程序?进程?线程
线程
个数设置
线程个数:N= N U (1 + wait time / compute time)
状态
create
runnable
runnig
blocking / waiting
terminate
interrupt
interrupt
isInterrupt
interrupted
查询+重置标记位
wait sleep join一起使用会报错:interruptException
synchronized lock等获取锁的线程一起使用不会(ReentryLock可以使用LockInterruptly打断)
停止
自然结束
stop
执行后直接停止线程,不管线程在干嘛,如果恰巧在进行共享变量的属性赋值,则直接中断该过程
suspend/resume
如果线程正持有一把锁,则直接停止线程,不释放锁(类似于stop),容易造成死锁
volatile属性
interrupt
启动方式
- Thread
- Runnable
- lambda
- 线程池
- callable
并发三大特性
可见性(主存 & 本地内存)
解决方法
volatile
-
synchronized
缓存行64bit(常见用long变量填充)
cache line padding | @Contended + -XX:-RestrictContented
why
结果多次实践获得
太大:内存命中率低,读取慢
- 太小:读取次数多,性能低
MESI(缓存一致性协议intel x86)
- modified
- Exclusive
- Shared
- Invalid
有序性
as-if-serial
在单线程中,如果不影响查询最后的一致性那么cpu就会对程序进行一定的重排序原子性
increment
synchronized
atomic
自旋longaddr
分段锁锁
synchronized(blocked)=>系统锁=>执行时间长,线程数多
支持可重入锁,当发生异常的时候会自动释放锁可重入锁:一个对象获得某种类型的锁后(还在使用)还可以获得该类锁
package multiThreading;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/4*/public class SynchronizedState {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {SynchronizedState synchronizedState = new SynchronizedState();Thread thread1 = new Thread(()-> {try {synchronizedState.m1();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});Thread thread2 = new Thread(()-> {try {synchronizedState.m2();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});thread1.start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);thread2.start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println(thread2.getState());}public synchronized void m1() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getState());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);}public synchronized void m2() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getState());TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);}}
lock(自旋=>waiting)=>用户锁=>执行时间短,线程数少
package multiThreading;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/4*/public class LockState {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{try{lock.lock();for (;;){}}catch (Exception e){}finally {lock.unlock();}});Thread thread2 = new Thread(()->{try{lock.lock();for(;;){}}catch (Exception e){}finally {}});thread1.start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);thread2.start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println(thread2.getState());}}
ReentryLock
CountDownLatch(类似于批处理的thead.join(),只可以使用一次)
package multiThreading;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/3*/public class CountDownLatchDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(100);Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {threads[i] = new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());countDownLatch.countDown();});}for(Thread t:threads){t.start();}try{countDownLatch.await();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {System.out.println("end latch");}}}
CyclicBarrier(等指定数量的线程执行完了后才放行,可以使用多次,多批次)
package multiThreading;import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/3*/public class CyclicBarrierDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws BrokenBarrierException, InterruptedException {// 每次等待20个线程CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(20,()->{System.out.println("go go go");});Thread[] threads = new Thread[100];for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {threads[i] = new Thread(()->{try {cyclicBarrier.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {e.printStackTrace();}});}for(Thread t:threads){t.start();}System.out.println("end");}}
phaser(跟cyclicbarrier很相似,只不过是可以具体的分不同的阶段,以及可以很方便的增加一些筛选条件)
package multiThreading;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/4*/public class PhaserDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {MyPhaser myPhaser = new MyPhaser();Thread[] threads = new Thread[]{new Thread(new Person(myPhaser,"张三"),"张三"), new Thread(new Person(myPhaser,"李四"),"李四"),new Thread(new Person(myPhaser,"王五"),"王五")};for (Thread t:threads){t.start();}}}class MyPhaser extends Phaser {@Overrideprotected boolean onAdvance(int phase, int registeredParties) {switch (phase){case 0:System.out.println("walk"+registeredParties);return false;case 1:System.out.println("go"+registeredParties);return false;case 2:System.out.println("stop"+registeredParties);return false;default:System.out.println("end");return true;}}}class Person implements Runnable{private MyPhaser myPhaser = null;private String name = null;public Person(MyPhaser myPhaser, String name){this.myPhaser = myPhaser;this.myPhaser.register();this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void run() {walk();go();stop();}public void walk(){System.out.println("走:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());this.myPhaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void go(){System.out.println("跑:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());this.myPhaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}public void stop(){if(!this.name.equals("张三")){this.myPhaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();}System.out.println("停止了"+Thread.currentThread().getName());}}
