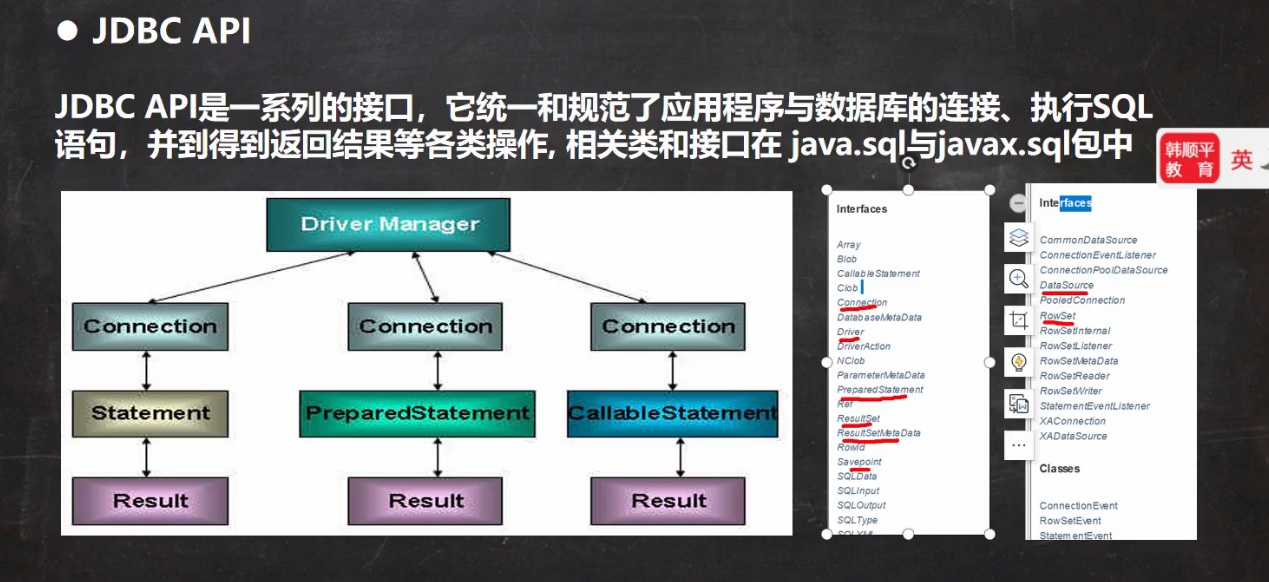
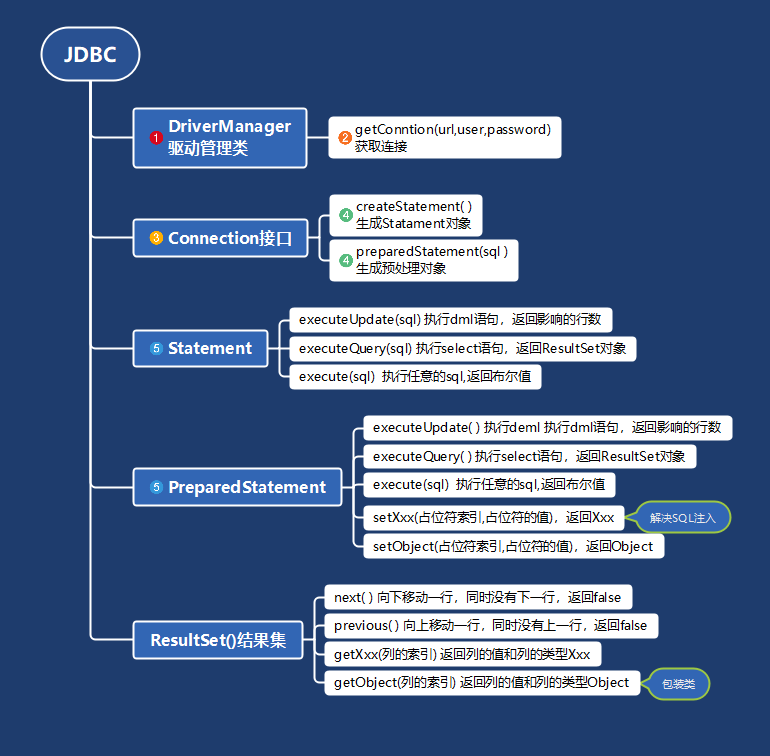
1 JDBC概述
2 JDBC快读入门
编写步骤:
- 注册驱动 - 加载Driver类
- 获取连接 - 得到Connection (与数据库的连接)
- 执行增删改查 - 发送SQL命令给mysql执行 (执行操作和返回结果)
-
3 课堂练习

-- 创建测试演员表CREATE TABLE actor(id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',gender CHAR(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '女',birthday DATETIME,cellphone VARCHAR(11));
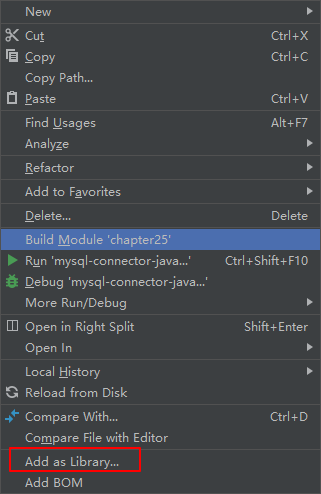
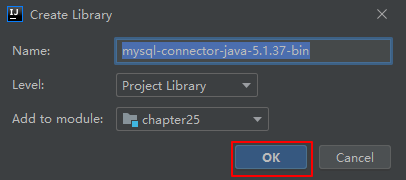
4 加载jar包
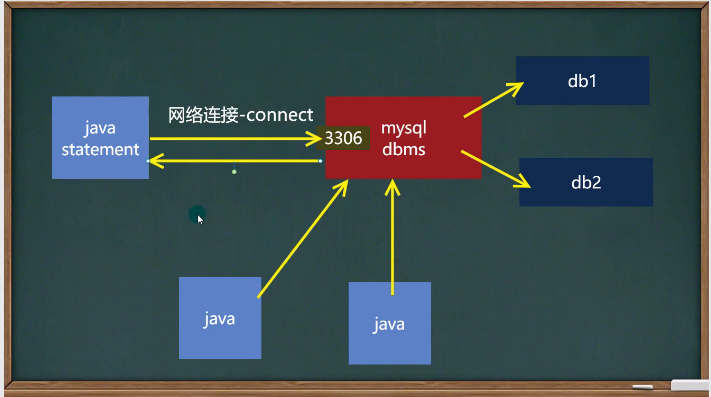
5 程序与mysql建立连接的原理图
步骤
Driver 驱动
- new
- Properties 用户和密码
- new
- property(“user”,”root”)
- property(“password”,”123456”);
- Connection 连接
- driver.connect(url,properties)
- Statament 执行Sql
- createStatement()
- executeUpdate(sql)
-
代码dml
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {//1.注册驱动Driver driver = new Driver();//创建driver对象//2.