Basic
CAS
compare and swap(exchange)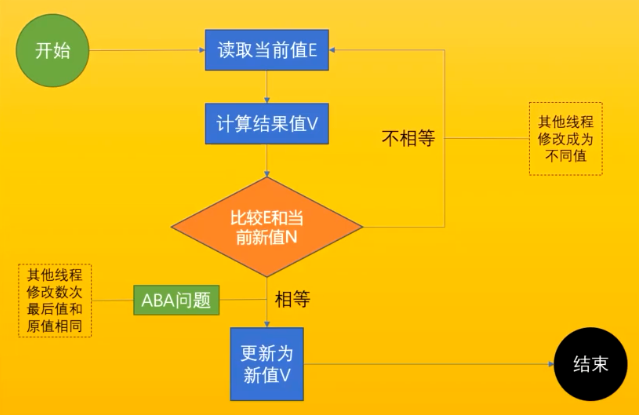
ABA 问题(读取的时候是 A,然后被别的线程修改成 B,然后再修改回 A)可以通过使用 AtomicStampedReference 来给值添加一个版本号,当修改值的时候,同时修改版本,比较值的时候同时比较版本号。(基础类型无所谓,但是引用类型被修改了其中的值,就会发生变化)
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);
lock cmpxchg 指令 cmpxchg 非原子性lock 指令在执行后面的指令的时候锁定一个北桥信号(硬件)
在线程数量比较多的情况下(未必):LongAdder(分段锁) > AtomicLong > Sychronized
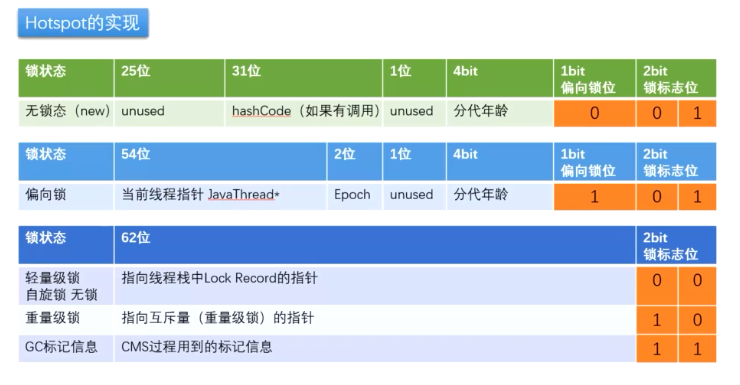
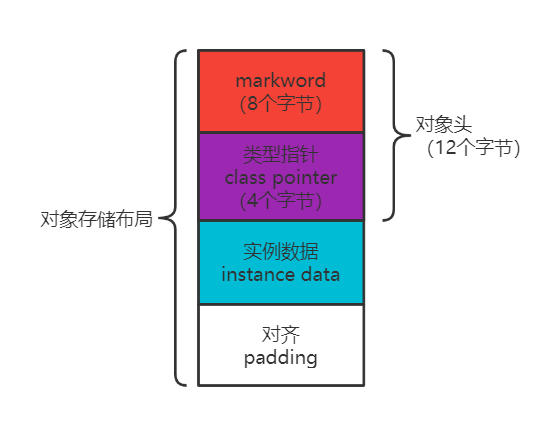
对象在内存中的存储布局
java -XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags -version
- 对象头 12 个字节:markword 8 个字节,class pointer 4 个字节(开启压缩,不开启:8 个字节)
- instance date 用来存放对象中的属性
- 对齐 padding:如果对象前面占用的内存不能被 8 整除,用来补全剩下的。
Object o = new Object(); o 在内存中占用 16 个字节(对象头 12 个字节,padding 4 个字节)
锁升级
过程
new - 偏向锁 - 轻量级锁(无锁,自旋锁,自适应自旋) - 重量级锁
对象 O 刚 new 出来为无锁态;线程 A 是第一个使用对象的线程,就在对象头的 MarkWord 里面添加自己的线程 id,然后这个时候升级为偏向锁;当有线程前来和线程 A 抢夺对象的使用权,这个时候进行 CAS,看哪个线程可以将自己线程生成的 Lock Record 存放到对象头中,然后别的线程会在旁边进行自旋等待,这个时候升级为轻量级锁;当有线程进行了 10 次自旋,或者CPU 线程占用到一半升级为重量级锁,这个时候除了正在使用对象的线程,其余的线程在锁的栈中进行等待。(用户态 -> 内核态)
锁消除(lock eliminate)
public void add(String str1, String str2) {StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();sb.append(str1).append(str2);//当这个StringBuffer只是在add这个方法中适用的时候,那么append就不需要再加锁了}
锁粗化(lock coarsening)
public void test(String str) {StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();int i = 1;while (i > 100) { //锁加在while循环上sb.append(str);i++;}}
Cache Line
MESI Cache 一致性协议
实现数据一致性(MESI,锁总线)
cpu 每个 cache line 标记四种状态
- Modified 修改
- Exclusive 独占
- Shared 共享
-
内存屏障
屏障两边的指令不可以重排!保障有序!(sfence mfence lfence)
JSR 内存屏障(Java Standard Request) LoadLoad 屏障:Load1;LoadLoad;Load2,在 Load2 及后续读取操作要读取的数据被访问前,保证 Load1 要读取的数据被读取完毕。
- StoreStore 屏障:Store1;StoreStore;Store2,在 Store2 及后续写入操作执行前,保证 Store1 的写入操作对其它处理器可见。
- LoadStore 屏障: Load1;LoadStore;Store2,在Store2 及后续写入操作执行前,保证 Load1 要读取的数据被读取完毕。
- StoreLoad 屏障:Store1;StoreLoad;Load2,在 Load2 及后续所有读取操作执行前,保证 Store1 的写入对所有处理器可见。
volatile 如何解决指令重排序
volatile:禁止指令重排;线程可见;不保证原子性
只是加了一个标记(ACC_VOLATILE)
涉及:DCL(Double Check Load)单例需要添加 volatile 吗?需要 ```java //DCL单例 private b = 5; private static volatile T instance;
public static T getInstance() { if (instance == null) { synchronized (instance) { if (instance == null) { instance = new T(); } } } return instance; }
```java0 new #2 <T> --------> 半初始化7 astore_1 --------> 执行构造方法4 invokespecial #3 <T.<init>> --------> 建立联系========== 指令重排 ============0 new #2 <T> --------> 半初始化4 invokespecial #3 <T.<init>> --------> 建立联系7 astore_1 --------> 执行构造方法========== 这个时候 =========if (isntance != null) xxx -> 使用了半初始化的对象(里面的属性的值只是默认值,并没有开始赋值)
============ jvm内存屏障 ==============StoreStoreBarriervolatile 写操作StoreLoadBarrier================LoadLoadBarriervolatile 读操作LoadStoreBarrier============ hotspot =============lock; addl (空操作)
Java 中的引用类型
强引用
软引用
//-Xmx20Mpublic class Soft {public static void main(String[] args) {SoftReference<byte[]> m = new SoftReference<>(new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10]);System.out.println(m.get());System.gc();try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(m.get());//新创建一个数组,heap装不下,这个时候会进行一次垃圾回收,将软引用的对象回收掉byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 11];System.out.println(m.get()); //null}}// 经常被用来当做缓存
弱引用
public class Weak {public static void main(String[] args) {WeakReference<M> m = new WeakReference<>(new M());System.out.println(m.get());System.gc();//进行垃圾回收的时候就会弱引用的对象回收,一次性System.out.println(m.get()); //null}}
