1.链式操作
var sched = {wakeup: function(){console.log('Running');return this;},morning: function(){console.log('Go Shopping');return this;},noon: function(){console.log('Having a reset');return this;},afternoon: function(){console.log('Studying');return this;},evening: function(){console.log('walking');return this;},night: function(){console.log('Sleeping');return this;}}sched.wakeup().morning().noon().afternoon().evening().night();
2.obj[‘xxx’]/ obj.xxx
最早的Js引擎 解析obj[‘xxx’],
会将obj.name => obj[‘name’]
var myLang = {No1: 'HTML',No2: 'CSS',No3: 'JavaScript',myStudyLang: function(num){console.log(this['No' + num]);}}myLang.myStudyingLang(3);
3.对象枚举, 遍历
// 数组var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];// for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){// console.log(arr[i]);// }for(var i in arr){ // 同上console.log(i);}// 对象var car = {brand: 'Benz',color: 'red',displacement: '3.0',lang: '5.0',width: '2.5'}for(var key in car){// console.log(car.key); // undefined// js引擎: car.key => car['key'] => undefinedconsole.log(car[key]); // 正确输出}
4. hasOwnProperty
- Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty()
方法会返回一个布尔值,指示对象自身属性中是否有指定的属性(也就是是否有指定的键).
- hasOwnProperty 是JavaScript中唯一一个处理属性并且不会遍历的原型链的方法 ```javascript var obj = { name: ‘xiaoye’, age: ‘32’ }
var res = obj.hasOwnProperty(‘name’); // true
// 枚举自己本身的属性 function Car(){ this.brand = ‘Benz’; this.color = ‘red’; this.displacement = ‘3.0’; }
Car.prototype = { lang: ‘5.0’, width: ‘2.5’ }
Object.prototype.name = ‘Object’;
var car = new Car(); console.log(car);
for(var key in car){ if(car.hasOwnProperty(key)){ // 只有是自身属性才进行输出 console.log(car[key]); } }
<a name="axLUj"></a># 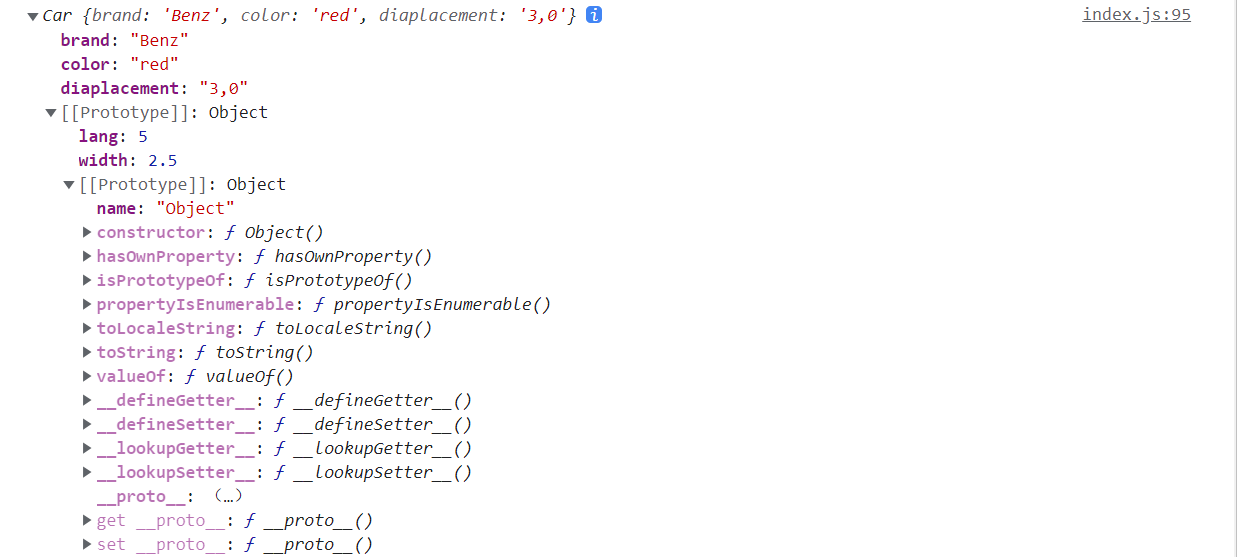5. str in xxx```javascriptvar car = {brand: 'Benz',color: 'red'}console.log(color in car); // 报错console.log('color' in car); // true// 原型上的属性也会查询到function Car(){this.brand = 'Benz';this.color = 'red';}Car.prototype.displacement = '3.0';var car = new Car();console.log('displacement' in car); // true
6. instanceof
instanceof 用于检测构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在某个实例对象的原型链上.