ReentrantReadWriteLock
package multiThreading;import java.time.LocalDate;import java.util.Random;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/5*/public class ReadWriteLockDemo {private static int value = 0;public static void main(String[] args) {Lock reentrantLockW = new ReentrantLock();Lock reentrantLockR = new ReentrantLock();ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock();ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock();Runnable readR = ()->read(readLock);Runnable readW = ()->write(writeLock, new Random().nextInt(100));for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){new Thread(readR).start();}for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {new Thread(readW).start();}}public static void read(Lock lock){try{lock.lock();System.out.println("read over\t"+value);Thread.sleep(1000);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {lock.unlock();}}public static void write(Lock lock,int newValue){try{lock.lock();value = newValue;System.out.println("write over");Thread.sleep(1000);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {lock.unlock();}}}
LockSupport(可以自定义阻塞锁(waiting))
package multiThreading;import java.sql.Timestamp;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/5*/public class LockSupportDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {if(i == 5){LockSupport.park();System.out.println("t当前时间:"+ System.currentTimeMillis() /1000);}System.out.println(i);try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}});thread.start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);// 若在park前执行unpark会导致park无效LockSupport.unpark(thread);// System.out.println("当前时间:"+ System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000);}}
锁的升级
无锁
偏向锁
markword 中记录了执行线程的id,此时没有其他线程竞争
轻量级锁(自旋)
当有其他线程竞争时,就会进入自旋等待锁的释放,自旋超过10次后进入重量级锁
重量级锁
进入os获取锁的资源
volatile
可见性
硬件层面保证数据一致性
锁总线
MESI
- modified
- exclusive
- shared
- invalid
有序性(禁止指令重排序)
CAS(compare and swap)
过程为cpu级别不可中断使用
cas(V,expected,newValue)问题:
ABA
获取的值和最初值一样,但是中间可能发生了某些改变。比如说:1 -> 2 -> 1解决方法:
加版本号引用
强
就普通的引用,当引用指向为null时,原被指向的内存才会被回收 ```java package multiThreading;
/**
- Created by Intellij IDEA. *
- @author JonnyJiang
- @date 2021/8/5
*/
public class StrongReference {
public static void main(String[] args) {
} }M m = new M();m = null;System.gc();
class M{ @Override protected void finalize() { System.out.println(“finalize被执行”); } }
<a name="6FQSI"></a>## 软当内存不足时才会被gc回收> 在运行时加上jvm参数:-Xms10M -Xmx10M```javapackage multiThreading;import java.lang.ref.SoftReference;/*** Created by Intellij IDEA.** @author JonnyJiang* @date 2021/8/5*/public class SoftReferenceDemo {public static void main(String[] args){SoftReference softReference = new SoftReference<>(new M());System.out.println(softReference.get());System.gc();System.out.println(softReference.get());byte[] bytes = new byte[1024*1024*7 - 1024*680]; // 设置过大就会报OOM,过小就不会触发fgcSystem.out.println(softReference.get());}}
弱
只要gc就会被回收,常用于threadlocal
package multiThreading;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/5
*/
public class WeakReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeakReference weakReference = new WeakReference<>(new M());
System.out.println(weakReference.get());
System.gc();
System.out.println(weakReference.get());
System.out.println(weakReference.get());
}
}
结果:

因为在使用threadlocal.set(k,v)时,k=>threadlocal,如果threadlocal指向空,那么threadlocalMap中的key就会造成内存泄漏,久而久之就会造成oom,因此在设计ThreadLocalMap时,它的entry就是设计成weakReference,当发生gc时才会被回收
注意:
虚
形同虚设,根据官方文档解释,在被回收时会将对象放入队列中:
Phantom reference objects, which are enqueued after the collector determines that their referents may otherwise be reclaimed. Phantom references are most often used for scheduling pre-mortem cleanup actions in a more flexible way than is possible with the Java finalization mechanism. If the garbage collector determines at a certain point in time that the referent of a phantom reference is phantom reachable, then at that time or at some later time it will enqueue the reference. In order to ensure that a reclaimable object remains so, the referent of a phantom reference may not be retrieved: The get method of a phantom reference always returns null. Unlike soft and weak references, phantom references are not automatically cleared by the garbage collector as they are enqueued. An object that is reachable via phantom references will remain so until all such references are cleared or themselves become unreachable.
