不正确地访问资源
boolean类型地数据是原子性操作,即赋值和返回值这样的操作不会有发生中断的可能。虽然虚拟机规范没有定义boolean类型数据所占的字节数,但通常一个bit位即可表示。
boolean: The boolean data type has only two possible values: true and false.Use this data type for simple flags that track true/false conditions.This data type represents one bit of information, but its "size" isn't something that's precisely defined
package com.thinking.in.java.course.chapter21;//外部条件控制代码的执行public abstract class IntGenerator {private volatile boolean canceled = false;//volatile+boolean即保证了可视性又保证了原子性public abstract int next();//具体的控制开关public void cancel(){canceled = true;}public boolean isCanceled(){return canceled;}}
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class EvenChecker implements Runnable{
private IntGenerator generator;//外部条件
private final int id;
public EvenChecker(IntGenerator gp,int ident){
generator = gp;
id = ident;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!generator.isCanceled()){
int num = generator.next();
// 并发去访问受限资源的话,由于无法保证网络的稳定性,存在诸多问题
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+num);
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//----------------------
if(num % 2 !=0) {
System.out.println(num + " is not even");
generator.cancel();
}
}
}
public static void testEven(IntGenerator generator,int count){
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
executorService.execute(new EvenChecker(generator,i));
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
public static void test(IntGenerator generator){
testEven(generator,10);
}
}
public class EvenGenerator extends IntGenerator{
private int currentEvenValue = 0;
//非同步的操作、非原子的操作
@Override
public int next() {
++currentEvenValue;
++currentEvenValue;
return currentEvenValue;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvenGenerator generator = new EvenGenerator();
EvenChecker.test(generator);
}
}
解决方案一
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class EvenGenerator extends IntGenerator{
private int currentEvenValue = 0;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public int next() {
lock.lock();
++currentEvenValue;
++currentEvenValue;
lock.unlock();
return currentEvenValue;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvenGenerator generator = new EvenGenerator();
EvenChecker.test(generator);
}
}
解决方案二
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class EvenGenerator extends IntGenerator{
private int currentEvenValue = 0;
@Override
public synchronized int next() {
++currentEvenValue;
++currentEvenValue;
return currentEvenValue;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvenGenerator generator = new EvenGenerator();
EvenChecker.test(generator);
}
}
解决资源共享竞争
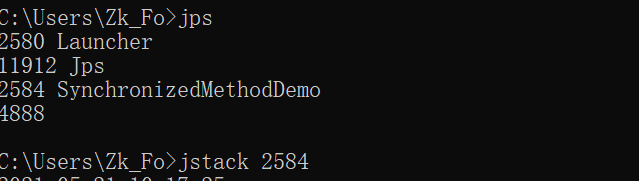
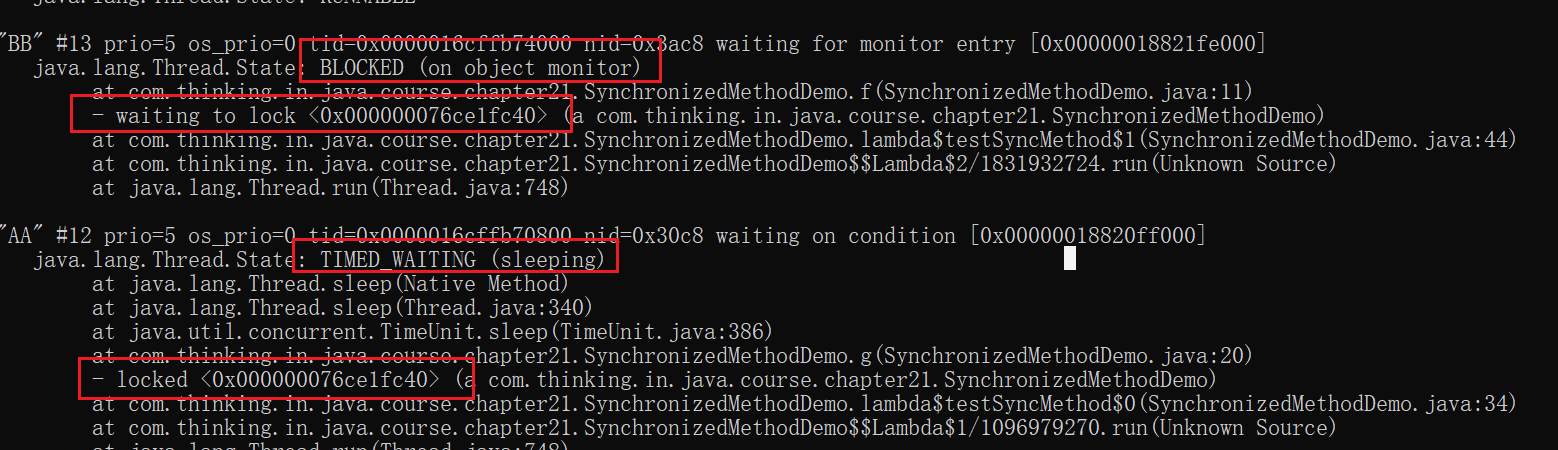
synchronized 修饰的方法,其实是实例(对象)锁

import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SynchronizedMethodDemo {
synchronized void f(){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+"f()");
}
synchronized void g(){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+"g()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronizedMethodDemo demo = new SynchronizedMethodDemo();
demo.testSyncMethod();
}
public void testSyncMethod(){
new Thread(()->{
g();
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
f();
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
f();
g();
},"BB").start();
}
}
synchronized +static 修饰的方法 其实是类锁

import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SynchronizedStaticDemo {
private static int ticketNum = 100;
public synchronized static void getTicket() {
if (ticketNum>0) {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println(e.getCause());
}
ticketNum--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" + ticketNum);
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" +"票已售罄");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public synchronized static void getTicket2() {