ThreadLocal
线程本地对象
public void set(T value) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread();ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;if (map != null)map.set(this, value); //将当前的ThreadLocal作为map的key,存入的值作为valueelsecreateMap(t, value);}private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);for (Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {if (e.get() == key) {e.clear();expungeStaleEntry(i);return;}}}static class ThreadLocalMap {//若使用强引用,即使使threadLocal = null;那么key的引用仍然使用ThreadLocal对象,对出现内存泄漏//但是弱引用还是存在内存泄漏,ThreadLocal被回收掉,那么key就为null,那么value就永远不可达//所以在使用ThradLocal之后,需要执行threadLocal.remove();static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}}
虚引用
管理堆外内存(Zero Copy)
public class Phantom {//NIO//当Queue里面的东西被回收了,就会触发private static final ReferenceQueue<M> QUEUE = new ReferenceQueue<>();public static void main(String[] args) {PhantomReference<M> phantomReference = new PhantomReference<>(new M(), QUEUE);System.out.println(phantomReference.get()); //nullSystem.gc();System.out.println(phantomReference.get()); //null}}
Lock
ReentrantLock
public class T_ReentrantLock {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();public void m() {try {lock.lock();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println(i);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}public void n() {try {lock.lock();System.out.println("n()...");} finally {lock.unlock();}}public static void main(String[] args) {T_ReentrantLock t = new T_ReentrantLock();new Thread(t :: m).start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}new Thread(t :: n).start();}}
- CAS VS Sync
tryLock();lockInterruptibly();可以进行公平锁和非公平锁的切换(判断锁的等待队列里面有没有线程在等待)
ReadLock
WriteLock
ReadWriteLock
```java public class T_ReadWriteLock {
static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private static int value;
static ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); static Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); //执行读操作的时候,允许其他的读操作共同执行,分享锁 static Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); //执行写操作的时候,不允许执行其他的写操作,排他锁
public static void read(Lock lock) {
try {lock.lock();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("read over");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}
}
public static void write(Lock lock, int var) {
try {lock.lock();Thread.sleep(1000);value = var;System.out.println("write over");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}
}
public static void main(String[] args) { // Lock lockRead = lock; // Lock lockWrite = lock;
Lock lockRead = readLock;Lock lockWrite = writeLock;for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++) {new Thread(() -> read(lockRead)).start();}for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {new Thread(() -> write(lockWrite, new Random().nextInt())).start();}
}
}
<a name="gBLE3"></a>### _CountDownLatch_```javapublic class T_CountDown {public static void usingCountDown() {Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(threads.length);for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {j++;}latch.countDown();});}for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {threads[i].start();}try {latch.await(); //拦截其他的线程,等待当前线程执行完毕} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(latch.getCount());}public static void main(String[] args) {usingCountDown();}}