function Car(){}var car = new Car();function Person(){}var p = new Person();console.log(car instanceof Car); // trueconsole.log(car instanceof Object);// trueconsole.log([] instanceof Object); // trueconsole.log([] instanceof Array); // trueconsole.log({} instanceof Object); // true
7. 判断对象的原型
var a = [];// 方法1console.log(a.constructor);// f Array()// 方法2 instanceof// 方法3 Object.prototype.toString.call()var a = [] || {};var str = Object.prototype.toString.call(a);if(str === '[object Array]'){console.log('是数组');}else{console.log('不是数组');}
//var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];// Array.prototype.toString() 返回一个字符串,表示指定的元素和数组console.log(arr.toString()); // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5// Object.prototype.toString() 返回一个表示该对象的字符串console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arr)); // '[object Array]'// 每个对象都有toString()方法,当该对象被表示为一个文本值时,或者一个对象以预期的字符串方式引用时自动调用.// 默认情况下,toString()方法被每个Object对象继承,如果此方法在自定义中未被覆盖,toString()返回 "[object type]", 其中type代表对象的类型
var toString = Object.prototype.toString;toString.call(new Date); // [object Date]toString.call(new String);// [object String]toString.call(new Math);// [object Math]// Since JavaScript 1.8.5toString.call(undefined);// [object undefined]toString.call(null); // [object null]
8. this
- 全局this => window
- 预编译函数this => window
- apply/call 改变this指向
- 构造函数的this指向实例化对象 ```javascript function test(b){ this.d = 3; var a = 1; function c(){} }
test(123); console.log(d); // 3 console.log(window.d); // 3 console.log(this.d) // 3
// AO = { // arguments: [123] // this: window // b: 123 // a: undefined // c: function c(){} // }
```javascriptfunction Test(){this.name = '123';}var test = new Test();// GO = {// Test: function Test(){}// test: undefined => {// __proto__: Test.prototype,// name: '123'// }// }//// AO = {// this: window => {// __proto__: Test.prototype,// name: '123'// }// }//
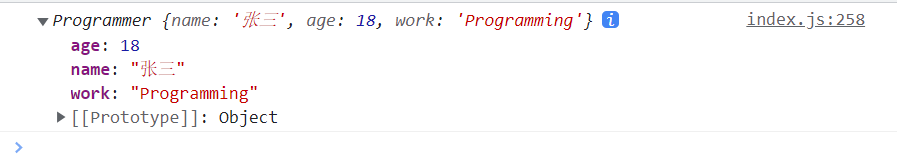
function Person(){this.name: '张三';this.age: 18}function Programmer(){Person.apply(this);this.work = 'Programming'}var p = new Person();console.log(p);
9. callee / caller
1. callee
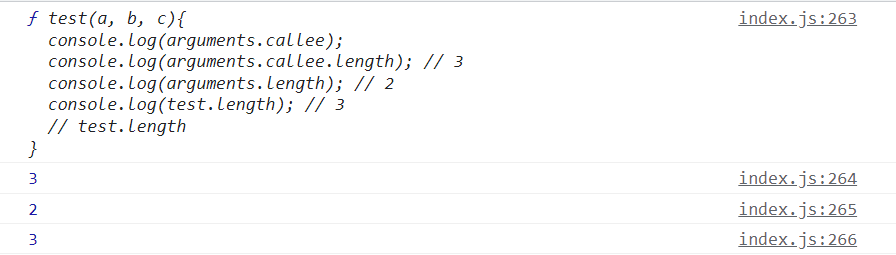
// arguments.callee 属性包含当前正在执行的函数// callee 是arguments 对象的一个属性.它可以用于引用该函数的函数体内当前正在执行的函数.// 这在函数的名称未知时很有用.function test(a, b, c){console.log(arguments.callee);console.log(arguments.callee.length);console.log(arguments.length);console.log(test.length);}test(1, 2);
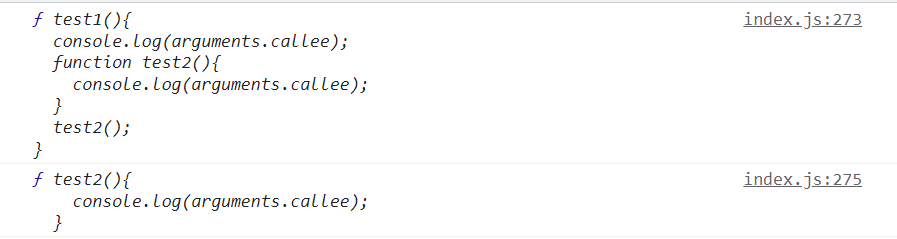
function test1(){console.log(arguments.callee);function test2(){console.log(arguments.callee);}test2();}test1();
function sum(n){if(n <= 1){return 1;}return n + sum(n - 1)}var res = sum(10);console.log(10); // 55var sum = (function(){if(n <= 1){return 1}return n + arguments.callee(n - 1);})(100)console.log(sum);
