字节流:I/O中以字节形式输入和输出的流
字节流概述:计算机中无论是文本还是视屏,图片、音频。都是以二进制(字节形式存在的),根据数据的传输方法分为输入流和输出流。
一、字节输入流(读取):
所有的字节输入流都继承InputStream,他的作用是用来表示那些从不同数据源产生输入的类;
1.字节流读写文件:在java中提供了两个类专门用来处理文件的读写操作
①:FileInputStream:是InputStream的子类专门用来读取文件中的数据
public class Example01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("src/text.txt");int read=0;while ((read=file.read())!=-1) {System.out.print((char) read);}file.close();}}Output:hello
②:通过FileOutputStream**把数据写入文件 **
public class Example02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("out.txt");String str="heole word";//将字符串转换为字节流fo.write(str.getBytes());fo.close();}}
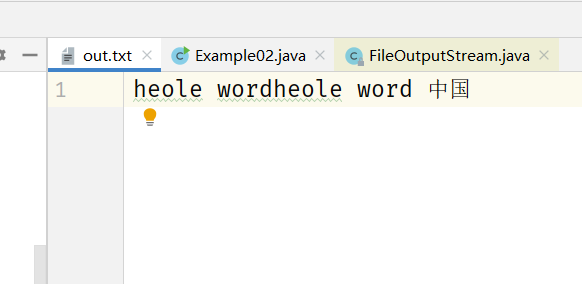
运行结果:<br />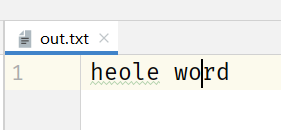<br /> ②-1:如果通过FileOutputStream向一个已经存在数据的文件中写入的话,那么该文件的数据将被覆盖。可以通过在FileOutputStream的构造器中**把append的参数设置为true,就不会覆盖之前数据并写入新的数据。 **
public class Example02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream("out.txt",true);String str="heole word 中国";//将字符串转换为字节流fo.write(str.getBytes());fo.close();}}
运行结果:
 5
5
二、文件的拷贝
public class CopyDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//先读取需要拷贝的文件FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream("./image.png");//创建文件的写入FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("./aa.png");int len=0;long beginTime=System.currentTimeMillis();//获得文件拷贝前的系统时间System.out.println(beginTime);while ((len=input.read())!=-1){output.write(len);//每读取一次文件的同时便写入}long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(endTime);System.out.println("花费的时间为:"+(endTime-beginTime)+"毫秒");input.close();output.close();}}
三、字节流的缓冲区:
我们在上一步进行文件的拷贝时候,是一个一个字节的进行拷贝的,如果文件过大,则拷贝的时间就会很长,所以为了提高传输的效率,我们可以定义一个字节数组来当成缓冲区,在拷贝文件的时候,就可以先将文件读入的字节数组中,然后在将数组中的文件一次性的写入新文件中。
public class ByteDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("./image.png");FileOutputStream OutputStream = new FileOutputStream("D:\\ideawork\\project03\\src\\com\\package18\\cc.png");int temp=0;byte [] bytes=new byte[10241];//缓冲区1024字节,文件缓冲区的容量越小时间越长long beingTime=System.currentTimeMillis();while ((temp=inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){OutputStream.write(bytes);}long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("文件拷贝的时间"+(endTime-beingTime)+"毫米");inputStream.close();OutputStream.close();}}OutPut:文件拷贝的时间3毫米
四、字节缓冲流:
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream这两个流的内部都定义一个大小为8192字节的数组。所以这两个流自带缓冲区。
源码所示:
publicclass BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192;protected volatile byte buf[];//通过两个构造器进行数组的赋值public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {this(in, DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);}public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {super(in);if (size <= 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");}buf = new byte[size];}
<br />
public class BufferedStreamTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedInputStream buffinput = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("./image.png"));BufferedOutputStream buffout = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\idea work\\project03\\src\\com\\package18\\ccccc.png"));int leng=0;long beginTime=System.currentTimeMillis();while ((leng=buffinput.read())!=-1){buffout.write(leng);}long l = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("结束时间"+(l-beginTime));buffinput.close();buffout.close();}}

