一、线程的状态
1.线程状态:
新建:当线程被创建的时候,会短暂处于这种状态。此时已经分配了系统资源,并执行了初始化。就绪:在这种状态下,只要调度器把cpu时间片分给线程就可以执行阻塞;线程可以运行,但摸个条件阻止它的运行。此时调度器将忽略线程,直到线程进入就绪状态才又可能执行操作死亡:处于死亡或终止状态的线程将不再是可以调度的,它的任务以结束,或不再是可运行的
二、线程进入阻塞的原因:
1.休眠时阻塞
class SleepBlock implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("InterruptedException");}System.out.println("Exiting SleepBlock run()");}}
2.等待阻塞
通过wait()将线程挂起,直到线程得到了notify()或notifyAll()消息(或者是concurrent类库中等价的signal或signalAll),线程才会进入就绪状态。
public synchronized void waxed() {//打蜡waxOn = true;notifyAll();}public synchronized void waitForWaxing() throws InterruptedException {while (waxOn == false)wait();}
3.I/O阻塞
等待某个输出/输入完成
//3.输入输出导致堵塞class IOBlock implements Runnable{private InputStream in;IOBlock(InputStream in){this.in=in;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println("等待输入");in.read();} catch (IOException e) {if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){System.out.println("Interrupted from block I/O");}else{throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("Exiting I/OBlock run()");}}
4.互斥时阻塞
任务试图在某个对象上调用其同步控制方法,但是对象锁不可用,因为另一个任务已经获取了这个锁。
class SynchroizedBlocked implements Runnable{public synchronized void f(){while (true){Thread.yiled();//程序将再次阻塞}public void run(){System.out.println("等待任务执行");f();//在f()循环的时候阻塞System.out.println("任务执行结束");}}
扩展:
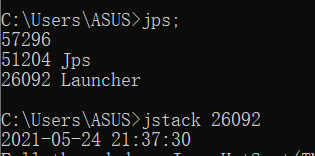
1.可以通过jps命令来查看阻塞的程序,通过jstack来查程序中阻塞的线程
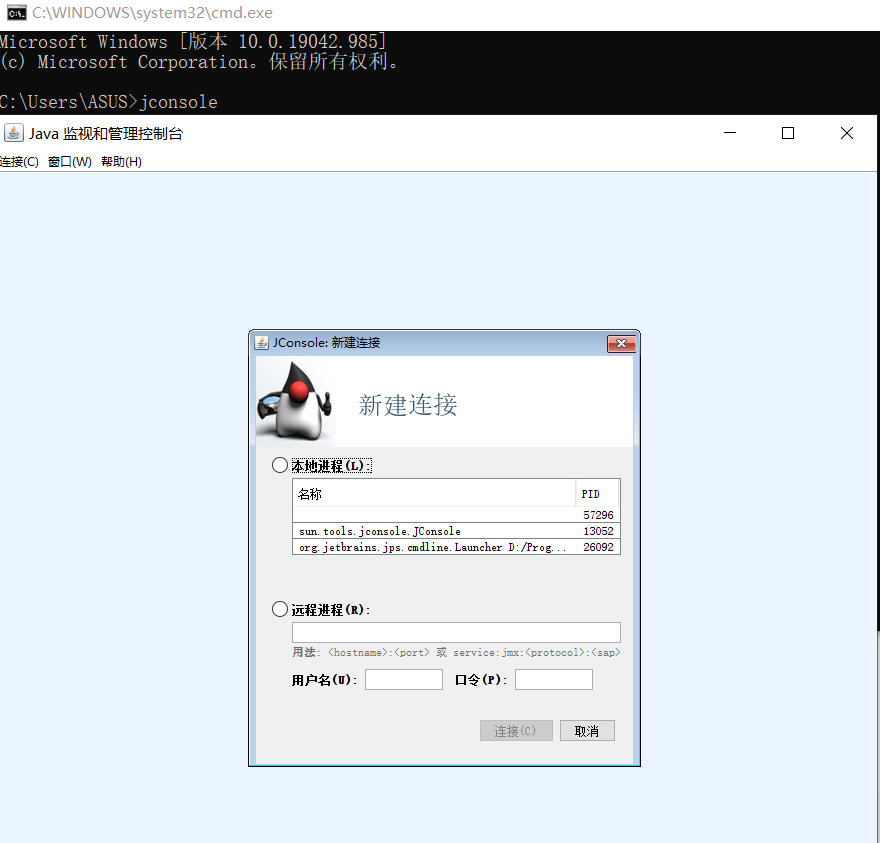
2.也可以通过jconsole来调用java后台监视系统:
三、 中断:
1.中断线程的方式:
Thread类中包含interrupt()方法,可以终止被阻塞的任务,被终止的任务将将抛出InterruptedException异常在Executor中调用showdowNow(),它将发送一个Interrupt()调用给它启动的所以线程。从而引发打断异常cancel()方法:是一种用来中断由Exceutor启动的单个线程的方式。Exceutor中的submit来创建线程,通过返回一个泛型的Future<?>,来调用cancel方法,来终止某个特定的任务。如果将true传统给该方法,那他就会拥有在该线程上调用interrupt()已停止这个线程的权限。
2.终止因休眠阻塞的线程:
/1.sleep导致阻塞class SleepBlock implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {try {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("InterruptedException");}System.out.println("Exiting SleepBlock run()");}}public class Interrupting {private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();static void test(Runnable r) throws InterruptedException {Future<?> f = executor.submit(r);TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);System.out.println("Interrupting "+r.getClass().getName());f.cancel(true);//中断任务System.out.println("Interrupting sent to"+r.getClass().getName());}//jstackpublic static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {test(new SleepBlock());//定时阻塞TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(50);System.out.println("系统关闭");System.exit(0);}}
3.中断I/O导致的阻塞(io阻塞不能中断)
class IOBlock implements Runnable{private InputStream in;IOBlock(InputStream in){this.in=in;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {System.out.println("等待输入");in.read();} catch (IOException e) {if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){System.out.println("Interrupted from block I/O");}else{throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("Exiting I/OBlock run()");}}public class Interrupting {private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();static void test(Runnable r) throws InterruptedException {Future<?> f = executor.submit(r);TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);System.out.println("Interrupting "+r.getClass().getName());f.cancel(true);//中断任务System.out.println("Interrupting sent to"+r.getClass().getName());}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {test(new IOBlock(System.in));//输入输出阻塞TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);System.out.println("系统关闭");System.exit(0);}}
我们发现,通过调用Future类中的cancel方法并不能中断IO,所以对于IO的阻塞去关闭底层的数据源:
public class CloseResource {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);InputStream inputStream = new Socket("localhost",8080).getInputStream();service.execute(new IOBlock(inputStream));service.execute(new IOBlock(System.in));TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(200);System.out.println("Shutting down all thread");service.shutdownNow();只能引发打断异常//关闭底层资源TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("Cloas"+inputStream.getClass().getName());inputStream.close();//只能中断SocketTimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("Cloas"+System.in.getClass().getName());System.in.close();//1.8以后不中断InputStream}}
