官方文档说明:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/collections/interfaces/list.html
List特点
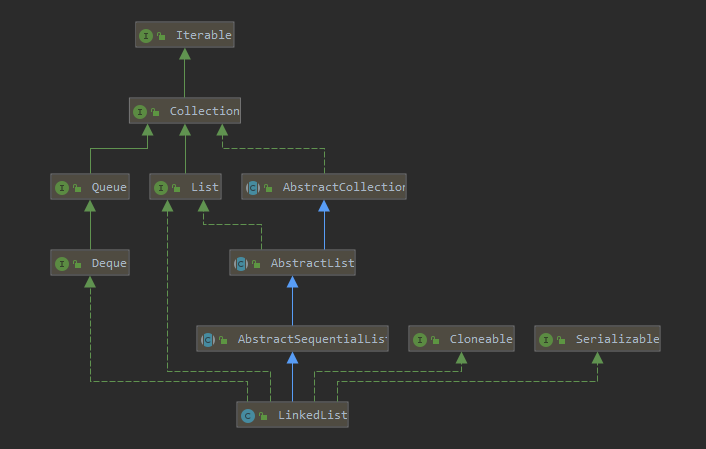
- A List is an ordered Collection (sometimes called a sequence). Lists may contain duplicate elements. In addition to the operations inherited from Collection.
- Two List objects are equal if they contain the same elements in the same order.
The cursor is always between two elements.
包含两种通用的List集合实现
The Java platform contains two general-purpose List implementations. ArrayList, which is usually the better-performing implementation, and LinkedList which offers better performance under certain circumstances.
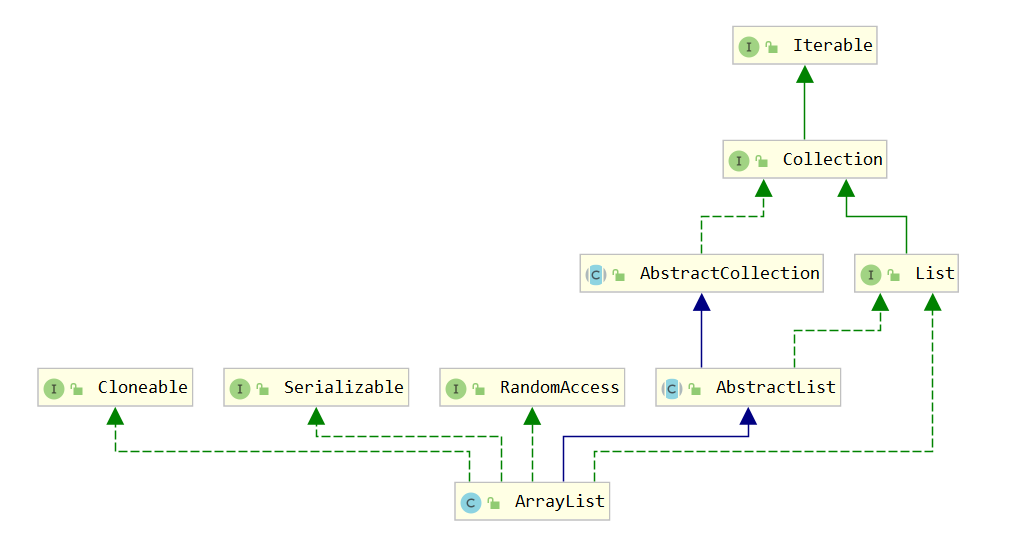