2. caller 返回当前被调用函数的函数引用
function test1(){test2();}function test2(){console.log(test2.caller);}test1();
10. 笔试题
- 案例1 ```javascript function foo(){ bar.apply(null, arguments); }
function bar(){ console.log(arguments); } // bar() => bar.call(arguments) => bar(arguments) foo(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
2. 案例2```javascript// typeof 返回多少种类型?// typeof 总是返回字符串// String, undefined, Number, null, Boolean, object, functiontypeof Math.LN2 === 'number';typeof Infinity === 'number';typeof NaN === 'number'; // 尽管它是 "Not-A-Number" (非数值) 的缩写typeof Number(1) === 'number'; // Number 会尝试把参数解析成数值typeof 42n === 'bigint';typeof `template literal` === 'string';typeof '1' === 'string'; // 注意内容为数字的字符串仍是字符串typeof (typeof 1) === 'string'; // typeof 总是返回一个字符串typeof String(1) === 'string'; // String 将任意值转换为字符串,比 toString 更安全typeof Boolean(1) === 'boolean'; // Boolean() 会基于参数是真值还是虚值进行转换typeof !!(1) === 'boolean'; // 两次调用 ! (逻辑非) 操作符相当于 Boolean()// 使用 Array.isArray 或者 Object.prototype.toString.call// 区分数组和普通对象typeof [1, 2, 4] === 'object';// 下面的例子令人迷惑,非常危险,没有用处。避免使用它们。typeof new Boolean(true) === 'object';typeof new Number(1) === 'object';typeof new String('abc') === 'object';
案例3
// 实参和形参是相互映射的关系,你改我也改function b(x, y, a){a = 10;alert(arguments[2]); // 10}b(1, 2, 3);
案例4
var f = (function f(){return '1';},function g(){return 2;});console.log(typeof f); // funtion//--------------------------------------------------------------var f = (function f(){return '1';},function g(){return 2;})();console.log(typeof(f)); // number
案例5 ```javascript console.log(undefined == null); // true console.log(undefined === null);// false console.log(isNaN(‘100’)); // false isNaN会进行对非数字类型,Number的隐式类型转换 // Number()类型转换 Number(‘1’) === 1 Number(‘1a’) => NaN Number(‘’) === 0 Number(null) === 0 Number(‘ ‘) === 0 Number(undefined) === NaN
console.log(parseInt(‘1a’)); // false parseInt(‘1a’) => 会转换到非数字结束为止
6. 案例6```javascriptfunction isNaN(num){var res = Number(num);if(res == NaN){return true;} else{return false;}}console.log(isNaN('ABC')); // false 因为NaN不等于任何值,包括他自己//function isNaN1(num){var res = Number(num) + ''; // 将Number(num) 出来的值隐式转换为字符串的'NaN'if(res == 'NaN'){return true;} else{return false;}}console.log(isNaN1('ABC')); // trueconsole.log(isNaN1('123')); // false
案例7
{} == {} // false 因为引用值对比的是地址 两个引用值存储在不同空间// 让他们相等的办法var obj = {}obj1 = obj;console.log(obj1 == obj) // true
案例8
var a = '1';function test(){var a = '2';this.a = '3';console.log(a);}test(); // 2new test(); // 2 // this 指向了全局console.log(a); // 3
案例9
var a = 5;function test(){a = 0;console.log(a);console.log(this.a);var a;console.log(a);}test(); // 0 5 0new test(); // 0 undefined 0