if (ticketNum>0) {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println(e.getCause());
}
ticketNum--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" + ticketNum);
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "->" +"票已售罄");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket();
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket();
}, "BBB").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket();
}, "CCC").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket();
}, "DDD").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket2();
}, "A-A").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket2();
}, "B-B").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket2();
}, "C-C").start();
new Thread(() -> {
getTicket2();
}, "D-D").start();
}
}
}
synchronized 与Lock的区别

①synchronized 尝试获取锁会一直处于阻塞状态 倔强派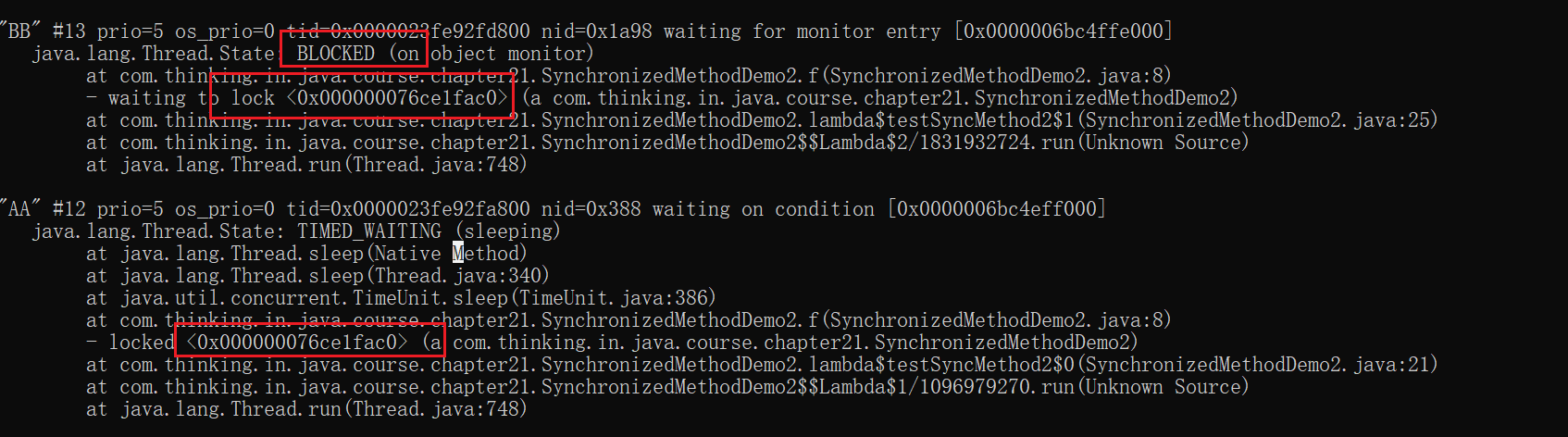
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SynchronizedMethodDemo2 {
synchronized void f(){
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->"+"f()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchronizedMethodDemo2 demo = new SynchronizedMethodDemo2();
demo.testSyncMethod2();
}
public void testSyncMethod2(){
new Thread(()->{
f();
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
f();
},"BB").start();
}
}
②lock会尝试着去获取锁,当锁没法获取的时候,就放弃 活套派
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.*;
public class AttemptLocking {
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void untimed() {
boolean captured = lock.tryLock();
try {
System.out.println("tryLock(): " + captured);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(30);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
if (captured)
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void timed() {
boolean captured = false;
try {
captured = lock.tryLock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
System.out.println("tryLock(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS): " + captured);
} finally {
if (captured)
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
final AttemptLocking al = new AttemptLocking();
new Thread(()->{al.untimed();}).start();
new Thread(()->{al.timed();}).start();
}
}
原子性与易变性
原子操作的定义
基本类型非原子操作示例一
package com.thinking.in.java.course.chapter21;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class AtomcityTest implements Runnable{
private int i = 0;
//返回是原子操作
public int getValue(){
return i;
}
//方法是同步的,但是对变量的修改 其他线程可以看到
//错误的理解:synchronized同步的方法,内部对成员变量的处理,
//在通过其他非同步方法访问的时候也是同步的
public synchronized void evenIncrement(){
i++;//非原子操作
i++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//System.out.println("---"+i+"---");
evenIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomcityTest atomcityTest = new AtomcityTest();
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
service.execute(atomcityTest);
while (true){
int value = atomcityTest.getValue();
System.out.println("==="+value+"===");
if(value % 2 !=0){
System.out.println(value);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
基本类型原子操作示例二
package com.thinking.in.java.course.chapter21;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class AtomcityTest2 implements Runnable{
private boolean flag = false;
public boolean getValue(){
return flag;
}
//此处不加synchronized也是可以的
public synchronized boolean evenIncrement(){
return flag = !flag;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("---"+flag+"---");
evenIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomcityTest2 test2 = new AtomcityTest2();
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
service.execute(test2);
while (true){
boolean flag = test2.getValue();
System.out.println("==="+flag+"===");
if(flag){
System.out.println(flag);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
临界区
synchronized 修饰的方法在一个线程获取锁的时候,并不影响其他线程对普通方法的调用
synchronized 修饰的this代码块方法在一个线程获取锁的时候,并不影响其他线程对普通方法的调用
synchronized void syncM(){}、void thisM(){ synchronized (this) {}}对同一对象来说 是同一把锁
