {@Beanpublic NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties(ApplicationContext context) {return context.getParent() != null && BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context.getParent(), NacosConfigProperties.class).length > 0 ? (NacosConfigProperties)BeanFactoryUtils.beanOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context.getParent(), NacosConfigProperties.class) : new NacosConfigProperties();}@Beanpublic NacosConfigManager nacosConfigManager(NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties) {return new NacosConfigManager(nacosConfigProperties);}// ignore...}
首先使用了 proxyBeanMethods = false
proxyBeanMethods:是用来指定@Bean注解标注的方法是否使用代理,默认是true使用代理,直接从IOC容器之中取得对象;如果设置为false,也就是不使用注解,每次调用@Bean标注的方法获取到的对象和IOC容器中的都不一样,是一个新的对象,所以我们可以将此属性设置为false来提高性能(在不存在方法调用的时候);
这里向容器内注册了一个 NacosConfigManager ,配置管理者,那么我可以这么理解:在容器初始化的时候根据 Nacos 的配置信息生成了 Nacos 的配置管理者
配置管理者 NacosConfigManager
public class NacosConfigManager {private static ConfigService service = null;public NacosConfigManager(NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties) {this.nacosConfigProperties = nacosConfigProperties;createConfigService(nacosConfigProperties);}static ConfigService createConfigService(NacosConfigProperties nacosConfigProperties) {if (Objects.isNull(service)) {Class var1 = NacosConfigManager.class;synchronized(NacosConfigManager.class) {try {if (Objects.isNull(service)) {service = NacosFactory.createConfigService(nacosConfigProperties.assembleConfigServiceProperties());}} catch (NacosException var4) {log.error(var4.getMessage());throw new NacosConnectionFailureException(nacosConfigProperties.getServerAddr(), var4.getMessage(), var4);}}}return service;}// ignore..}
- 可以看到该配置管理者的静态方法,返回了一个 ConfigService 是一个接口,从名字上我们可以猜测,这是配置服务的抽象接口,抽象了客户端进行配置相关的行为
- Nacos配置管理者(NacosConfigManager)保存了对于 ConfigService (NacosConfigService)的引用
配置拉取的落地 NacosConfigService
对于ConfigService而言,其只有一个实现,就是 NacosConfigService ,这里就直接贴上该类的代码
@SuppressWarnings("PMD.ServiceOrDaoClassShouldEndWithImplRule")public class NacosConfigService implements ConfigService {/*** will be deleted in 2.0 later versions*/@DeprecatedServerHttpAgent agent = null;/*** long polling.*/private final ClientWorker worker;private final ConfigFilterChainManager configFilterChainManager;public NacosConfigService(Properties properties) throws NacosException {ValidatorUtils.checkInitParam(properties);initNamespace(properties);this.configFilterChainManager = new ConfigFilterChainManager(properties);ServerListManager serverListManager = new ServerListManager(properties);serverListManager.start();this.worker = new ClientWorker(this.configFilterChainManager, serverListManager, properties);// will be deleted in 2.0 later versionsagent = new ServerHttpAgent(serverListManager);}@Overridepublic String getConfig(String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {return getConfigInner(namespace, dataId, group, timeoutMs);}private String getConfigInner(String tenant, String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {group = blank2defaultGroup(group);ParamUtils.checkKeyParam(dataId, group);ConfigResponse cr = new ConfigResponse();cr.setDataId(dataId);cr.setTenant(tenant);cr.setGroup(group);// use local config first 首先使用本地配置String