In this category, you will learn about the Ecolab business capability model, including the concept of value streams, the business capabilities (or processes) within each of the value streams, how to identify Capability Owners, and when to work with them on projects.
Ecolab Business Capability Model
A capability is a set of processes within a value stream, usually under the ownership of one business process owner and aligning with a single function or business area.
The guiding principles of the capability model are:
1. Capabilities are defined by six dimensions (mission, insights, process, technology, talent, and governance) and focused on creating value
2. There is clear accountability and ownership across capabilities
3. The capability model provides a framework (standards, templates, naming conventions, and a governance model) and discipline (when change is implemented or decisions are made, all six capability dimensions should be considered)
4. Direct relationships between processes and capabilities should be established (all processes need to be assigned to a capability)
CaseWise is an online tool that allows you to navigate through the Ecolab capability model and value streams, and to obtain information about each Global Stakeholder, Capability Owner, and Global Process Owner.
Value Streams
These are the key value streams:
Idea to Market
Describes the phases of new product development through product launch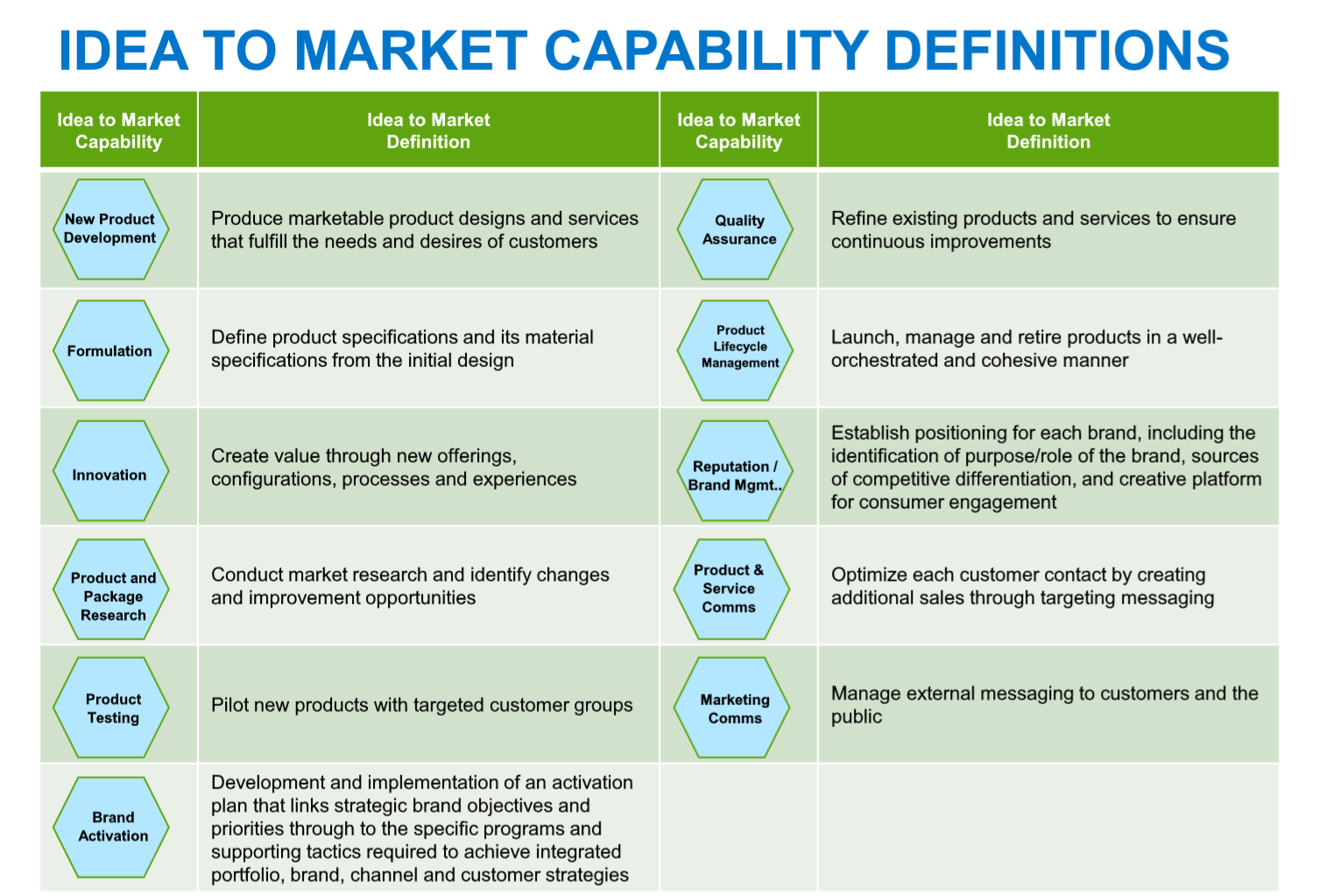
Order to Cash
Refers to a company’s business process for the entire order processing system and generally includes Customer Service, Warehouse, Distributor Finance, Planning, Credit Billing, and Master Data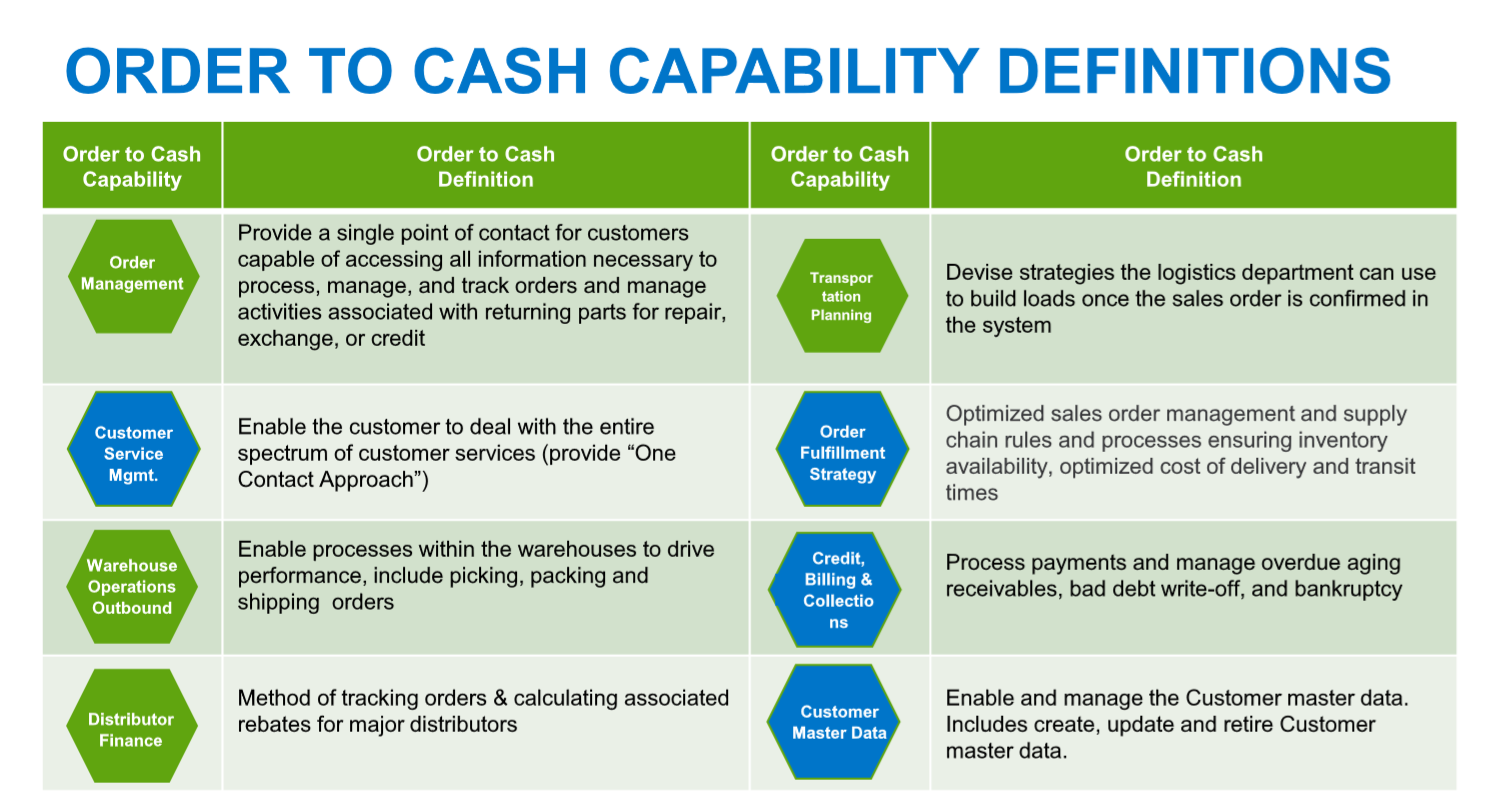
Forecast to Stock
