什么是中间件
中间件的本质就是一种在特定场景下使用的函数,它负责完成某个特定的功能。Koa没有绑定中间件,但Koa 所有的功能基本上都是通过中间件来实现的。
中间件机制
洋葱模型,它就是 Koa 中间件的一种串行机制,并且是支持异步的。Koa中间件机制就是函数式组合概念 Compose的概念,将一组需要顺序执行的函数复合为一个函数,外层函数的参数实际是内层函数的返回值。洋葱圈模型可以形象表示这种机制。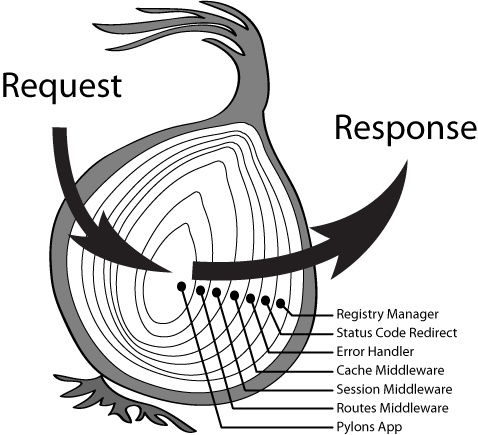
中间件的参数
const middleware = async (ctx, next) => {next()};
中间件包含两个参数 ctx 和 next:
- ctx: 作为上下文使用,包括基本的
ctx.request和ctx.response - next: 中间件通过next函数联系, 执行 next() 后会将控制权交给下一个中间件, 直到没有中间件执行next后将会沿路折返,将控制权交换给前一个中间件,因此next()后面的代码会在后面中间件执行结束后执行。
简单来说:ctx 就是网络处理上下文,next函数指向下个中间件,内部通过 dispatch 函数形成了一条处理请求的流水线。
常见中间件实现
koa中间件的规范:
- 一个async函数
- 接收ctx和next两个参数
- 任务结束需要执行next 中间件
const middleware= async (ctx, next) => {// 来到中间件,洋葱圈左边next() // 进入下一个中间件// 再次来到中间件,洋葱圈右边};
router 中间件实现
class Router {constructor() {this.stack = [];}register(path, methods, middleware) {let route = {path, methods, middleware}this.stack.push(route);}// 现在只支持get和post,其他的同理get(path,middleware){this.register(path, 'get', middleware);}post(path,middleware){this.register(path, 'post', middleware);}routes() {let stock = this.stack;return async function(ctx, next) {let currentPath = ctx.url;let route;for (let i = 0; i < stock.length; i++) {let item = stock[i];if (currentPath === item.path && item.methods.indexOf(ctx.method) >= 0) {// 判断path和methodroute = item.middleware;break;}}if (typeof route === 'function') {route(ctx, next);return;}await next();};}}module.exports = Router;
router中间件使用
const Koa = require('./koa')const Router = require('./router')const app = new Koa()const router = new Router();router.get('/index', async ctx => {console.log('index,xx')ctx.body = 'index page';});router.get('/post', async ctx => { ctx.body = 'post page'; });router.get('/list', async ctx => { ctx.body = 'list page'; });router.post('/index', async ctx => { ctx.body = 'post page'; });// 路由实例输出父中间件 router.routes()app.use(router.routes());app.listen(3000, () => {console.log('server runing on port 9092')})
静态文件服务 static 中间件实现
其功能类似于 koa-static 中间件:
- 配置绝对资源目录地址,默认为 static
- 获取文件或者目录信息
- 静态文件读取、返回
// static.jsconst fs = require("fs");const path = require("path");module.exports = (dirPath = "./public") => {return async (ctx, next) => {if (ctx.url.indexOf("/public") === 0) {// public开头 读取文件const url = path.resolve(__dirname, dirPath);const fileBaseName = path.basename(url);const filepath = url + ctx.url.replace("/public", "");console.log(filepath);// console.log(ctx.url,url, filepath, fileBaseName)try {stats = fs.statSync(filepath);if (stats.isDirectory()) {const dir = fs.readdirSync(filepath);// constconst ret = ['<div style="padding-left:20px">'];dir.forEach(filename => {console.log(filename);// 简单认为不带小数点的格式,就是文件夹,实际应该用statSyncif (filename.indexOf(".") > -1) {ret.push(`<p><a style="color:black" href="${ctx.url}/${filename}">${filename}</a></p>`);} else {// 文件ret.push(`<p><a href="${ctx.url}/${filename}">${filename}</a></p>`);}});ret.push("</div>");ctx.body = ret.join("");} else {console.log("文件");const content = fs.readFileSync(filepath);ctx.body = content;}} catch (e) {// 报错了 文件不存在ctx.body = "404, not found";}} else {// 否则不是静态资源,直接去下一个中间件await next();}};};
静态文件服务 static 中间件使用
const static = require('./static')app.use(static(__dirname + '/public'));
请求拦截中间件实现
请求拦截应用非常广泛:登录状态验证、CORS头设置等
// iptable.jsmodule.exports = async function (ctx, next) {const { res, req } = ctx;const blackList = ['127.0.0.1'];const ip = getClientIP(req);if (blackList.includes(ip)) {//出现在黑名单中将被拒绝ctx.body = "not allowed";} else {await next();}};function getClientIP(req) {return (req.headers["x-forwarded-for"] || // 判断是否有反向代理 IPreq.connection.remoteAddress || // 判断 connection 的远程 IPreq.socket.remoteAddress || // 判断后端的 socket 的 IPreq.connection.socket.remoteAddress);}
请求拦截中间件使用
// app.jsconst Koa = require('./koa')const Router = require('./router')const app = new Koa()app.use(require("./interceptor"));app.listen(3000, '0.0.0.0', () => {console.log("监听端口3000");});