content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getFailover(worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);if (content != null) {LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get failover ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}",worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content));cr.setContent(content);String encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor.getEncryptDataKeyFailover(agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);content = cr.getContent();return content;}try {ConfigResponse response = worker.getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, timeoutMs, false);cr.setContent(response.getContent());cr.setEncryptedDataKey(response.getEncryptedDataKey());configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);content = cr.getContent();return content;} catch (NacosException ioe) {if (NacosException.NO_RIGHT == ioe.getErrCode()) {throw ioe;}LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get from server error, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, msg={}",worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ioe.toString());}LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get snapshot ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}",worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content));content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getSnapshot(worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);cr.setContent(content);String encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor.getEncryptDataKeyFailover(agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);configFilterChainManager.doFilter(null, cr);content = cr.getContent();return content;}}
**NacosFactory.createConfigService(nacosConfigProperties.assembleConfigServiceProperties())**在NacosConfigManager代码里面(第14行)通过 NacosFactory 创建的 NacosConfigService,由其构造器可以看出,首先校验了配置文件的参数,接着new了三个对象并保存起来,分别是:ConfigFilterChainManager,ServerListManager,ClientWorker。**ConfigFilterChainManager**和过滤相关,而**ServerListManager**和服务相关,接着调用的start方法,可以看出本质上启动了一个线,**ClientWorker**启动了一个名为**com.alibaba.nacos.client.Worker**的守护线程,用来长轮询 这三个具体有什么用,暂时先不往里面深挖**getConfig/getConfigInner**这个方法从名称上可以知道,这个应该就是拉取配置的实现细节**ServerHttpAgent**这个看别的文档,说的是利用HTTP请求查询配置、发布配置 ,不过在2.0+的版本里,通讯已经使用grpc的方式来进行调用,所以说该方法被废除了-
客户端拉取配置的时间点
这里先说两个结论,在启动项目的时候Nacos会去服务端拉取配置,其次会在服务端变更配置文件之后也会去拉取配置
这里我本地只启动了server1服务,配置中心写了两个配置,一个是给server1的配置,另一个是给未启动的server2
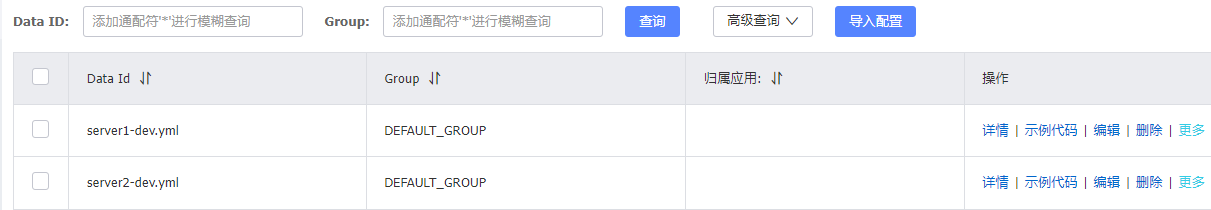
启动Nacos服务后,在 **NacosConfigManager#getConfigInner**也就是拉取配置的方法上打了断点,以此来看客户端都会在什么时候拉取配置
- 第一次是在项目启动的时候
- 第二次是在更新server1-dev.yml配置文件的时候
- 同时,我更新server2-dev.yml,是并不会更新配置的,所以说明了一点,配置更改只会通知相应的服务,不会通知所有的
- 其次,一次拉取配置的行为,走了多次断点,我这里放一下日志:
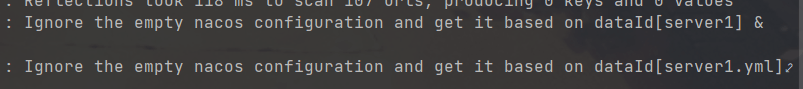
可以看到,会依次走 dataId 等于 server1 和 server1.yml 的文件去拉取配置,显而易见的此时拉取到的content是null的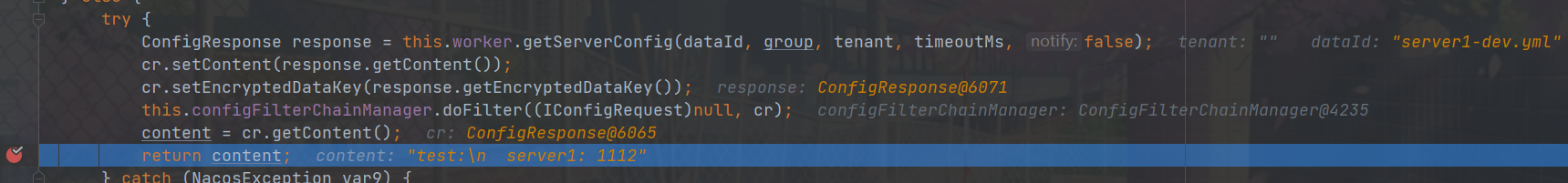 接着又去拉取 dataId 等于 server1-dev.yml 的文件,此时就会拉取到我在Nacos上配置的server1-dev.yml
接着又去拉取 dataId 等于 server1-dev.yml 的文件,此时就会拉取到我在Nacos上配置的server1-dev.yml
拉取本地配置
