返回函数
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1016959663602400/1017451447842528
函数作为返回值
闭包(closure)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/453787908
匿名函数(lambda)
见python内置函数
装饰器
当需要增加一个函数的功能,又不希望直接改变其定义时,这种在代码运行期间动态增加功能的方式,称之为“装饰器”(Decorator)
本质:
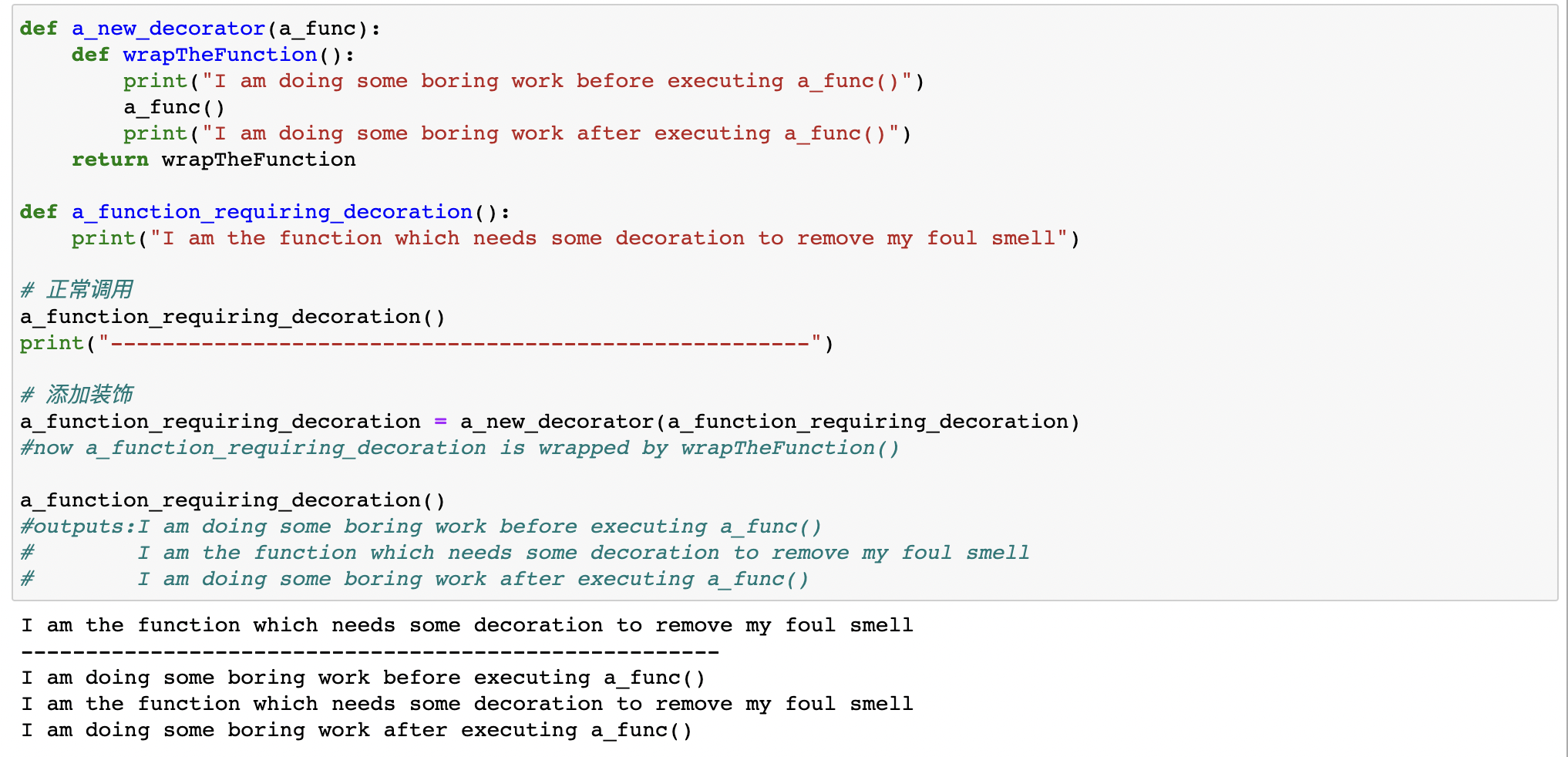
所谓“装饰器”,就是封装了一个函数,并添加额外功能,然后返回一个新的函数
def a_new_decorator(a_func):def wrapTheFunction():print("I am doing some boring work before executing a_func()")a_func()print("I am doing some boring work after executing a_func()")return wrapTheFunctiondef a_function_requiring_decoration():print("I am the function which needs some decoration to remove my foul smell")# 正常调用a_function_requiring_decoration()# 添加装饰a_function_requiring_decoration = a_new_decorator(a_function_requiring_decoration)#now a_function_requiring_decoration is wrapped by wrapTheFunction()a_function_requiring_decoration()#outputs:I am doing some boring work before executing a_func()# I am the function which needs some decoration to remove my foul smell# I am doing some boring work after executing a_func()
用@来实现装饰器
the @a_new_decorator is just a short way of saying:
a_function_requiring_decoration = a_new_decorator(a_function_requiring_decoration)
标准示例:
这里的函数addition_func在调用时,实际是被warpTheFunction替代了,它重写了我们函数的名字和注释文档(docstring)。要想正常输出函数名,可以通过functools.wraps进行处理(第4行的@wraps(func))
from functools import wrapsdef logit(func):@wraps(func)def warpTheFunction(*args, **kwargs):return func(*args, **kwargs) # 这里传可变参数实际上是没有意义的,addition_func定义时,只接受一个位置参数(但是可以用这种方式,透传可变参数)return warpTheFunction@logitdef addition_func(x):return x + xresult = addition_func(4)print(result) # 8print(addition_func.__name__) # addition_func(如果不import warps,得到的是warpTheFunction)
待参数的装饰器
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1016959663602400/1017451662295584
如果decorator本身需要传入参数,那就需要编写一个返回decorator的高阶函数,写出来会更复杂。比如,要自定义log的文本:
def log(text):def decorator(func):def wrapper(*args, **kw):print('%s %s():' % (text, func.__name__))return func(*args, **kw)return wrapperreturn decorator@log('execute')def now():print('2015-3-25')# 执行>>> now()execute now():2015-3-25# 实际执行效果>>> now = log('execute')(now)
首先执行log(‘execute’),返回的是decorator函数,再调用返回的函数,参数是now函数,返回值最终是wrapper函数。

