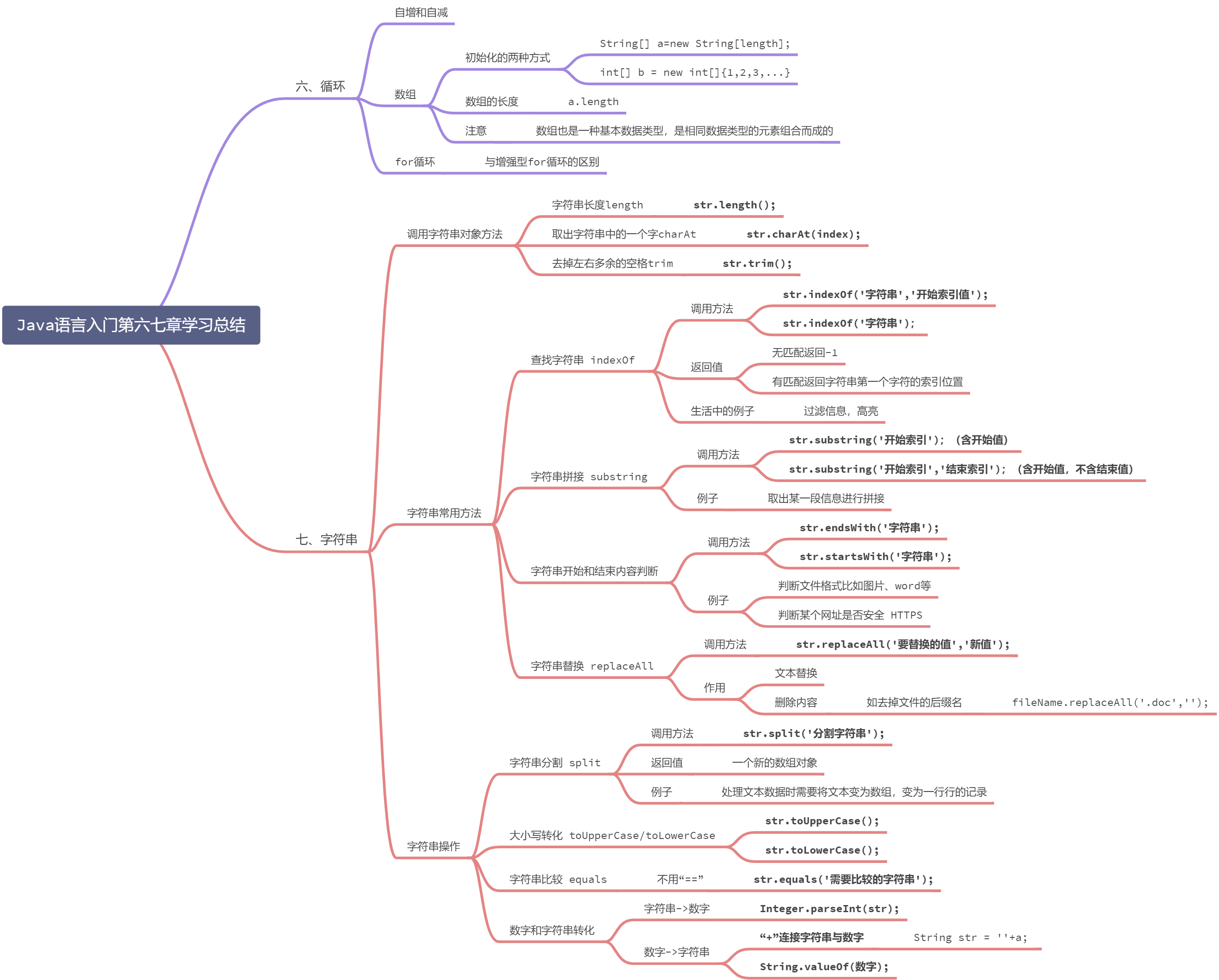
一些需要注意的点
数组
- 数组有两种初始化的方式
String[] a=new String[length]; //为数组开辟length长度的空间int[] b = new int[]{1,2,3,...};//一定要确定数组元素和长度
for循环
- 增强型for循环的格式 ```java for(元素的数据类型 变量 : Collection集合or数组){
}
- 用法1. 遍历数组```javaint[] tables = new int[]{11,12,13};for(int item : tables){//变量item代表被遍历到的数组元素System.out.println(item);}//等同于for(int i=0;i < tables.length;i++){String item = tables[i];System.out.println(item);}
- 遍历集合
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>();coll.add("a1");coll.add("a2");coll.add("a3");coll.add("a4");for(String str : coll){//变量Str代表被遍历到的集合元素System.out.println(str);}
- 字符串操作的例子
- 我的代码(有问题的代码) ```java
public class Test94 {
public static void main(String[] args) { String str = “姓名|英文名称|年龄|性别\n张三|Zhang San|20|男\n李四|Li Si|18|男\n小花|xiaohua|18|女”;
String[] infos = eachStudent(str);System.out.println("名称:"+infos[0]+" 英文名称:"+infos[1].toUpperCase()+" 年龄:"+infos[2]+" 性别:"+infos[3]);
} //没有判断是否是女生,不符合需求 public static String[] eachStudent(String t){
String[] str = t.split("\n");String[] lines = new String[6];//这里我随便开辟了空间for (int i = 0;i<=str.length-1 ;i++ ){lines = str[i].split("\\|");}return lines;//由于return语句放在了for循环外面,所以返回的是最后一条数据,前面的数据都被覆盖掉了
}
}
2. 标准代码```javapublic class Test94 {public static void main(String[] args) {String text = "姓名|英文名称|年龄|性别\n张三|Zhang San|20|男\n李四|Li Si|18|男\n小花|xiaohua|18|女";String[] infos = eachStudent(text);System.out.println("名称:" + infos[0] + " 英文名称:" + infos[1].toUpperCase() + " 年龄:" + infos[2] + " 性别:" + infos[3]);}public static String[] eachStudent(String text) {// 使用 split 进行换行符的分隔,得到一个新的数组对象String[] data = text.split("\n");// 忽略第一行标题数据,所以我们把 i 设为1for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++) {// 使用 \\| 进行字符串分隔,得到一个新数组对象String[] lines = data[i].split("\\|");if (lines[3].equals("女")) {return lines;}}return null;}}
一些反思
String不可变StringBuffer和StringBuilder可变2. 线程安全
String的不可变性天生具备线程安全StringBuffer不是线程安全的StringBuilder是线程安全的,内部使用synchronized进行同步String Pool - 字符串常量池
String Pool保存着所有字符串字面量, 这些字面量在编译时期就确定。intern()方法
当一个字符串调用此方法时,如果
String Pool中已经存在一个字符串和该字符串相等,那么就会返回String Pool中字符串的引用;否则,就会在String Pool中添加一个新的字符串,并返回这个字符串的引用。//s1,s2采用new String()的方式新建了两个不同的字符串//而s3,s4是通过s1.intern()取得同一个字符串引用String s1 = new String("aaa");String s2 = new String("aaa");System.out.println(s1 == s2); // falseString s3 = s1.intern();String s4 = s1.intern();System.out.println(s3 == s4); // true
如果采用字面量的形式创建字符串,会自动地将字符串放入
String Pool中。String s5 = "bbb";String s6 = "bbb";System.out.println(s5 == s6); // true
new String(“abc”)
使用这种方式一共会创建两个字符串对象,(前提是
String Pool中还没有"abc"字符串对象)" abc"属于字符串面量,编译时期会在String Pool中创建一个字符串对象,指向这个字符串面量- 而使用
new的方式会在堆中创建一个字符串对象