一、拷贝的引入
Ⅰ、引用拷贝
创建一个指向对象的引用变量的拷贝:
@Datapublic class Teacher {private String name;private int age;public Teacher(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}}
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {Teacher teacher_1 = new Teacher("greamrod", 27);Teacher teacher_2 = teacher_1;System.out.println("teacher_1 = " + teacher_1);System.out.println("teacher_2 = " + teacher_2);System.out.println("teacher_1 == teacher_2 --> " + (teacher_1 == teacher_2));}}
输出如下:
teacher_1 = Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27)teacher_2 = Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27)teacher_1 == teacher_2 --> true
由输出结果teacher_1 == teacher_2 --> true可以看出,它们的地址值是相同的,那么它们肯定是同一个对象。teacher_1和teacher_2的只是引用而已,他们都指向了一个相同的对象new Teacher("greamrod", 27)。 这就叫做引用拷贝。
Ⅱ、对象拷贝
使用原型模式,创建对象本身的一个副本:
@Datapublic class Teacher implements Cloneable {private String name;private int age;public Teacher(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public Teacher clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {Teacher object = (Teacher) super.clone();return object;}}
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {Teacher teacher_1 = new Teacher("greamrod", 27);Teacher teacher_2 = teacher_1.clone();System.out.println("teacher_1 = " + teacher_1);System.out.println("teacher_2 = " + teacher_2);System.out.println("teacher_1 == teacher_2 --> " + (teacher_1 == teacher_2));}}
输入如下:
teacher_1 = Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27)teacher_2 = Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27)teacher_1 == teacher_2 --> false
由输出结果teacher_1 == teacher_2 --> false可以看出,它们的地址是不同,也就是说创建了新对象, 而不是把原对象的地址赋给了一个新的引用变量,这就叫做对象拷贝。
二、浅拷贝
概念:
- ①:对于数据类型是基本数据类型的成员变量:浅拷贝会直接进行值传递,也就是将该属性值复制一份给新的对象。
- ②:对于数据类型是引用数据类型的成员变量:例如成员变量是某个数组、某个类的对象等,那么浅拷贝会进行引用传递,也就是只是将该成员变量的引用值(内存地址)复制一份给新的对象。因为实际上两个对象的各自成员变量都指向同一个实例。在这种情况下,在一个对象中修改自身成员变量,会影响到另一个对象的该成员变量值。
实现方式:
- ①:使用默认
cloen()方法来实现深拷贝。
@Datapublic class Teacher {private String name;private int age;public Teacher(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}}
@Datapublic class Student implements Cloneable {private String name;private int age;private Teacher teacher;public Student(String name, int age, Teacher teacher) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.teacher = teacher;}public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {Object object = super.clone();return object;}}
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {Teacher teacher = new Teacher("greamrod", 27);Student student_1 = new Student("jack", 10, teacher);Student student_2 = (Student) student_1.clone();System.out.println("student_1 = " + student_1);System.out.println("student_2 = " + student_2);System.out.println("student_1 == student_2 --> " + (student_1 == student_2));System.out.println("\n-------------修改老师的信息后-------------");teacher.setName("peter");teacher.setAge(50);System.out.println("student_1 = " + student_1);System.out.println("student_2 = " + student_2);System.out.println("student_1 == student_2 --> " + (student_1 == student_2));}}