CyclicBarrier
public class T_CyclicBarrier {public static void main(String[] args) {CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(20, () -> System.out.println("满员"));for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {new Thread(() -> {try {barrier.await(); //等待满20个线程,执行barrier} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();}}}
Semaphore
限流
public class T_Semaphore {public static void main(String[] args) {Semaphore s = new Semaphore(2); //代表可以同时执行几个线程new Thread(() -> {try {s.acquire(); //将Semaphore中的1置为0,其他的线程不允许访问System.out.println("T1 running ...");Thread.sleep(500);System.out.println("T1 end ...");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {s.release(); //将Semaphore中的0置为1,其他的线程可以开始访问}}).start();new Thread(() -> {try {s.acquire();System.out.println("T2 running ...");Thread.sleep(500);System.out.println("T2 end ...");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {s.release();}}).start();}}
Exchanger
public class T_Exchanger {static Exchanger<String> exchanger = new Exchanger();public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(() -> {String s = "T1";try {s = exchanger.exchange(s); //线程堵塞,等待下一个可以交换的线程//然后将两个值进行交换,线程继续执行} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + s);}, "s1").start();new Thread(() -> {String s = "T2";try {s = exchanger.exchange(s);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + s);}, "s2").start();}}
LockSupport
public class T_LockSupport {public static void main(String[] args) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {System.out.println(i);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}if (i == 5) {LockSupport.park(); //当i等于5的时候,线程阻塞}}});thread.start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(8);System.out.println("after 8 seconds");} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}LockSupport.unpark(thread); //让线程继续运行}}
Phaser
//分段,等到所有需要执行这个阶段的线程执行阶段完毕,进入下一个阶段public class T_Phaser {static MarryPhaser phaser = new MarryPhaser();public static void main(String[] args) {phaser.bulkRegister(7);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {new Thread(new Person("person" + i, 0)).start();}new Thread(new Person("新郎", 1)).start();new Thread(new Person("新娘", 1)).start();}static class Person implements Runnable {String name;int id;public Person(){}public Person(String name, int id) {this.name = name;this.id = id;}public void arrive() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println(name + "已经到达");phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void eat() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println(name + "吃完");phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void leave() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println(name + "离开");phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void intoBridalRoom() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);if (id == 1) {System.out.println(name + "入洞房");phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();} else {phaser.arriveAndDeregister();}}public void getUp() throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);if (id == 1) {System.out.println(name + "起床");phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}}@Overridepublic void run() {try {arrive();eat();leave();intoBridalRoom();getUp();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}static class MarryPhaser extends Phaser {@Overrideprotected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {switch (phase) {case 0:System.out.println("所有人都到齐:" + registeredParties);System.out.println();return false;case 1:System.out.println("所有人吃完饭:" + registeredParties);System.out.println();return false;case 2:System.out.println("所有人离开:" + registeredParties);System.out.println();return false;case 3:System.out.println("新娘新郎入洞房:" + registeredParties);System.out.println();return false;case 4:System.out.println("新娘新郎起床:" + registeredParties);return true;default:return false;}}}}
Test_01
/*** 实现一个容器,提供两个方法add,size* 写两个线程,线程1添加10个元素到容器中,* 线程2实现监控元素的个数,当个数到5个时,线程2给出提示并结束*/
Using CountDownLatch
//使用CountDownLatchpublic class T_Test_02 {//volatile尽量不要用来使用修饰引用对象// volatile List lists = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList<>());volatile List lists = new LinkedList();public void add(Object o) {lists.add(o);}public int size() {return lists.size();}public static void main(String[] args) {T_Test_02 t = new T_Test_02();CountDownLatch latch1 = new CountDownLatch(1);CountDownLatch latch2 = new CountDownLatch(1);new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("t2 start");if (t.size() != 5) {try {latch1.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}latch2.countDown();System.out.println("t2 end");}, "t2").start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("t1 start");for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {t.add(new Object());System.out.println("add " + i);if (t.size() == 5) {latch1.countDown();try {latch2.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}// try {// TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);// } catch (InterruptedException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// }}System.out.println("t1 end");}, "t1").start();}}
Using LockSupport
//LockSupport//condition1public class T_Test_03 {volatile List lists = new LinkedList();public void add(Object o) {lists.add(o);}public int size() {return lists.size();}public static void main(String[] args) {T_Test_03 t = new T_Test_03();Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {t.add(new Object());System.out.println("add " + t.size());if (t.size() == 5) {LockSupport.park();}}}, "t1");t1.start();new Thread(() -> {while (true) {if (t.size() == 5) {LockSupport.unpark(t1);break;}}System.out.println("t2 end");}, "t2").start();}}//condition2public class T_Test_03 {volatile List lists = new LinkedList();public void add(Object o) {lists.add(o);}public int size() {return lists.size();}static Thread t1, t2;public static void main(String[] args) {T_Test_03 t = new T_Test_03();t2 = new Thread(() -> {System.out.println("t2 start");LockSupport.park();System.out.println("t2 end");LockSupport.unpark(t1);}, "t2");t2.start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}t1 = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {t.add(new Object());System.out.println("add " + t.size());if (t.size() == 5) {LockSupport.unpark(t2);LockSupport.park();}}}, "t1");t1.start();}}
Using Synchronized