private String getConfigInner(String tenant, String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {//ignore ..String content = LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getFailover(this.worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant);if (content != null) {LOGGER.warn("[{}] [get-config] get failover ok, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, config={}", new Object[]{this.worker.getAgentName(), dataId, group, tenant, ContentUtils.truncateContent(content)});cr.setContent(content);encryptedDataKey = LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor.getEncryptDataKeyFailover(this.agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant);cr.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);this.configFilterChainManager.doFilter((IConfigRequest)null, cr);content = cr.getContent();return content;}// ignore ..}public static String getFailover(String serverName, String dataId, String group, String tenant) {File localPath = getFailoverFile(serverName, dataId, group, tenant);if (localPath.exists() && localPath.isFile()) {try {return readFile(localPath);} catch (IOException var6) {LOGGER.error("[" + serverName + "] get failover error, " + localPath, var6);return null;}} else {return null;}}
本人localPath是在:**C:\Users\xxxx\nacos\config\config_rpc_client_nacos\data\config-data\DEFAULT_GROUP\server1**
- 由上面的代码可以看出,优先会去拉取本地的配置
**LocalConfigInfoProcessor.getFailover** - 如果获取到的内容
**content**的话,就会通过本地加密数据密钥处理器拿到密钥,并且进行解密的操作,并且返回 可见 4-12 行
拉取远端配置
private String getConfigInner(String tenant, String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs) throws NacosException {// ignore ...ConfigResponse response = this.worker.getServerConfig(dataId, group, tenant, timeoutMs, false);cr.setContent(response.getContent());cr.setEncryptedDataKey(response.getEncryptedDataKey());this.configFilterChainManager.doFilter((IConfigRequest)null, cr);content = cr.getContent();return content;}
- 我们可以看到,在这里调用了
**worker.getServerConfig(xxx)**拉取的远端的配置 - 之后从响应体中获取到内容 以及数据密钥,并且进行解密操作之后,将配置返回
那么,我们看看这个worker是怎么做的,其内部具体实现了什么操作?
从**getServerConfig**从这个方法点进去后,经过一系列套娃,这里放上代码
public ConfigResponse queryConfig(String dataId, String group, String tenant, long readTimeouts, boolean notify) throws NacosException {// ignore ..ConfigQueryResponse response = (ConfigQueryResponse)this.requestProxy(rpcClient, request, readTimeouts);ConfigResponse configResponse = new ConfigResponse();if (response.isSuccess()) {LocalConfigInfoProcessor.saveSnapshot(this.getName(), dataId, group, tenant, response.getContent());configResponse.setContent(response.getContent());String configType;if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(response.getContentType())) {configType = response.getContentType();} else {configType = ConfigType.TEXT.getType();}configResponse.setConfigType(configType);String encryptedDataKey = response.getEncryptedDataKey();LocalEncryptedDataKeyProcessor.saveEncryptDataKeySnapshot(ClientWorker.this.agent.getName(), dataId, group, tenant, encryptedDataKey);configResponse.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);return configResponse;}}
- 可以看到这里通过
**requestProxy**方法请求的服务端 - 接着获取到配置后,如果成功,则
**LocalConfigInfoProcessor.saveSnapshot**保存快照 - 其次 从相应体中保存了密钥信息到本地的快照里
_**saveEncryptDataKeySnapshot**_
再次向里面看,看看 requestProxy 是如何请求数据的
……. 未完待续,这里底层用的 grpc 这技术没用过,我先看看官方文档,之后再写 TAT
这是官方文档的简介,先摆上来:https://grpc.io/docs/what-is-grpc/introduction/
- 使用grpc 的好处是: 就算服务端是Java,但是客户端可以使用其他语言,来维持通讯,调用服务端的方法!!!
you can easily create a gRPC server in Java with clients in Go, Python, or Ruby.