This process includes demand planning to forecast market demand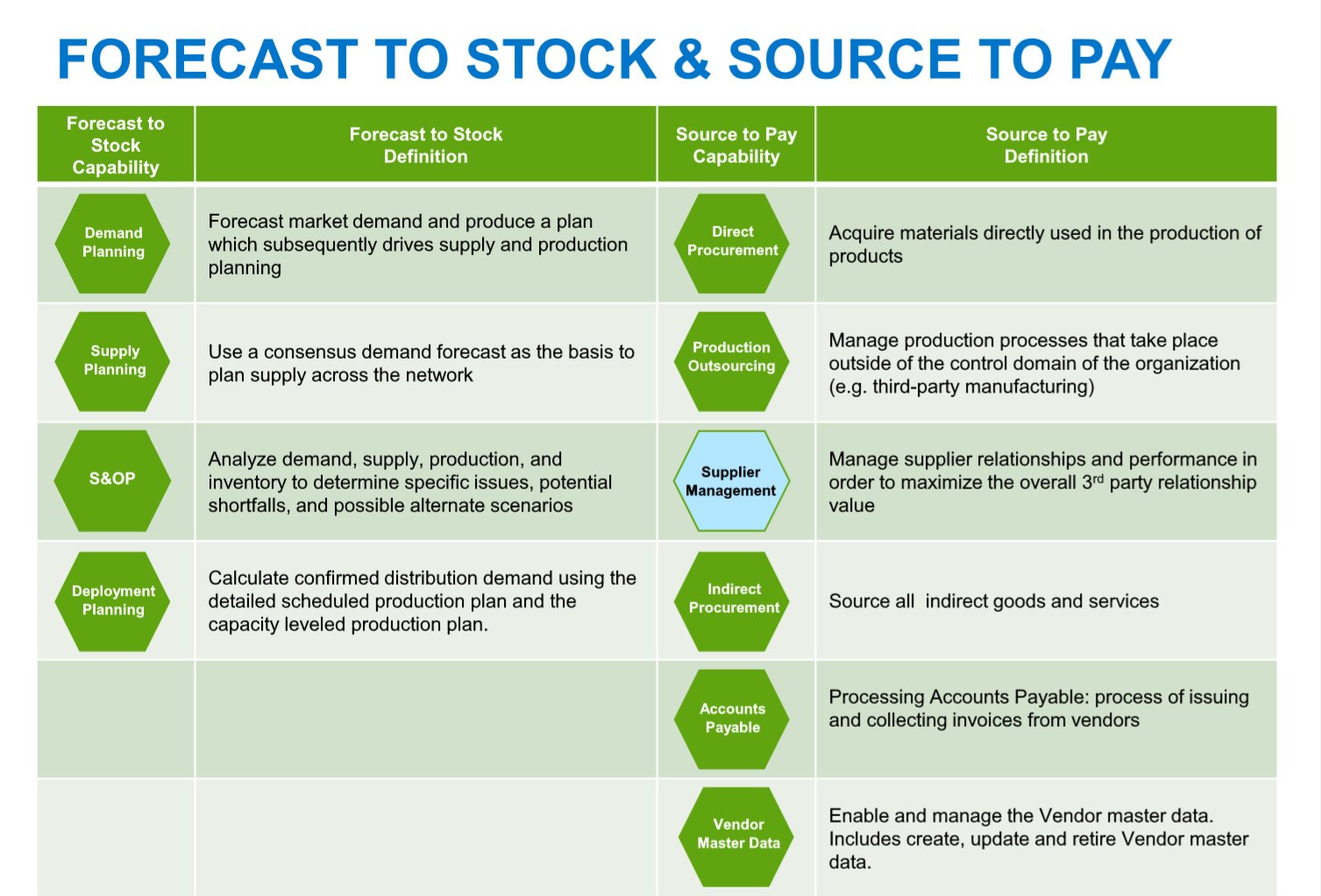
Quote to Order
Refers to the process of preparing a quote for a new or existing customer and all the different steps until the customer is ready to order from its vendor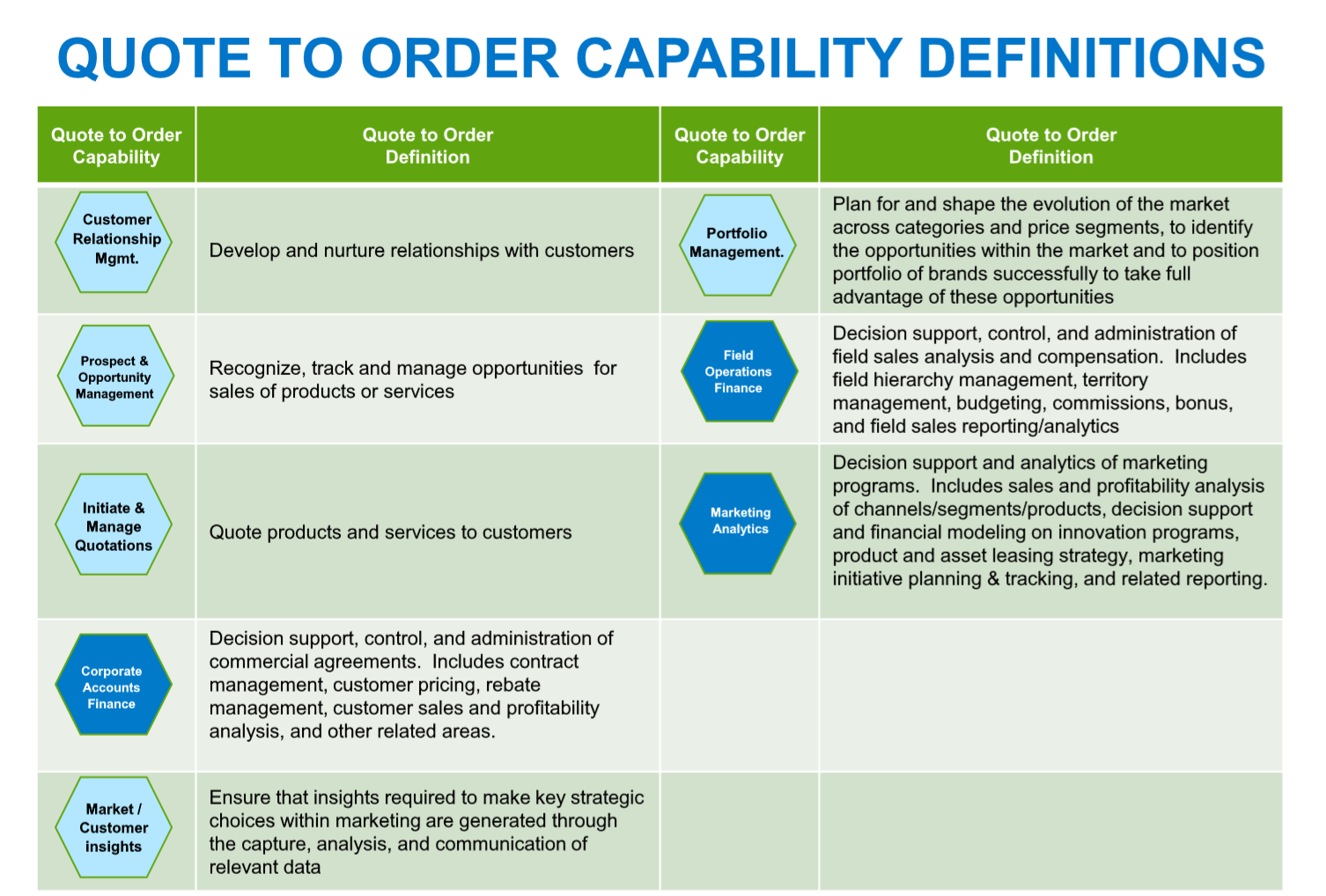
Request to Service
Refers to the process covering the moment a customer communicates a Service Request until the service is provided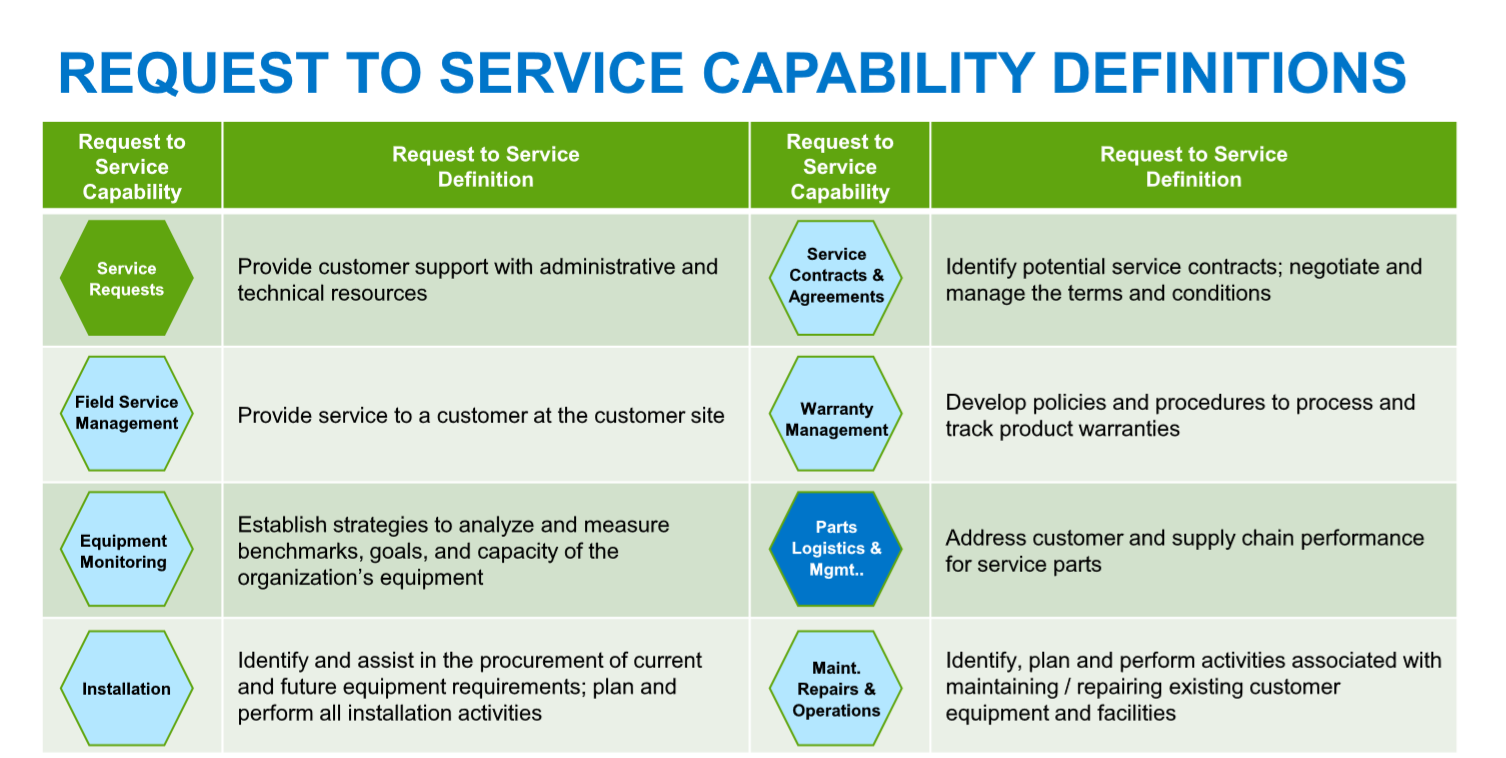
Source to Pay
Refers to the process that starts with finding, negotiating with, and contracting with the suppliers of goods, and culminates in final payment for those goods
