基于:Dubbo SPI
使用Wrapper 类对扩展点进行自动包装。Wrapper 类也实现了扩展点接口,但是 Wrapper 不是扩展点的真正实现。它的用途主要是包装真正的扩展点实现。即从 ExtensionLoader 中返回的实际上是 Wrapper 类的实例,Wrapper 持有了实际的扩展点实现类。
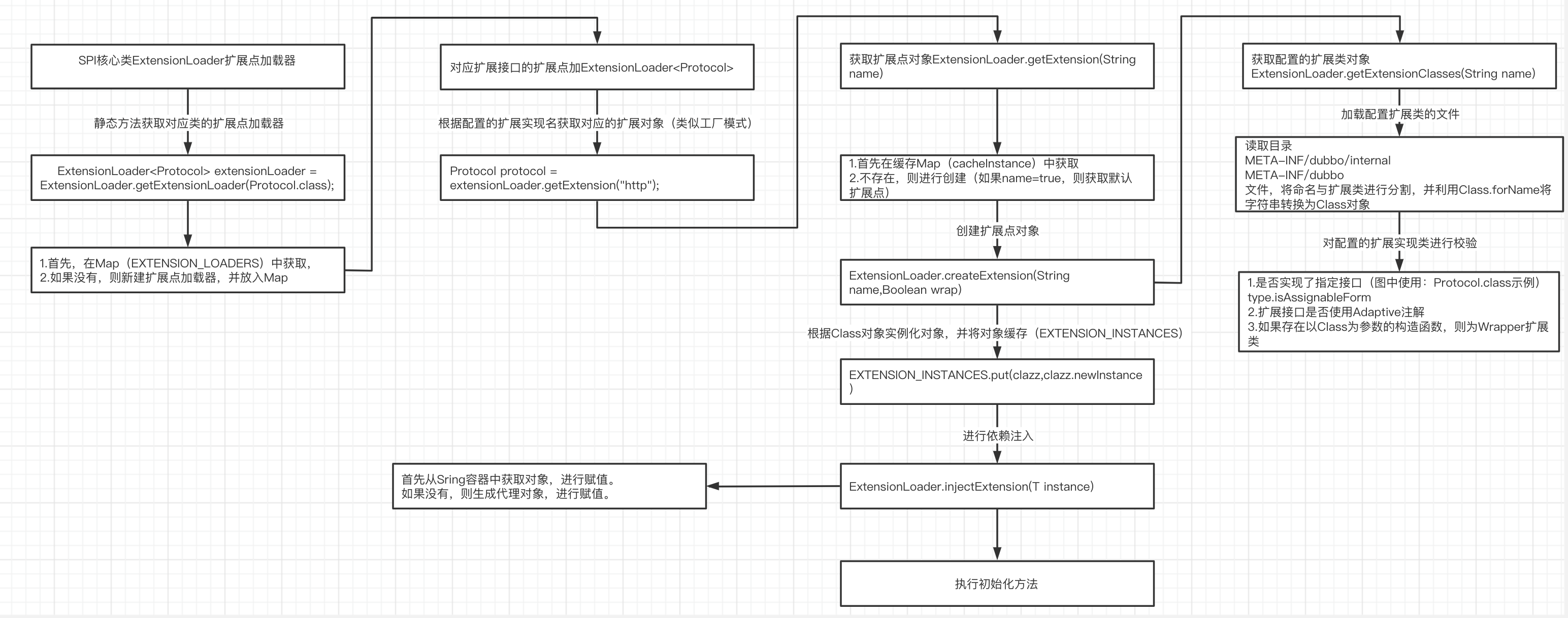
一、加载流程
ExtensionLoader<Protocol> extensionLoader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class);//获取到的实例为Wrapper类型Protocol protocol = extensionLoader.getExtension("http");System.out.println(protocol);
- 入参:扩展点接口Class(例如:Protocol.class)类型,初始化扩展点加载器。
- 首先利用JDK SPI机制加载所有dubbo扩展点加载策略(即开启dubbo spi功能)。ExtensionLoader#loadLoadingStrategies();
- 在构造函数中,利用加载器type记录,扩展点接口Class类型,
- 在构造函数中,初始化扩展点工厂实例(objectFactory)仍然是先。
- 如果是ExtensionFactory.class,则不需要工厂实例
- 如果非ExtensionFactory.class,则先通过步骤1,获取ExtensionFactory.class加载器,并调用getAdaptiveExtension(),获得工厂实例(objectFactory)
- 加载ExtensionFactory类型实现类,并实例化。路径:META-INF/dubbo/internal/org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionFactory
- 根据名称(例如:http),从缓存cachedClasses中获取具体实现类
- 获取SPI注解,在接口(例如:Protocol.class)配置的默认实现类名称
- 加载扩展点接口Class(例如:Protocol.class)类型所有实现类。并缓存至cachedClasses
- 反射实例化、依赖注入
- 生成包装类型,并调用初始化方法
SPI 加载器初始化
public static <T> ExtensionLoader<T> getExtensionLoader(Class<T> type) {//1.非空判断if (type == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type == null");}//2.Class类必须为接口if (!type.isInterface()) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type (" + type + ") is not an interface!");}//3.接口类必须被 @SPI 标记if (!withExtensionAnnotation(type)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Extension type (" + type +") is not an extension, because it is NOT annotated with @" + SPI.class.getSimpleName() + "!");}//4.根据Class,从本地缓存中获取加载器。如果为空初始化加载器,并放入缓存中ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);if (loader == null) {EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);}return loader;}
加载SPI 扩展点
SPI 加载流程