输出如下:
student_1 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27))student_2 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27))student_1 == student_2 --> false-------------修改老师的信息后-------------student_1 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=peter, age=50))student_2 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=peter, age=50))student_1 == student_2 --> false
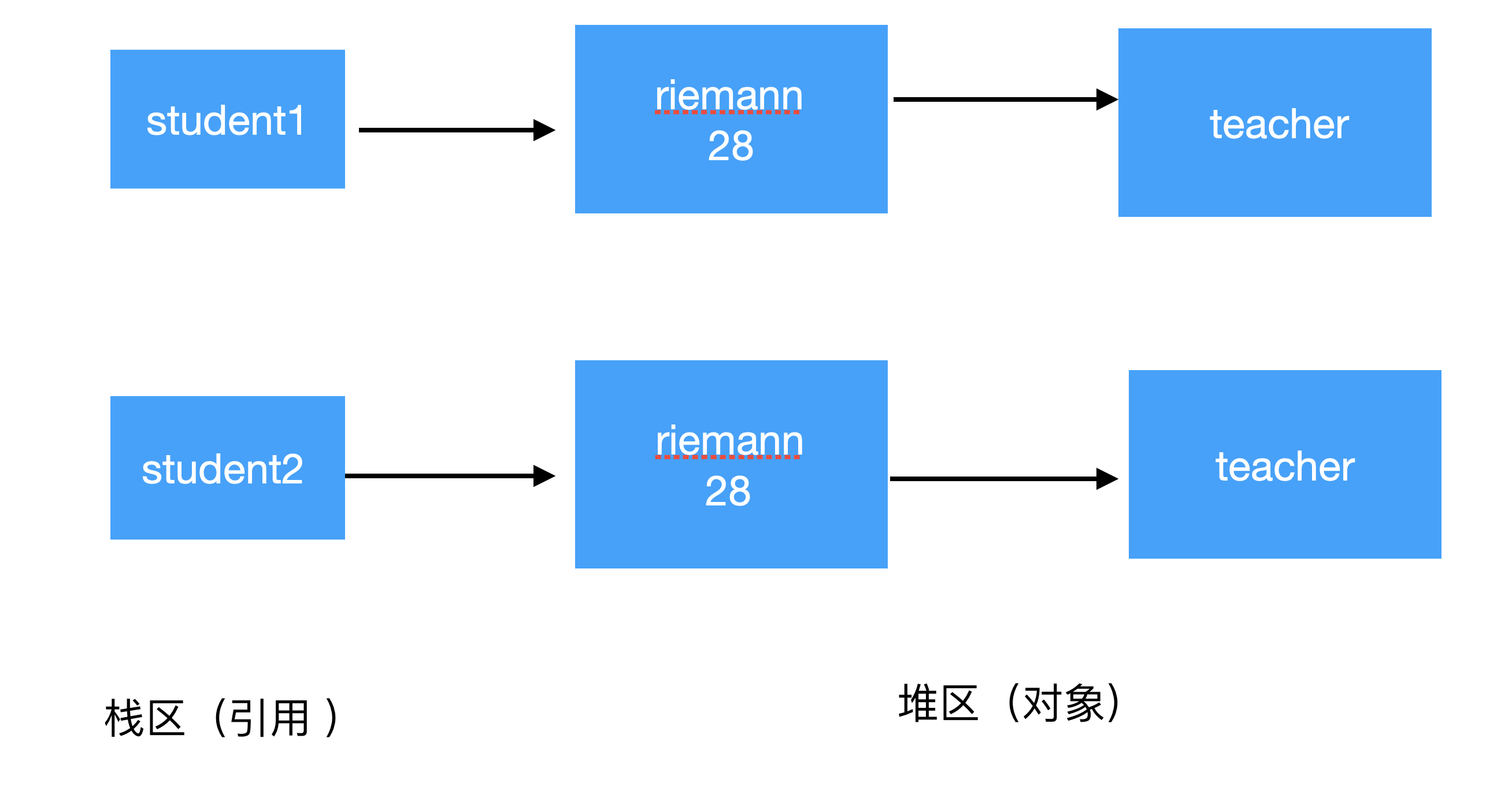
结果分析,两个引用student_1和student2分别指向,两个不同Student对象。但两个Student对象的teacher成员变量的引用,指向的是同一个对象,所以说明是浅拷贝。
三、深拷贝
概念:
- ①:复制对象的所有基本数据类型的成员变量值。
- ②:为所有引用数据类型的成员变量申请存储空间,并复制每个引用数据类型成员变量所指向的对象,直到该对象可达的所有对象。也就是说,对象进行深拷贝,要对整个对象进行拷贝。
实现方式:
- ①:重写
cloen()方法来实现深拷贝,对象中所有引用数据类型都要实现Cloneable接口。 - ②:通过对象序列化、反序列化实现深拷贝。
Ⅰ、重写cloen()方法来实现深拷贝
代码如下:
@Datapublic class Teacher implements Cloneable {private String name;private int age;public Teacher(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Overrideprotected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {return super.clone();}}
@Datapublic class Student implements Cloneable {private String name;private int age;private Teacher teacher;public Student(String name, int age, Teacher teacher) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.teacher = teacher;}public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {Student student = (Student) super.clone();Teacher teacher = (Teacher) student.teacher.clone();student.setTeacher(teacher);return student;}}
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {Teacher teacher = new Teacher("greamrod", 27);Student student_1 = new Student("jack", 10, teacher);Student student_2 = (Student) student_1.clone();System.out.println("student_1 = " + student_1);System.out.println("student_2 = " + student_2);System.out.println("student_1 == student_2 --> " + (student_1 == student_2));System.out.println("\n-------------修改老师的信息后-------------");teacher.setName("peter");teacher.setAge(50);System.out.println("student_1 = " + student_1);System.out.println("student_2 = " + student_2);System.out.println("student_1 == student_2 --> " + (student_1 == student_2));}}
输出如下:
student_1 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27))student_2 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27))student_1 == student_2 --> false-------------修改老师的信息后-------------student_1 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=peter, age=50))student_2 = Student(name=jack, age=10, teacher=Teacher(name=greamrod, age=27))student_1 == student_2 --> false
两个引用student_1和student_2分别指向,两个不同Student对象。但两个Student对象的teacher成员变量的引用,指向两个不同Teacher对象。修改student_1对象的teacher成员变量,不会影响student_2对象的teacher成员变量,所以说是深拷贝。