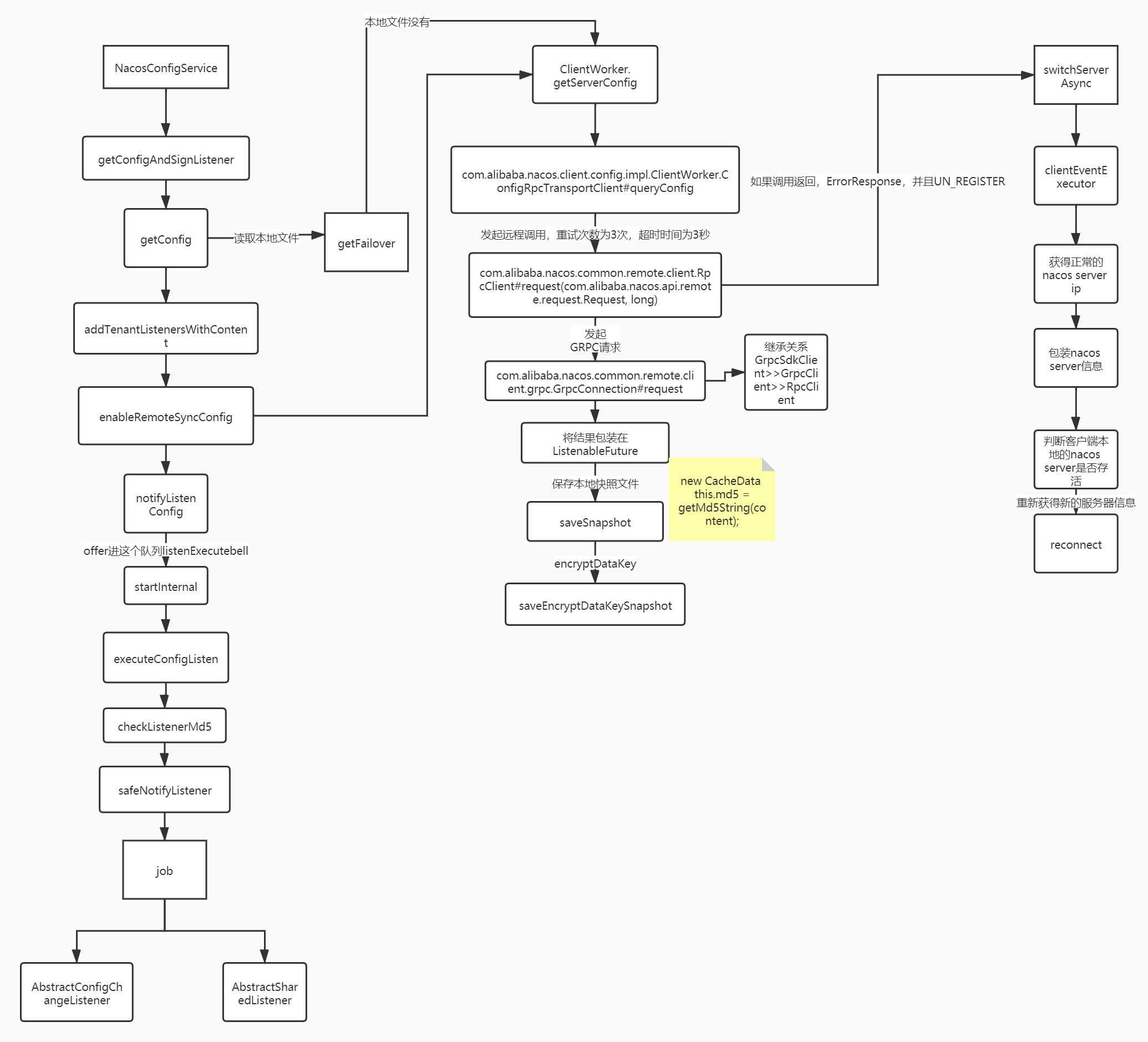
这里贴一下从别处扒的流程图