4.中断由SynchroizedBlocked锁导致的阻塞:
示列一:
class SynchroizedBlocked implements Runnable{public synchronized void f(){while (true)Thread.yield();//有一个任务已经获得锁则其他任务进不来,该任务则一直在运行,从而造成阻塞}public SynchroizedBlocked(){new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {f();System.out.println("其他业务逻辑代码");}}.start();}@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("Trying to call f()");f();System.out.println("Exiting synchoizedBlock.run()");}}public class Interrupting {private static ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();static void test(Runnable r) throws InterruptedException {Future<?> f = executor.submit(r);TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);System.out.println("Interrupting "+r.getClass().getName());f.cancel(true);//中断任务System.out.println("Interrupting sent to"+r.getClass().getName());}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);System.out.println("系统关闭");System.exit(0);}}
示列二:
当被锁的任务为死循环时:
class SynchroizedBlocked implements Runnable{private volatile AtomicInteger count=new AtomicInteger();private volatile boolean falg=false;public synchronized void f(){while (!falg){int i = count.addAndGet(2);if (i==50)falg=true;}}
当循环次数超过设定的次数时候,原子性操作的Boolean将变为true从而跳出循环。
注意:我们去不能去终止正在试图获取Synchronized锁或者试图执行I/O操作的线程。
示列三:一个同一个互斥被同一个任务多次获得
package com.package21.multilock;public class MultiLock {public synchronized void f1(int count){if (count-->0){System.out.println("f1() and f2() "+count);f2(count);}}public synchronized void f2(int count){if (count-->0){System.out.println("f2() and f1() "+count);f1(count);}}public static void main(String[] args) {MultiLock multiLock = new MultiLock();new Thread (){@Overridepublic void run() {multiLock.f1(10);}}.start();}}
5.ReentranLock中断阻塞:
无论何时,只要任务不可中断式被阻塞,都有潜在锁住程序的可能,而ReentranLock上阻塞的任务具备可以被中断的能力。
public class BlockedMutex {private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();public BlockedMutex() {lock.lock();//加锁}public void f() {try {lock.lockInterruptibly();//如果当前线程未被中断则获得锁,如果当前线程被中断则出现异常。System.out.println("lock f()");} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("Interrupted form lpck in f()");}}}class BlockedMutex_Two implements Runnable {BlockedMutex blockedMutex = new BlockedMutex();@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("waiting for f() in BlockedMutex");blockedMutex.f();System.out.println("Broken out of blocked call");}}class Interrupting2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(new BlockedMutex_Two());thread.start();TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("Issuing t.interrupt()");thread.interrupt();}}
四、检查中断:
1. 通过interrupted()方法来检查线程是否中断
//标识类class NeedsCleanup {private final int id;public NeedsCleanup(int ident) {id = ident;System.out.println("NeedsCleanup " + id);}public void cleanup() {System.out.println("Cleaning up " + id);}}class Blocked3 implements Runnable {private volatile double d = 0.0;public void run() {try {while (!Thread.interrupted()) {//检查线程是否中断NeedsCleanup n1 = new NeedsCleanup(1);try {System.out.println("Sleeping");TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);NeedsCleanup n2 = new NeedsCleanup(2);try {System.out.println("Calculating");for (int i = 1; i < 2500000; i++)d = d + (Math.PI + Math.E) / d;System.out.println("Finished time-consuming operation");} finally {n2.cleanup();}}finally {n1.cleanup();}}System.out.println("Exiting via while() test");} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("Exiting via InterruptedException");}}}public class InterruptingIdiom {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Thread t = new Thread(new Blocked3());t.start();TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2010);t.interrupt();}}
注意:所有可能中断需要被清理的对象创建操作的后面。都必须紧跟Try-finally子句,从而使无论run循环如何退出,清理都会发生。