Record to Report
This is a Finance and Accounting (F&A) management process that involves collecting, processing, and delivering relevant, timely, and accurate information used for providing strategic, financial, and operational feedback to understand how a business is performing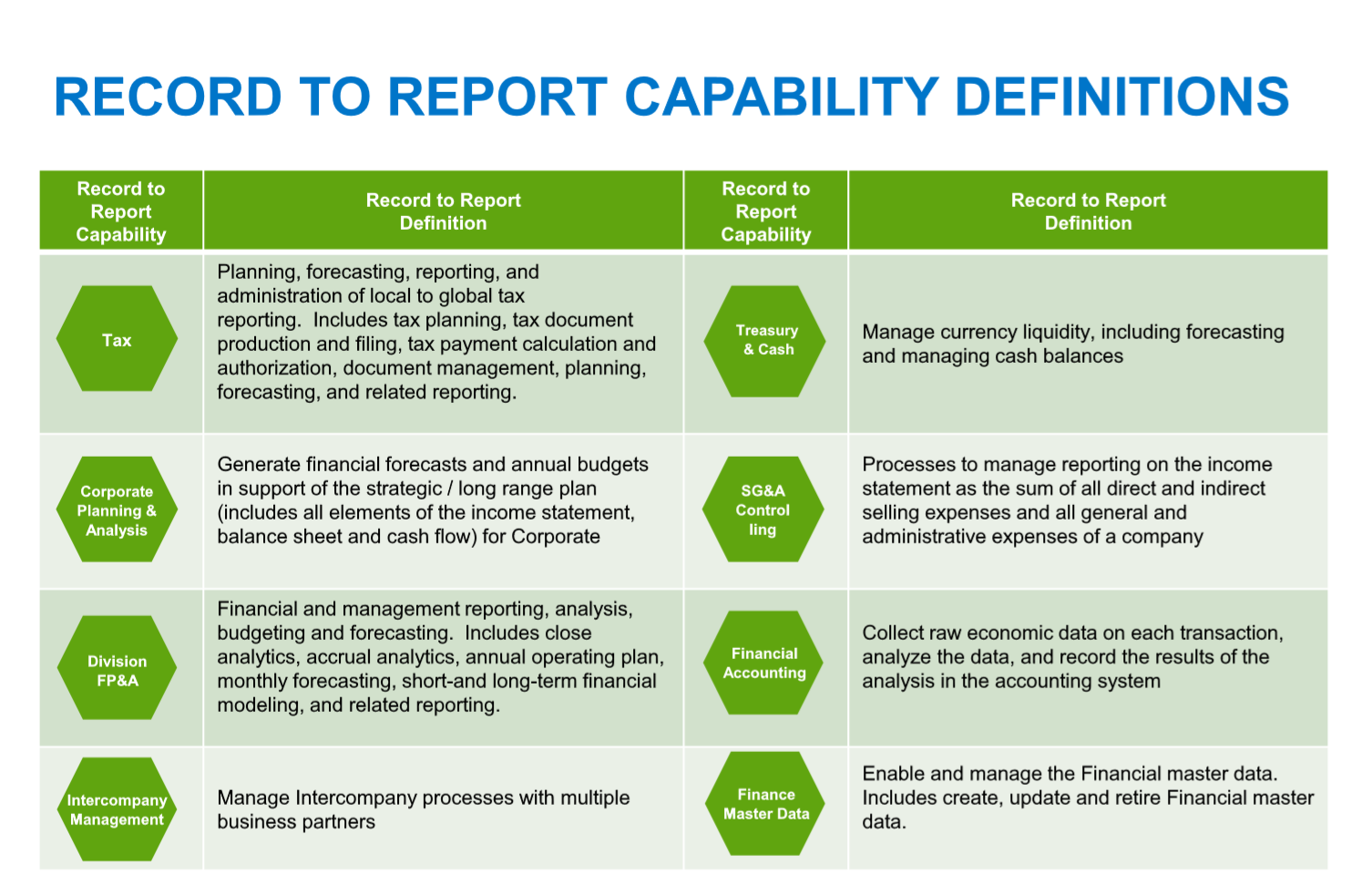
Make to Deploy
This process covers manufacturing execution and strategy and Supply Chain processes, including quality controls and environmental and safety factors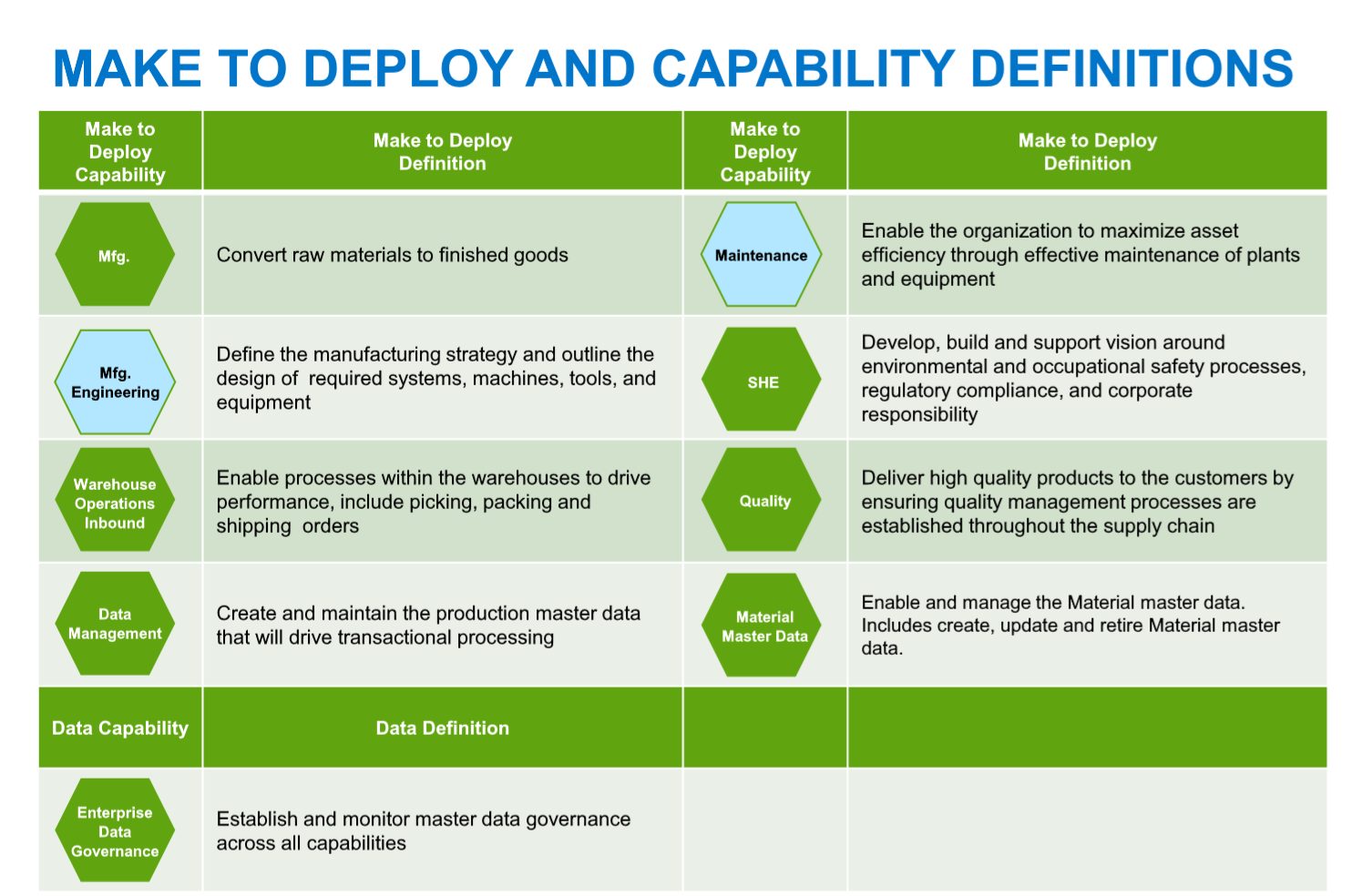
Data Governance includes:
