1. 概览
大多数的 JavaScript 转译器(transpiler) 都比 Typescript 简单 因为它们几乎没提供代码分析的方法。
典型的 JavaScript 转换器 只有以下流程
源码 ~~ 扫描器 ~~ Tokens ~~ 解析器 ~~ AST ~~ 发射器 ~ JavaScript
上述架构确实对于 简化 Typescript生成 Javascript 的理解有帮助 但缺少了一个关键功能 即 Typescript 的语义系统。 为了协助(检查器)类型检查。 绑定器将源码的各部分连接成一个相关的类型系统, 供检查器使用。
绑定器的主要职责是创建符号(Symbol)
2. 符号
此时又引入一个新的概念 那就是符号。 我们先看下官方的解析 符号将AST的声明节点 与 其他声明连接到相同的实体上。 符号是语义系统的基本构造块。 符号的构造器定义在 core.ts
(绑定器实际上通过 objectAllocator.getSymbolConstructor 来获取构造器)
function Symbol(this: Symbol, flags: SymbolFlags, name: string) {this.flags = flags;this.name = name;this.declarations = undefined;}
我们先看 对于 Symbol 的定义
export interface Symbol {flags: SymbolFlags; // Symbol flagsname: string; // Name of symboldeclarations?: Declaration[]; // Declarations associated with this symbolvalueDeclaration?: Declaration; // First value declaration of the symbolmembers?: SymbolTable; // Class, interface or literal instance membersexports?: SymbolTable; // Module exportsglobalExports?: SymbolTable; // Conditional global UMD exports/* @internal */ id?: number; // Unique id (used to look up SymbolLinks)/* @internal */ mergeId?: number; // Merge id (used to look up merged symbol)/* @internal */ parent?: Symbol; // Parent symbol/* @internal */ exportSymbol?: Symbol; // Exported symbol associated with this symbol/* @internal */ constEnumOnlyModule?: boolean; // True if module contains only const enums or other modules with only const enums/* @internal */ isReferenced?: boolean; // True if the symbol is referenced elsewhere/* @internal */ isReplaceableByMethod?: boolean; // Can this Javascript class property be replaced by a method symbol?/* @internal */ isAssigned?: boolean; // True if the symbol is a parameter with assignments}
其次 还有 SymbolFlags 的定义 符号标志是个标志枚举,用于识别额外的符号类别(例如:变量作用域标志 FunctionScopedVariable 或 BlockScopedVariable 等)
export const enum SymbolFlags {None = 0,FunctionScopedVariable = 1 << 0, // Variable (var) or parameterBlockScopedVariable = 1 << 1, // A block-scoped variable (let or const)Property = 1 << 2, // Property or enum memberEnumMember = 1 << 3, // Enum memberFunction = 1 << 4, // FunctionClass = 1 << 5, // ClassInterface = 1 << 6, // InterfaceConstEnum = 1 << 7, // Const enumRegularEnum = 1 << 8, // EnumValueModule = 1 << 9, // Instantiated moduleNamespaceModule = 1 << 10, // Uninstantiated moduleTypeLiteral = 1 << 11, // Type Literal or mapped typeObjectLiteral = 1 << 12, // Object LiteralMethod = 1 << 13, // MethodConstructor = 1 << 14, // ConstructorGetAccessor = 1 << 15, // Get accessorSetAccessor = 1 << 16, // Set accessorSignature = 1 << 17, // Call, construct, or index signatureTypeParameter = 1 << 18, // Type parameterTypeAlias = 1 << 19, // Type aliasExportValue = 1 << 20, // Exported value marker (see comment in declareModuleMember in binder)ExportType = 1 << 21, // Exported type marker (see comment in declareModuleMember in binder)ExportNamespace = 1 << 22, // Exported namespace marker (see comment in declareModuleMember in binder)Alias = 1 << 23, // An alias for another symbol (see comment in isAliasSymbolDeclaration in checker)Prototype = 1 << 24, // Prototype property (no source representation)ExportStar = 1 << 25, // Export * declarationOptional = 1 << 26, // Optional propertyTransient = 1 << 27, // Transient symbol (created during type check)Enum = RegularEnum | ConstEnum,Variable = FunctionScopedVariable | BlockScopedVariable,Value = Variable | Property | EnumMember | Function | Class | Enum | ValueModule | Method | GetAccessor | SetAccessor,Type = Class | Interface | Enum | EnumMember | TypeLiteral | ObjectLiteral | TypeParameter | TypeAlias,Namespace = ValueModule | NamespaceModule | Enum,Module = ValueModule | NamespaceModule,Accessor = GetAccessor | SetAccessor,// Variables can be redeclared, but can not redeclare a block-scoped declaration with the// same name, or any other value that is not a variable, e.g. ValueModule or ClassFunctionScopedVariableExcludes = Value & ~FunctionScopedVariable,// Block-scoped declarations are not allowed to be re-declared// they can not merge with anything in the value spaceBlockScopedVariableExcludes = Value,ParameterExcludes = Value,PropertyExcludes = None,EnumMemberExcludes = Value | Type,FunctionExcludes = Value & ~(Function | ValueModule),ClassExcludes = (Value | Type) & ~(ValueModule | Interface), // class-interface mergability done in checker.tsInterfaceExcludes = Type & ~(Interface | Class),RegularEnumExcludes = (Value | Type) & ~(RegularEnum | ValueModule), // regular enums merge only with regular enums and modulesConstEnumExcludes = (Value | Type) & ~ConstEnum, // const enums merge only with const enumsValueModuleExcludes = Value & ~(Function | Class | RegularEnum | ValueModule),NamespaceModuleExcludes = 0,MethodExcludes = Value & ~Method,GetAccessorExcludes = Value & ~SetAccessor,SetAccessorExcludes = Value & ~GetAccessor,TypeParameterExcludes = Type & ~TypeParameter,TypeAliasExcludes = Type,AliasExcludes = Alias,ModuleMember = Variable | Function | Class | Interface | Enum | Module | TypeAlias | Alias,ExportHasLocal = Function | Class | Enum | ValueModule,HasExports = Class | Enum | Module,HasMembers = Class | Interface | TypeLiteral | ObjectLiteral,BlockScoped = BlockScopedVariable | Class | Enum,PropertyOrAccessor = Property | Accessor,Export = ExportNamespace | ExportType | ExportValue,ClassMember = Method | Accessor | Property,/* @internal */// The set of things we consider semantically classifiable. Used to speed up the LS during// classification.Classifiable = Class | Enum | TypeAlias | Interface | TypeParameter | Module,}
3. 检查器 对 绑定器的使用
实际上 绑定器在检查器 内部调用 而检查器又被程序调用。 简化的调用栈如下所示
program.getTypeChecker ->ts.createTypeChecker(检查器中)->initializeTypeChecker(检查器中) ->for each SourceFile `ts.bindSourceFile`(绑定器中)// followed byfor each SourceFile `ts.mergeSymbolTable`(检查器中)
而 SourceFile 是绑定器的工作单元 binder.ts 由 checker.ts 驱动
bindSourceFile 和 mergeSymbolTable 是 两个关键的绑定器函数
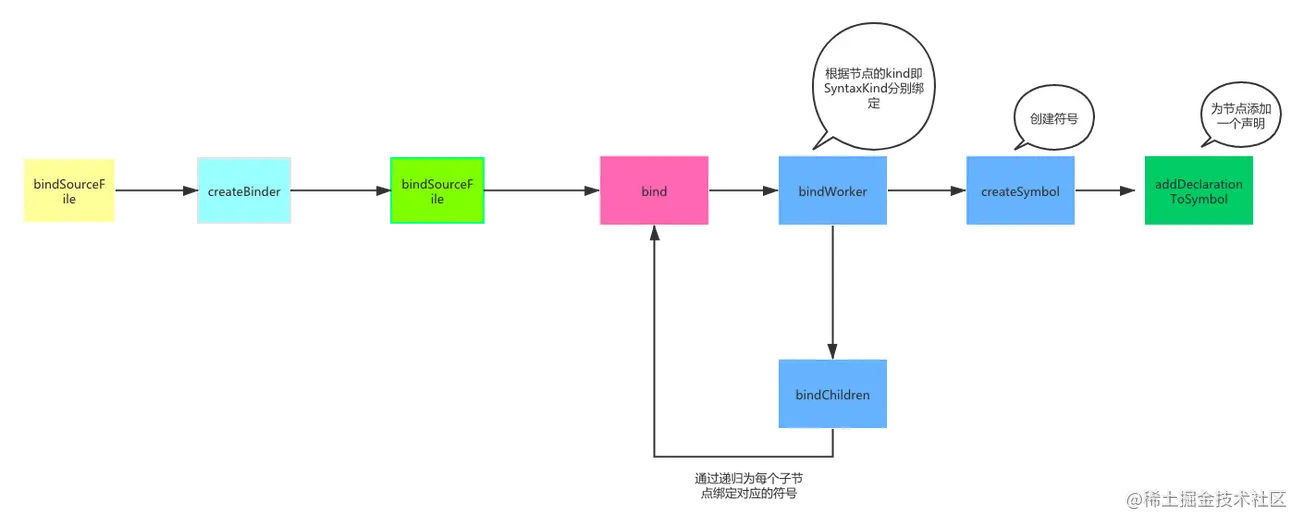
3.1 bindSourceFile
export function bindSourceFile(file: SourceFile, options: CompilerOptions) {performance.mark("beforeBind");binder(file, options);performance.mark("afterBind");performance.measure("Bind", "beforeBind", "afterBind");}
这里的 performance 相关的函数 我们可以先 忽略 这里 可以看到 bindSourceFile 的参数 是 SourceFile 主要执行的 是 binder 方法 那我们继续往下看
3.2 binder