package com.thinking.in.java.course.chapter21;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
class Moo{
/**
* synchronized void syncM(){}
* void thisM(){ synchronized (this) {}}
* 对同一对象来说 是同一把锁
*/
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger();
//synchronized 修饰的方法在一个线程获取锁的时候,并不影响其他线程对普通方法的调用
synchronized void syncM(){
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Moo sync method");
}
//synchronized 修饰的this方法在一个线程获取锁的时候,并不影响其他线程对普通方法的调用
void thisM(){
synchronized (this) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("Moo this method");
}
}
void commonM(){
System.out.println("Moo common method");
}
}
class MooTask implements Runnable{
Moo moo;
MooTask(Moo moo){this.moo = moo;}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
moo.syncM();
}
}
}
class Moo2Task implements Runnable{
Moo moo;
Moo2Task(Moo moo){this.moo = moo;}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
//moo.thisM();
moo.atomicInteger.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
public class CriticalSection2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Moo moo = new Moo();
executorService.execute(new MooTask(moo));
//TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
executorService.execute(new Moo2Task(moo));
}
}
在其他对象上同步
package com.thinking.in.java.course.chapter21;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
通过jps、jstack 查看lock的对象是不一样的
*/
class DualSynch {
public Object syncObject = new Object();
//同步方法 其实就是 实例锁
public synchronized void f() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("f() =>"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.yield();
}
}
public void g() throws InterruptedException {
//对象锁
synchronized (syncObject) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("g()");
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
}
public class SyncObject {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final DualSynch ds = new DualSynch();
new Thread() {
public void run() {
ds.f();
}
}.start();
ds.g();
}
}
线程的本地存储
对于实例变量、静态字段、构成数组对象的元素,线程会共享,造成资源冲突,解决的方式使用ThreadLocal进行包裹。
实例变量示例一
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadLocalNoDemo {
//实例变量
private String str = "abc";
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ThreadLocalNoDemo threadLocalNoDemo = new ThreadLocalNoDemo();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
threadLocalNoDemo.str +=1;
System.out.println(threadLocalNoDemo.str);
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
threadLocalNoDemo.str +="w";
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(threadLocalNoDemo.str);
}).start();
}
}
实例变量示例二
public class ThreadLocalWithDemo {
//采用ThreadLocal包裹的实例变量
ThreadLocal<String> value = new ThreadLocal<String>(){
@Override
protected String initialValue() {
return "abc";
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ThreadLocalWithDemo threadLocalWithDemo = new ThreadLocalWithDemo();
new Thread(()->{
final String s = threadLocalWithDemo.value.get();
threadLocalWithDemo.value.set(s+"1111");
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(threadLocalWithDemo.value.get());
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
final String s = threadLocalWithDemo.value.get();
threadLocalWithDemo.value.set(s+"wwww");
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(threadLocalWithDemo.value.get());
}).start();
}
}
局部变量与方法参数属于线程私有,不会被共享
package com.thinking.in.java.course.chapter21;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadLocalNoDemo2 {
//方法中的参数,属于线程独有的 并不会共享
public void testMethodParam(String str){
String s = "hello";
str+=s;
System.out.println(str);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocalNoDemo2 demo2 = new ThreadLocalNoDemo2();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
demo2.testMethodParam("1111");
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
demo2.testMethodParam("2222");
}).start();
}
}


