官方说明:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/collections/interfaces/map.html
Map的特点:
- A Map is an object that maps keys to values,each key can map to at most one value.
- A map cannot contain duplicate keys
- Map strengthens the requirements on the equals and hashCode methods so that two Map objects can be compared for logical equality without regard to their implementation types.
- Two Map instances are equal if they represent the same key-value mappings.
包含三种通用的Map集合实现
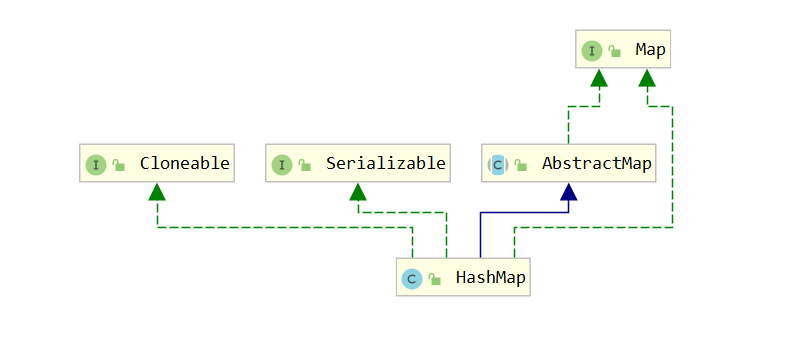
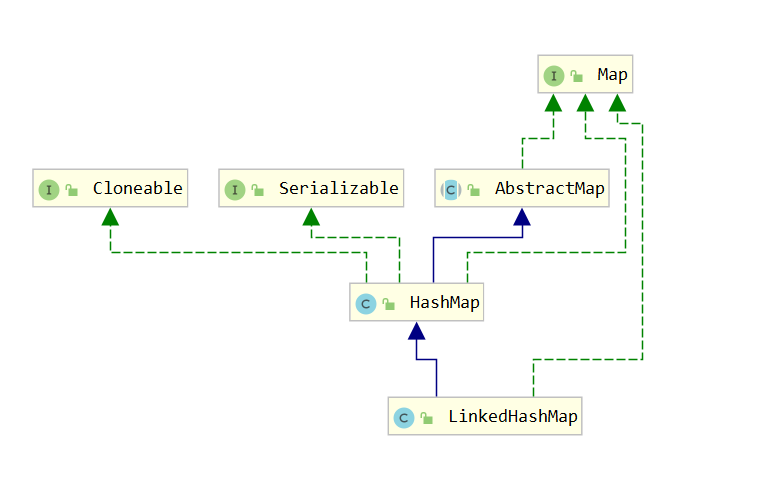
- HashMap
HashMap是基于哈希表实现的,是无序的,同时也是性能最好的,非线程安全。
HashMap所有的方法如下: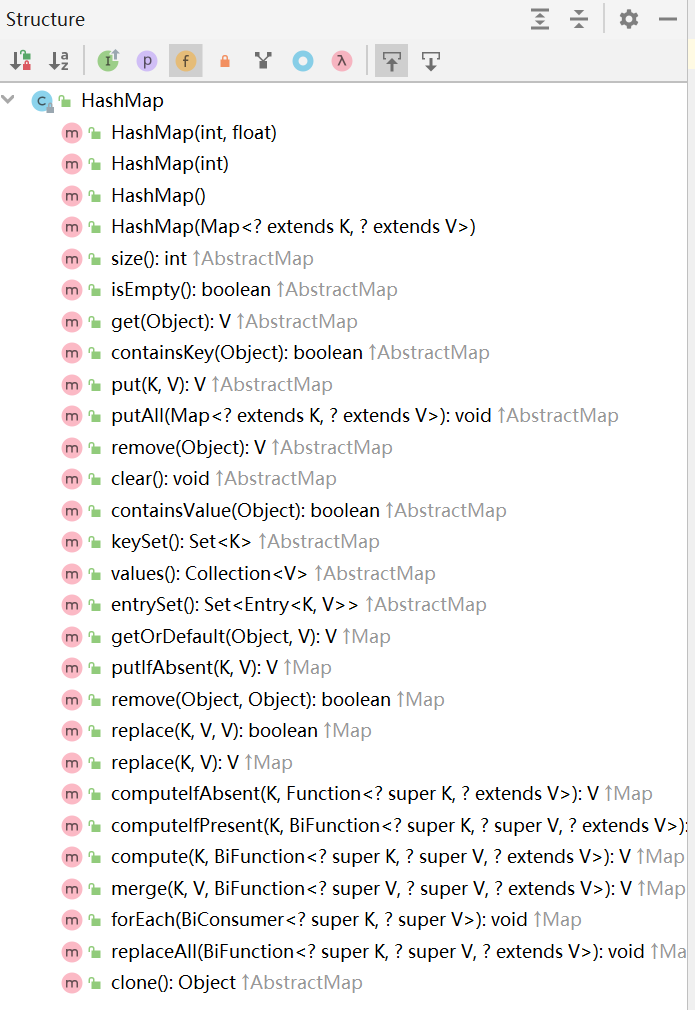
- TreeMap
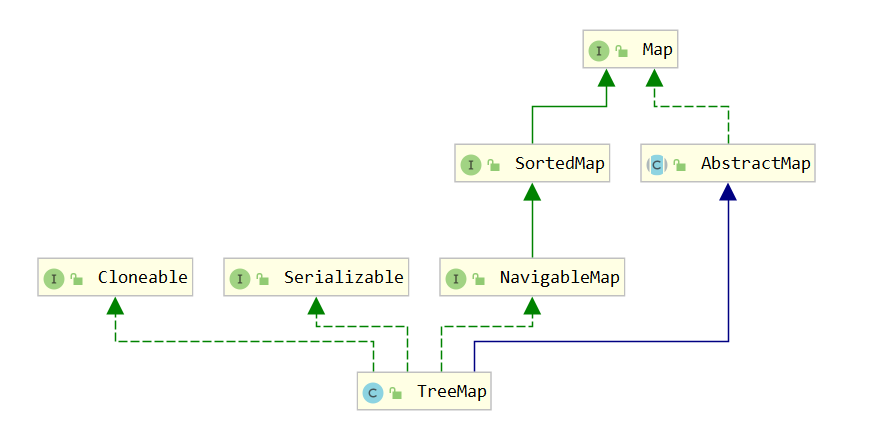
TreeMap基于红黑树来实现的,非线程安全,存储的键值对可以根据Key进行自然排序或者定制排序,当使用自然排序的时候,key的类型需要实现equals() 和 compareTo(),如果使用定制排序,通过查看TreeMap的源码**private final **Comparator<? **super **K> **comparator**;则直接传递一个Comparator 对象给构造器即可,无需实现equals() 和 compareTo()。
TreeMap所有的方法如下: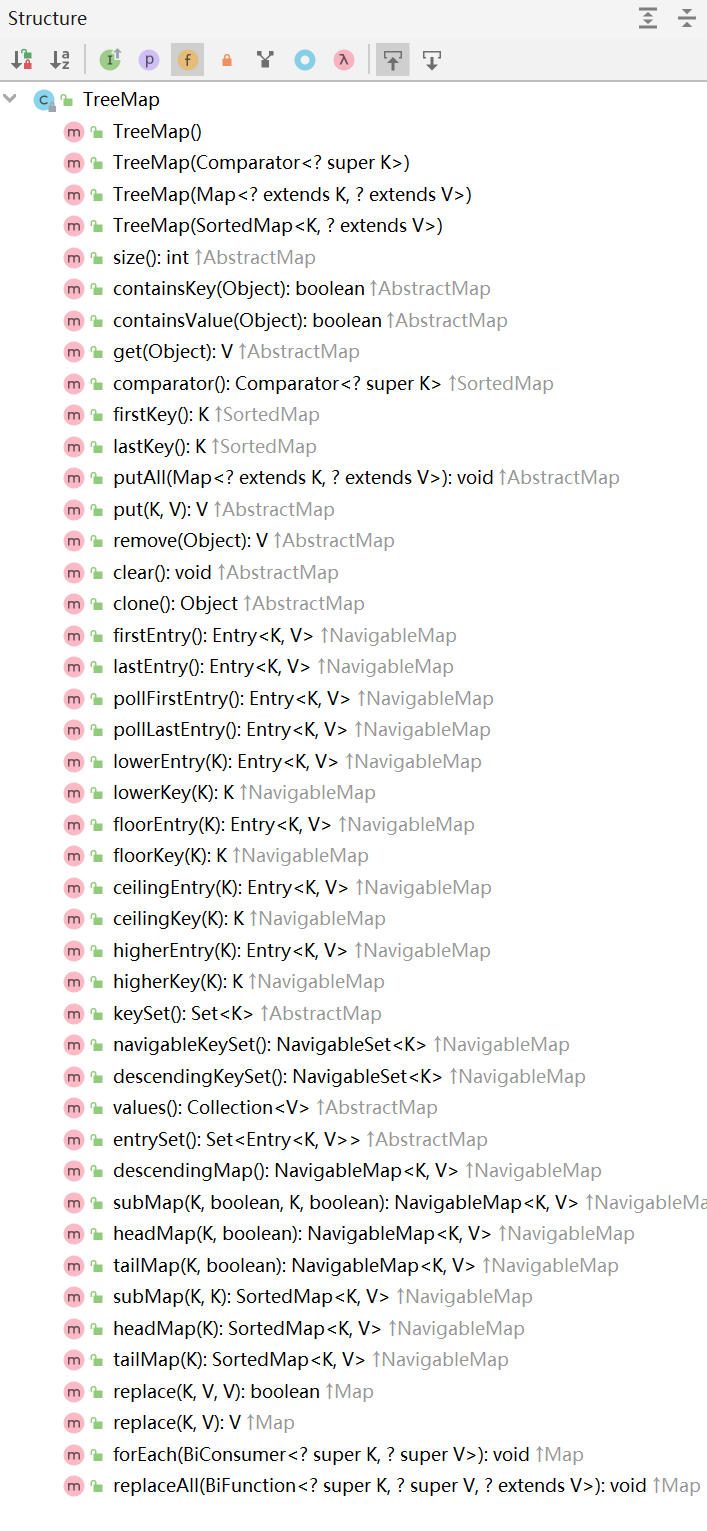
- LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap是非线程安全的,可以按照元素插入的顺序进行排序。
LinkedHashMap所有的方法如下:
总结:
- HashMap:适用于在Map中插入、删除和定位元素,Treemap:适用于按自然顺序或自定义顺序遍历键(key)。
- 建议优先使用HashMap,在一些需要进行排序操作的时候才使用TreeMap。
- HashMap允许Key为null值,但是只能有一个,其他的Map都不允许key为null
扩展案例
案例1:按照部门进行员工对象的分组
案例2:计算各个部门员工的总薪水Map<Department, List<Employee>> byDept = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDepartment));
案例3:将学生按照是否通过进行分组Map<Department, Integer> totalByDept = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getDepartment,Collectors.summingInt(Employee::getSalary)));
案例4:按城市将人分组Map<Boolean, List<Student>> passingFailing = students.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.getGrade()>= PASS_THRESHOLD));
案例5:双重Map,按省和市分组Map<String, List<Person>> peopleByCity= personStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getCity));
Map<String, Map<String, List<Person>>> peopleByStateAndCity= personStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getState,Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getCity)))