const binder = createBinder();function createBinder(): (file: SourceFile, options: CompilerOptions) => void {function bindSourceFile(f: SourceFile, opts: CompilerOptions) {file = f;options = opts;languageVersion = getEmitScriptTarget(options);inStrictMode = bindInStrictMode(file, opts);classifiableNames = createMap<string>();symbolCount = 0;skipTransformFlagAggregation = file.isDeclarationFile;Symbol = objectAllocator.getSymbolConstructor();if (!file.locals) {bind(file);file.symbolCount = symbolCount;file.classifiableNames = classifiableNames;}// ...}return bindSourceFile;// ...}
我们可以看到 这里的 binder 的执行 最终步骤 还是 执行的 bindSourceFile 方法。
该函数主要是检查 file.locals 是否定义 如果 没有 则交给 bind 来处理。
/* @internal */ locals?: SymbolTable; // Locals associated with node (initialized by binding)
注意: locals 定义在节点上 其 类型是 SymbolTable。 SourceFile 也是一个节点(事实上也是 AST 中的根节点)
而一开始的 file 肯定是没有被定义的 因为我们可以往下走 bind 的逻辑
3.3 bind
function bind(node: Node): void {if (!node) {return;}node.parent = parent;const saveInStrictMode = inStrictMode;// Even though in the AST the jsdoc @typedef node belongs to the current node,// its symbol might be in the same scope with the current node's symbol. Consider://// /** @typedef {string | number} MyType */// function foo();//// Here the current node is "foo", which is a container, but the scope of "MyType" should// not be inside "foo". Therefore we always bind @typedef before bind the parent node,// and skip binding this tag later when binding all the other jsdoc tags.if (isInJavaScriptFile(node)) bindJSDocTypedefTagIfAny(node);// First we bind declaration nodes to a symbol if possible. We'll both create a symbol// and then potentially add the symbol to an appropriate symbol table. Possible// destination symbol tables are://// 1) The 'exports' table of the current container's symbol.// 2) The 'members' table of the current container's symbol.// 3) The 'locals' table of the current container.//// However, not all symbols will end up in any of these tables. 'Anonymous' symbols// (like TypeLiterals for example) will not be put in any table.bindWorker(node);// Then we recurse into the children of the node to bind them as well. For certain// symbols we do specialized work when we recurse. For example, we'll keep track of// the current 'container' node when it changes. This helps us know which symbol table// a local should go into for example. Since terminal nodes are known not to have// children, as an optimization we don't process those.if (node.kind > SyntaxKind.LastToken) {const saveParent = parent;parent = node;const containerFlags = getContainerFlags(node);if (containerFlags === ContainerFlags.None) {bindChildren(node);}else {bindContainer(node, containerFlags);}parent = saveParent;}else if (!skipTransformFlagAggregation && (node.transformFlags & TransformFlags.HasComputedFlags) === 0) {subtreeTransformFlags |= computeTransformFlagsForNode(node, 0);}inStrictMode = saveInStrictMode;}
- 它为当前节点 添加一个 parent
- 调用 bindWorker 根据不同的节点调用与之对应的绑定函数
- 调用bindChildren对 当前节点 的每个子节点进行一一绑定 bindChildren 内部也是通过递归调用bind 对每一个节点进行一一绑定
3.4 bindWorker
