一、AQS概念
AbstractQueuedSynchronized简称AQS,AQS定义了一套多线程访问共享资源的同步器框架,是一个依赖状态state的同步器。具备如下特性:
阻塞等待队列
共享锁/独占锁
公平锁/非公平锁
可重入 - 通过对state进行 +1来实现重入
允许中断
子类可以通过重写以下方法来控制AQS内部的一个state同步变量实现各种功能。
独占式 - 资源互斥,一次只能一个线程获取锁(ReentrantLock)
共享模式 - 资源共享
AQS提供了四个空实现,前两个为独占式,后两个为共享式
//独占式获取锁protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg)//独占式释放锁protected boolean tryRelease(int arg//共享式获取锁,返回值表示获取锁后还剩余的许可数量protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg)//共享式释放锁protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg)
二、设计要点
- 状态:一个被volatile修饰的int变量,已保证可见性,共享资源
- 队列:队列通常是一个等待的集合,大多数以链表的形式实现。队列采用的是悲观锁的思想,表示当前所等待的资源,状态或者条件短时间内可能无法满足。因此,它会将当前线程包装成某种类型的数据结构,扔到一个等待队列中,当一定条件满足后,再从等待队列中取出。
CAS:CAS操作是最轻量的并发处理,采用的是乐观锁的思想,因此常常伴随着自旋,如果发现当前无法成功地执行CAS,则不断重试,直到成功为止,自旋的的表现形式通常是一个死循环
for(;;)。CAS操作保证了同一个时刻,只有一个线程能修改成功,从而保证了线程安全,CAS操作基本是由Unsafe工具类的compareAndSwapXXX来实现的;三、核心实现
状态
state表示共享资源,当state=0,表示无锁,state != 0,表示有线程持有锁,当state > 1时,表示锁重入
private volatile int state;protected final int getState()protected final void setState(int newState)//通过cas进行设置值protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update)
如何查看哪个线程持有锁
//持有锁的线程private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
队列
AQS中,队列的实现是一个双向链表,被称为sync queue,它表示所有等待锁的线程的集合;在AQS中用Node节点来包装线程
static final class Node {/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */static final Node SHARED = new Node();/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode */static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */static final int CANCELLED = 1;/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */static final int SIGNAL = -1;/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */static final int CONDITION = -2;/*** waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should* unconditionally propagate*/static final int PROPAGATE = -3;volatile int waitStatus;volatile Node prev;volatile Node next;volatile Thread thread;Node nextWaiter;final boolean isShared() {return nextWaiter == SHARED;}final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {Node p = prev;if (p == null)throw new NullPointerException();elsereturn p;}Node() {}Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiterthis.nextWaiter = mode;this.thread = thread;}Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Conditionthis.waitStatus = waitStatus;this.thread = thread;}}
Node的属性很多,但是可以分为四类 ```java // 节点所代表的线程 volatile Thread thread;
// 双向链表,每个节点需要保存自己的前驱节点和后继节点的引用 volatile Node prev; volatile Node next;
// 线程所处的等待锁的状态,初始化时,该值为0,表示当前没有现成获得锁 volatile int waitStatus; //表示超时或者中断,节点被设置为取消状态,被设置为取消状态的节点不应该再去竞争锁,他应该是一直 //被取消状态,不能变为其他状态, static final int CANCELLED = 1; //后继节点的线程处于等待状态,当前节点的线程释放了同步状态或者取消,会通知后继节点去获取锁 //表示后继结点在等待当前结点唤醒。后继结点入队时,会将前继结点的状态更新为SIGNAL static final int SIGNAL = -1; static final int CONDITION = -2; static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
// 该属性用于条件队列或者共享锁 Node nextWaiter;
waitStatus - 表示当前node所代表的线程等待锁的状态<br />在独占锁模式下,我们只需关注CANCELLED SIGNAL两种状态即可<br />nextWaiter属性,它在独占模式下永远为null,仅仅起到一个标记作用,没有任何意义<a name="mPDdk"></a>### sys queue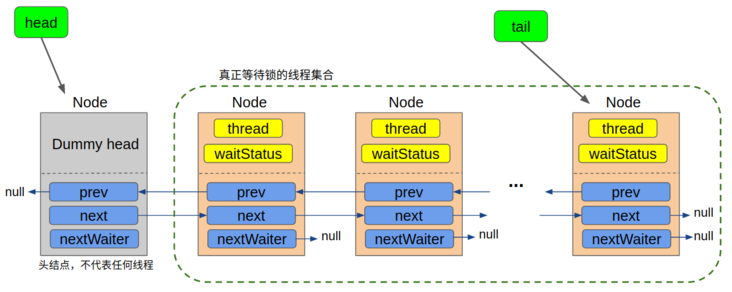<br />AQS中的队列是一个CLH队列,**它的head节点永远是一个哑节点**(new Node()的实例对象),不持有任何线程,因此head所指向的node的thread属性永远为null,只有从次头节点往后的所有节点才代表了所有等待锁的线程。也就是说,在当前线程没有抢到锁被包装成Node扔到队列中时,**即使队列是空的,它也会排在第二个。**- `thread`:表示当前Node所代表的线程- `waitStatus`:表示节点所处的等待状态,共享锁模式下只需关注三种状态:`SIGNAL` `CANCELLED` `初始态(0)`- `prev` `next`:节点的前驱和后继- `nextWaiter`:进作为标记,值永远为null,表示当前处于独占锁模式<a name="tlqud"></a>## CAS操作都是通过Unsafe类的compareAndSwapXXX方法实现```javaprotected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);}private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update);}private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);}private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node, int expect,int update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset, expect, update);}private static final boolean compareAndSetNext(Node node, Node expect, Node update) {return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(node, nextOffset, expect, update);}