上代码:
package multiThreading;
import java.lang.ref.PhantomReference;
import java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/5
*/
public class PhantomReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReferenceQueue referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue();
PhantomReference phantomReference = new PhantomReference<Object>(new M(), referenceQueue);
phantomReference.enqueue();
System.out.println(phantomReference.get());
System.out.println(referenceQueue.poll());
}
}

大多数用与NIO中记录直接内存(堆外内存)的地址,用于记录被回收的对象的信息,方便以后回收堆外内存
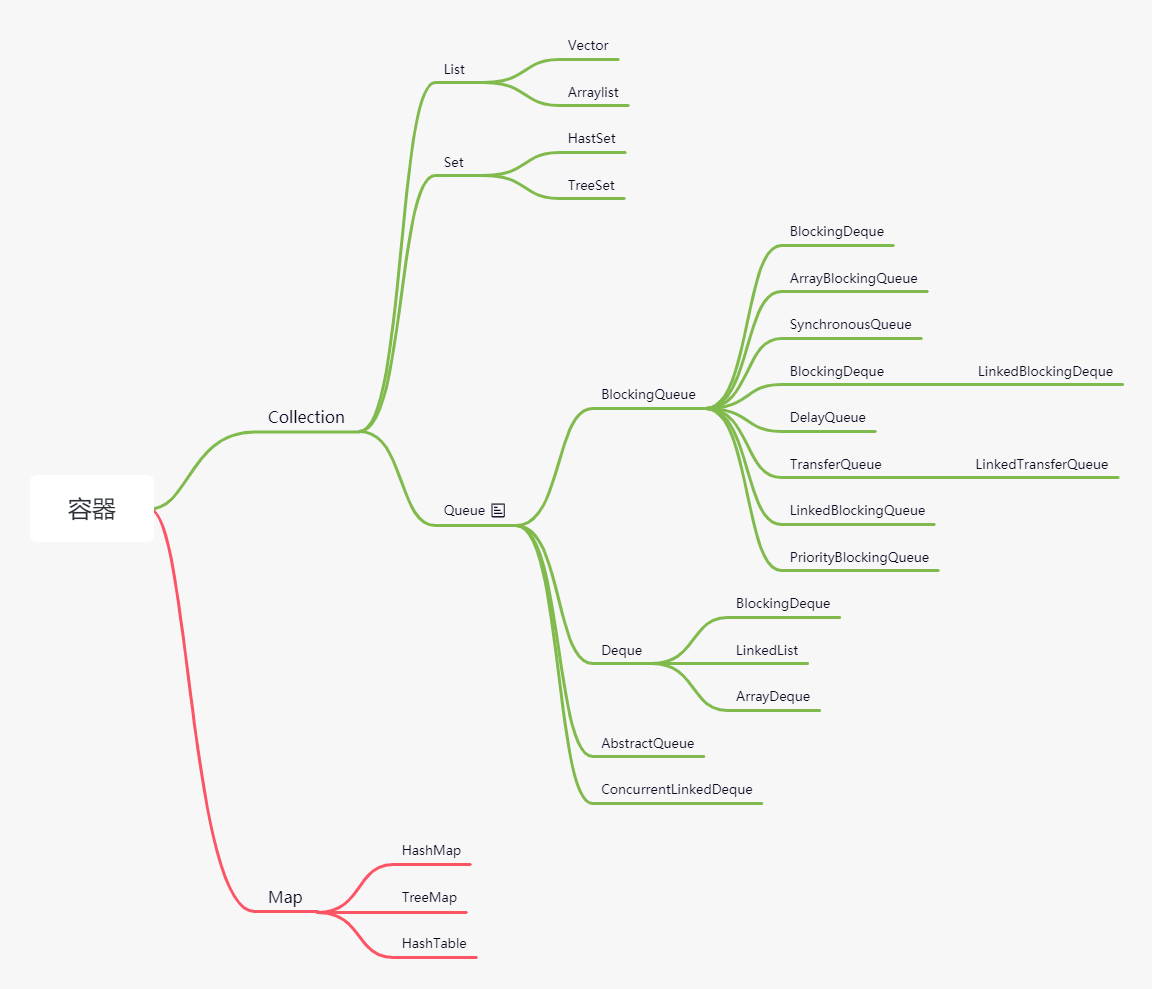
常见的容器
LinkedBlockingQueue
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class LinkedBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
// 阻塞
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
// 空
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
// 报错
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
}
}
ArrayBlockingQueue
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class ArrayBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// 阻塞
blockingQueue.put(i);
// 报错
blockingQueue.add(i);
// 不能添加
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer(i));
}
}
}
PriorityDeque
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class PriorityBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue();
blockingQueue.put(2);
blockingQueue.put(1);
System.out.println(blockingQueue);
}
}
DelayQueue
package multiThreading;
import com.mysql.cj.jdbc.MysqlDataSource;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class DelayQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BlockingQueue<MyTask> blockingQueue = new DelayQueue<>();
blockingQueue.put(new MyTask("a", 1000));
blockingQueue.put(new MyTask("b",500));
for (MyTask myTask : blockingQueue) {
System.out.println(myTask);
}
}
static class MyTask implements Delayed{
private String name;
private long time;
public MyTask(String name, long time){
this.name = name;
this.time = time;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public long getTime(){
return this.time;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.toNanos(time);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
if(this.time < ((MyTask)o).getTime()){
return -1;
}else if(this.time > ((MyTask)o).getTime()){
return 1;
}else {
return 0;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTask{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", time=" + time +
'}';
}
}
}
SynchronousQueue
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
* SynchronousQueue:要求必须先有消费者准备着,然后将元素放入队列中,元素才会被拿,否则一直被阻塞,确保队列中的元素被所有
* 消费者使用完
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronousQueue<Integer> synchronousQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try {
while (true){
System.out.println("到我表演了:"+synchronousQueue.take());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
synchronousQueue.put(1);
synchronousQueue.put(2);
}
}
LinkedTransferQueue