function bindWorker(node: Node) {switch (node.kind) {/* Strict mode checks */case SyntaxKind.Identifier:// for typedef type names with namespaces, bind the new jsdoc type symbol here// because it requires all containing namespaces to be in effect, namely the// current "blockScopeContainer" needs to be set to its immediate namespace parent.if ((<Identifier>node).isInJSDocNamespace) {let parentNode = node.parent;while (parentNode && parentNode.kind !== SyntaxKind.JSDocTypedefTag) {parentNode = parentNode.parent;}bindBlockScopedDeclaration(<Declaration>parentNode, SymbolFlags.TypeAlias, SymbolFlags.TypeAliasExcludes);break;}// ....}}
单论截取的这段代码 我们可以看出 bindWork 里面做的事情是根据 node.kind (SyntaxKind类型) 进行分别绑定,并且将工作委托交给 bindXXX 函数进行实际的绑定操作。
下面就以 Identifier 作为例子 我们看下 bindBlockScopedDeclaration 做了什么
3.5 bindBlockScopedDeclaration
function bindBlockScopedDeclaration(node: Declaration, symbolFlags: SymbolFlags, symbolExcludes: SymbolFlags) {switch (blockScopeContainer.kind) {case SyntaxKind.ModuleDeclaration:declareModuleMember(node, symbolFlags, symbolExcludes);break;case SyntaxKind.SourceFile:if (isExternalModule(<SourceFile>container)) {declareModuleMember(node, symbolFlags, symbolExcludes);break;}// falls throughdefault:if (!blockScopeContainer.locals) {blockScopeContainer.locals = createMap<Symbol>();addToContainerChain(blockScopeContainer);}declareSymbol(blockScopeContainer.locals, /*parent*/ undefined, node, symbolFlags, symbolExcludes);}}
我们最后发现 基本上大多数的定义都会走到 declareSymbol 函数 当然 其他 declareModuleMember 其实最终也会走到 declareSymbol 来定义符号
3.6 declareSymbol
function declareSymbol(symbolTable: SymbolTable, parent: Symbol, node: Declaration, includes: SymbolFlags, excludes: SymbolFlags): Symbol {Debug.assert(!hasDynamicName(node));const isDefaultExport = hasModifier(node, ModifierFlags.Default);// The exported symbol for an export default function/class node is always named "default"const name = isDefaultExport && parent ? "default" : getDeclarationName(node);let symbol: Symbol;if (name === undefined) {symbol = createSymbol(SymbolFlags.None, "__missing");}else {symbol = symbolTable.get(name);addDeclarationToSymbol(symbol, node, includes);symbol.parent = parent;// ..return symbol;}
从上面描述的来看 declareSymbol 其实主要做了两件事情
- createSymbol
- addDeclarationToSymbol
createSymbol
function createSymbol(flags: SymbolFlags, name: string): Symbol {symbolCount++;return new Symbol(flags, name);}
createSymbol主要是简单地更新 symbolCount(一个 bindSourceFile 的本地变量),并使用指定的参数创建符号。创建了符号之后需要进行对节点的绑定。
addDeclarationToSymbol
function addDeclarationToSymbol(symbol: Symbol, node: Declaration, symbolFlags: SymbolFlags) {symbol.flags |= symbolFlags;node.symbol = symbol;if (!symbol.declarations) {symbol.declarations = [];}symbol.declarations.push(node);if (symbolFlags & SymbolFlags.HasExports && !symbol.exports) {symbol.exports = createMap<Symbol>();}if (symbolFlags & SymbolFlags.HasMembers && !symbol.members) {symbol.members = createMap<Symbol>();}if (symbolFlags & SymbolFlags.Value) {const valueDeclaration = symbol.valueDeclaration;if (!valueDeclaration ||(valueDeclaration.kind !== node.kind && valueDeclaration.kind === SyntaxKind.ModuleDeclaration)) {// other kinds of value declarations take precedence over modulessymbol.valueDeclaration = node;}}}
addDeclarationToSymbol函数内主要做了两件事情:
1. 创建 AST 节点到 symbol 的连接 ( node.symbol = symbol;)
2. 为节点添加一个声明(symbol.declarations.push(node); )。
4. 整体流程