- Enterprise Data Governance: ensures master data quality and drives robust maintenance processes
- Enterprise Reporting and Analytics: extracts meaningful insights that can be used to better understand and improve business performance and to monitor how different areas of a business are performing
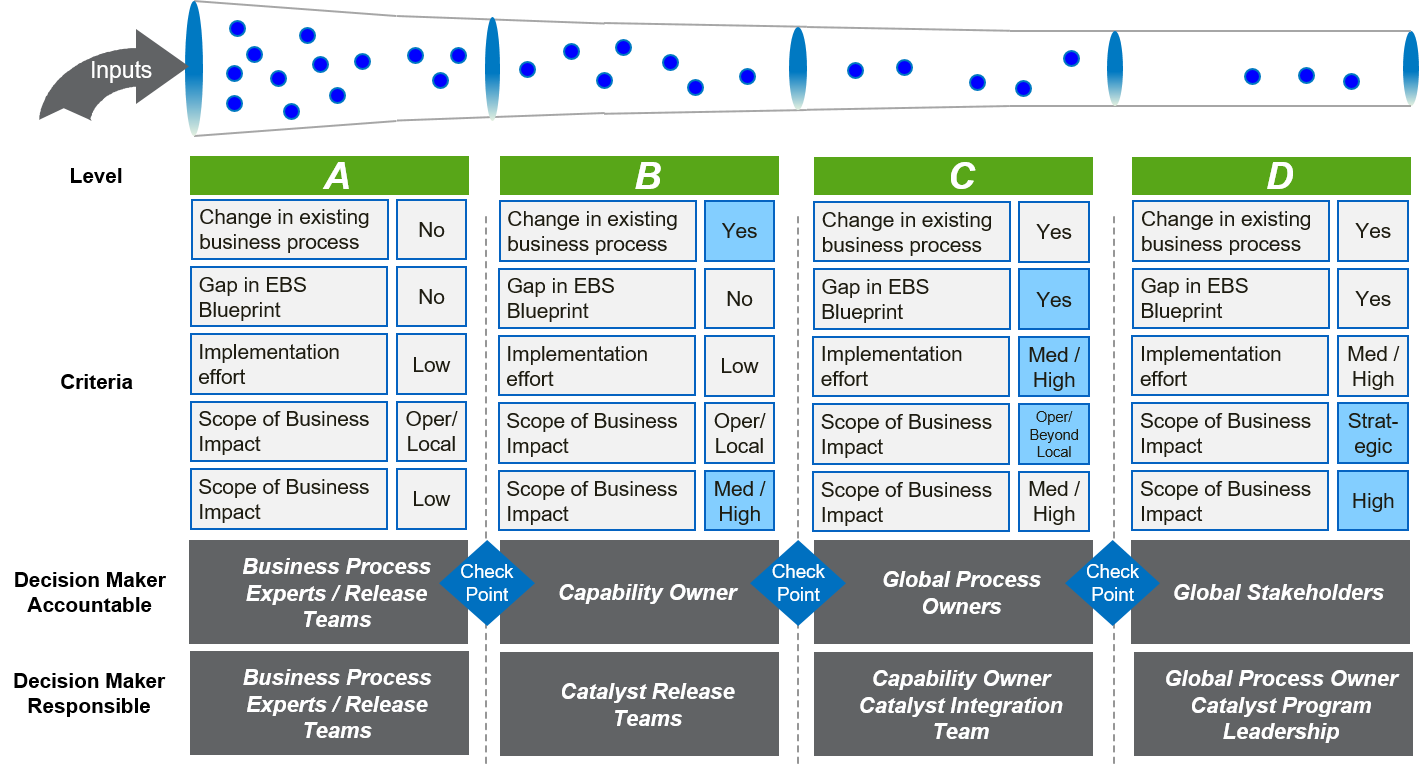
Capability Owners
A Capability Owner is accountable for all aspects of the capability within their area of responsibility. You can use CaseWise to find the relevant contact people for each value stream and capability.
Here are examples of typical cases in which you would want to involve the Capability Owner:
- A change in existing business processes
- The scope of the business impact is Medium or High, or you are unsure of the possible impact
- Implementation of a solution requires Medium or High efforts, or you are unsure of the potential impact
- There is a gap in the Ecolab Business Solution (EBS) blueprint
Business Outcomes
Business outcomes are the results or consequences of doing something. In project management terms, it is the business results that are expected after executing a project. The results provide a solution to the business’s need, which is the basis of the project request from the very beginning. Business outcomes close this loop and determine customer satisfaction.
Business outcomes can be measured and are tied to company strategies and goals. For example, is the solution provided increasing revenue, driving process improvement, or reducing costs? What is the value being provided? If a project has no business outcomes, it has no value for the organization.
Identifying the business outcomes that are most important to the company’s success makes decision-making easier and helps to achieve business objectives faster.