得到连接//1) jdbc:mysql:// 规定标准协议,通过JDBC的方式连接musql//2) localhost 本机,或者IP地址//3) 3306 表示mysql监听的端口//4) hsp_db02 连接msyql的那个数据库//5) mysql连接的本质就是socket连接String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02";//将用户名和密码放入properties对象中Properties properties = new Properties();//说明:user和password是规定好的properties.setProperty("user", "root");//用户properties.setProperty("password", "crossfire395612");//密码//Driver每个驱动必须实现的接口,根据给定的url连接数据库//connect就是网络连接Connection connect = driver.connect(url, properties);//3.执行sqlString sql = "insert into actor values(1,'刘德华','男','1961-9-27','110')";//statement:用于发送执行静态sql语句并返回结果的对象Statement statement = connect.createStatement();//executeUpdate执行sql语句,返回的结果代表受影响数据库的行数,等于0数据添加失败int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");//4.关闭连接资源statement.close();connect.close();}
mysql更改密码
mysqladmin -uroot -pcrossfire395612 password root
6 连接数据库的五种方式
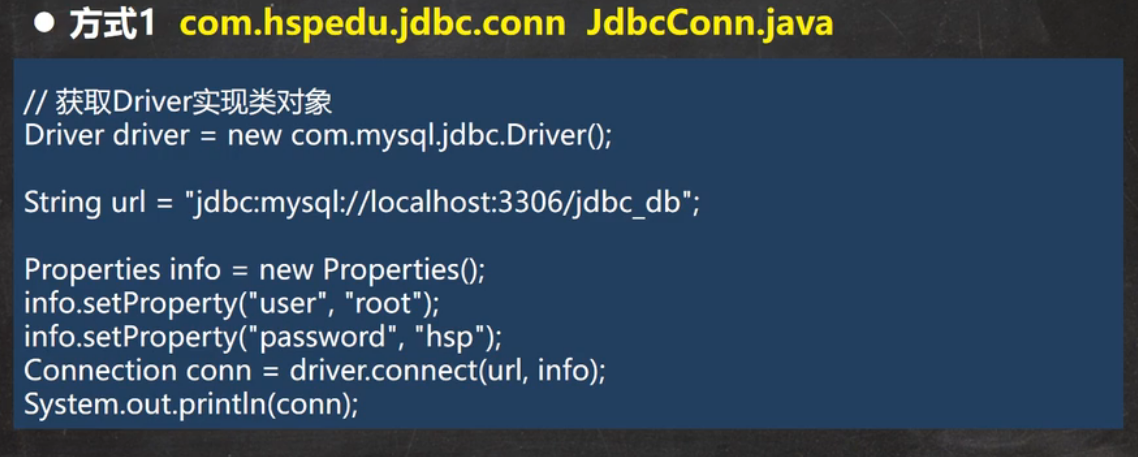 ```java
public void connect01() throws SQLException {
Driver driver = new Driver();
String url = “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02”;
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty(“user”,”root”);
info.setProperty(“password”,”root”);