//synchronizedpublic class T_Test_04 {volatile List lists = new LinkedList();public void add(Object o) {lists.add(o);}public int size() {return lists.size();}public static void main(String[] args) {T_Test_04 t = new T_Test_04();final Object lock = new Object();new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {System.out.println("t2 start");if (t.size() != 5) {try {lock.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("t2 end");lock.notify();}}, "t2").start();try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}new Thread(() -> {synchronized (lock) {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {t.add(new Object());System.out.println("add " + t.size());if (t.size() == 5) {lock.notify();try {lock.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}, "t1").start();}}
Test_02
/*** 写一个固定容量同步容器,拥有put和get方法,以及getCount方法,* 能够支持2个生产者线程以及10个消费者线程的阻塞调用*/
Using Synchronized
//synchronizedpublic class MyContainer_01<T> {final private LinkedList<T> list = new LinkedList<>();final private int MAX = 10;private int count = 0;private synchronized void put(T t) {while (list.size() == MAX) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}list.add(t);++count;System.out.println("当前有" + count + "个");this.notifyAll(); //通知消费者线程进行消费}private synchronized T get() {T t = null;while (list.size() == 0) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}t = list.removeFirst();-- count;System.out.println("当前有" + count + "个");this.notifyAll(); //通知生产者进行生产return t;}public static void main(String[] args) {MyContainer_01<String> c = new MyContainer_01<>();//启动消费者线程for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {System.out.println(c.get());}}, "c" + i).start();}try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//启动生产者线程for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 25; j++) {c.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + j);}}, "p" + i).start();}}}
Using Condition
public class MyContainer_02<T> {final private LinkedList<T> list = new LinkedList<>();final private int MAX = 10;private int count = 0;private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private Condition producer = lock.newCondition();private Condition consumer = lock.newCondition();private void put(T t) {try {lock.lock();while (list.size() == MAX) {producer.await();}list.add(t);++count;consumer.signalAll(); //通知消费者线程消费} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}}private T get() {T t = null;try {lock.lock();while (list.size() == 0) {consumer.await();}t = list.removeFirst();-- count;producer.signalAll(); //通知生产者生产} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {lock.unlock();}return t;}public static void main(String[] args) {MyContainer_02<String> c = new MyContainer_02<>();//启动消费者线程for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {System.out.println(c.get());}}, "c" + i).start();}try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//启动生产者线程for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {new Thread(() -> {for (int j = 0; j < 25; j++) {c.put(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + j);}}, "p" + i).start();}}}
AQS
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
AQS 就是基于 CLH 队列,用 volatile 修饰共享变量 state,线程通过 CAS 去改变状态符,成功则获取锁成功,失败则进入等待队列,等待被唤醒。
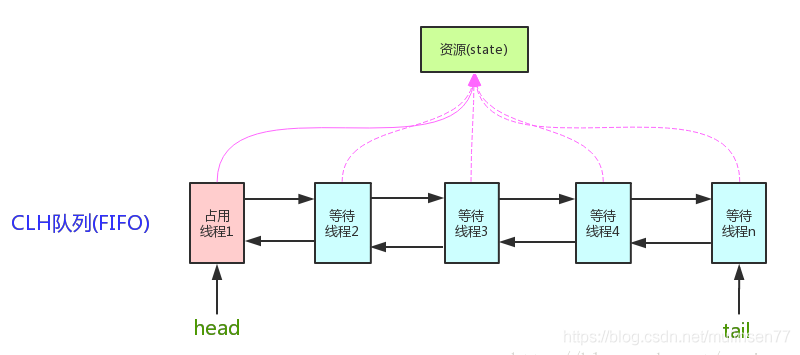
reentrantLock.lock();
//ReentrantLockpublic void lock() {sync.lock();}final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();int c = getState();if (c == 0) {if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);return true;}}else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) // overflowthrow new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");setState(nextc);return true;}return false;}//AbstractQueuedSynchronizer/*** The synchronization state.*/private volatile int state;