ArrayList
ArrayList底层是采用数组进行存储的,(所以在进行数据的查找操作的时候的效率比LinkedList高很多),在创建ArrayList的时候,如果提前知道大小的话,提前初始化该长度,这样就避免ArrayList数据的迁移,因为要是不声明大小的话,ArrayList默认赋值为16,要是之后容量超过16,就会使用grow函数进行扩增,然后将原来的数据赋值到新的数组里面(增长为原来的1.5倍)。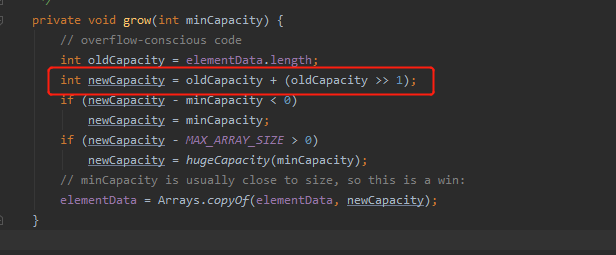
ArrayList所有的方法如下: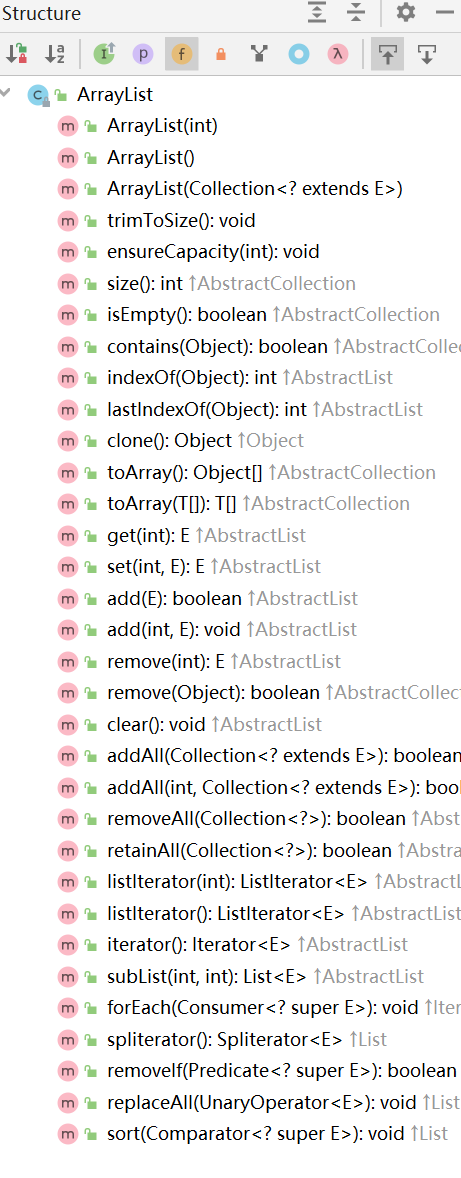
- LinkedList
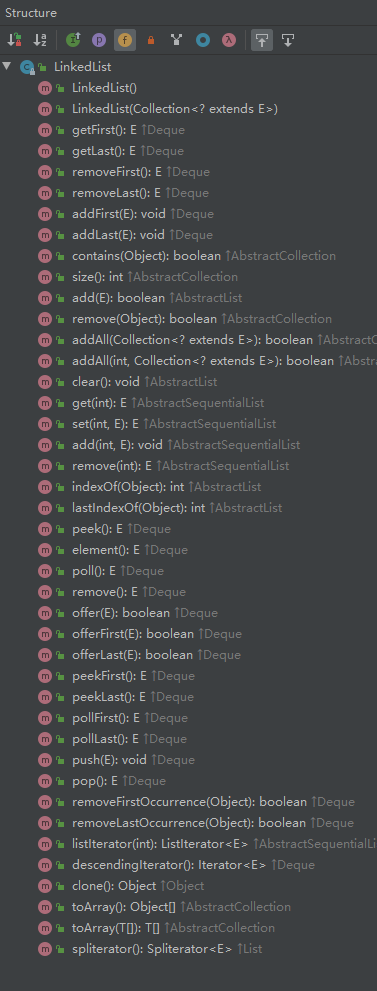
LinkedList的底层实现是双向链表,遍历的速度大大慢于ArrayList,而增加、删除的效率却大大地优于ArrayList,因为LinkedList在进行查找指定元素的时候,都需要从首节点开始,而ArrayList直接通过下表即可获取,但是在进行数据的增加和删除的时候,可以通过修改头尾两个节点的地址就可以完成,而ArrayList还需要将元素的位置进行迁移,从而耗费很多时间。
总结:
ArrayList 和LinkedList使用场景可以看作是数组和链表的使用场景,因为ArrayList底层采用数组,适用于查找操作多、增加删除操作少的场景;LinkedList底层采用链表,适合用于增加、删除多,查找少的场景。