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedTransferQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class TransferQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LinkedTransferQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedTransferQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println("开始表演:"+blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
blockingQueue.put(1);
blockingQueue.put(2);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.size());
// System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
}
}
交替打印实现
synchronize+wait/notify
package multiThreading;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class AlternatePrint {
static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "123456789".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFGHI".toCharArray();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (lock){
for(char c:aI){
try {
System.out.print(c);
lock.wait();
lock.notify();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (lock){
for(char c:aC){
try {
System.out.print(c);
lock.notify();
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
volatile + 自旋
package multiThreading;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class AlternatePrint {
static final Object lock = new Object();
// 先打印数字,在打印字母
static volatile boolean pI = true;
static volatile boolean pC = false;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "123456789".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFGHI".toCharArray();
// 打印数字
new Thread(()->{
for(char c:aI){
if (pI){
System.out.print(c);
pI = false;
pC = true;
}
for(;!pI && c != aI[aI.length - 1];){}
}
}).start();
// 打印字母
new Thread(()->{
for(char c:aC){
if (pC){
System.out.print(c);
pI = true;
pC = false;
}
for(;!pC && c != aC[aC.length - 1];){}
}
}).start();
}
}
ReentrantLock
注意:wait/notify 不能和reentrantLock一起使用,只能结合synchronized使用,可以通过使用reentrantLock的await/signal来代替
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class AlternatePrint {
static final Lock LOCK = new ReentrantLock();
static final Condition CONDITION = LOCK.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "123456789".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFGHI".toCharArray();
new Thread(()->{
try{
LOCK.lock();
for (char c:aI){
System.out.print(c);
CONDITION.await();
CONDITION.signal();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
try{
LOCK.lock();
for (char c:aC){
System.out.print(c);
CONDITION.signal();
CONDITION.await();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}).start();
}
}
LockSupport
package multiThreading;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
/**
* Created by Intellij IDEA.
*
* @author JonnyJiang
* @date 2021/8/6
*/
public class AlternatePrint {
static Thread T1 = null;
static Thread T2 = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] aI = "123456789".toCharArray();
char[] aC = "ABCDEFGHI".toCharArray();
T1 = new Thread(()->{
for(char c:aI){
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(T2);
LockSupport.park();
}
LockSupport.unpark(T2);
});
T2 = new Thread(()->{
// 保证数字先打印
LockSupport.park();
for(char c:aC){
System.out.print(c);
LockSupport.unpark(T1);
LockSupport.park();
}
LockSupport.unpark(T1);
});
T1.start();
T2.start();
}
}
线程池
拒绝策略
abort
discard
discardOldest
CallerRuns
调用者处理任务