Connection conn = driver.connect(url, info);
System.out.println(conn);
```java
public void connect01() throws SQLException {
Driver driver = new Driver();
String url = “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02”;
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty(“user”,”root”);
info.setProperty(“password”,”root”);
Connection conn = driver.connect(url, info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
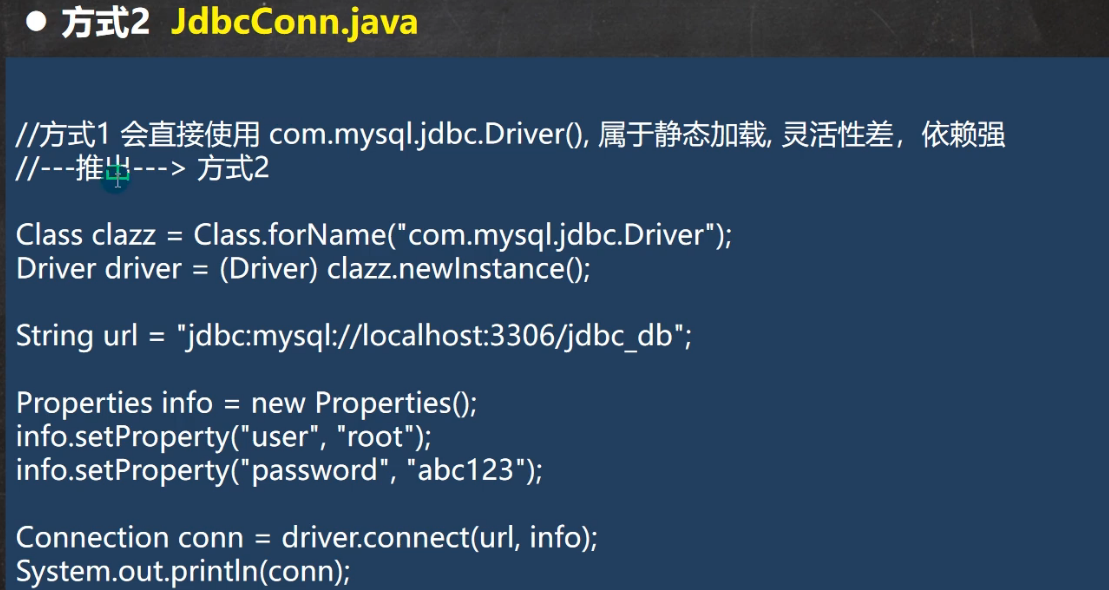```java//方式二:使用反射加载Driver类public void connect02() throws Exception {//使用反射加载Driver类.动态加载,更加灵活,减少依赖性Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");Driver driver = (Driver)aClass.newInstance();String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02";Properties pro = new Properties();pro.setProperty("user","root");pro.setProperty("password","root");Connection conn = driver.connect(url, pro);System.out.println(conn);}
DriverManager优势
DriverManager-用户管理JDBC驱动的基本服务
getConnection( ) : 连接数据库
registerDriver() :注册给定的驱动程序DriverManager
//方式三:使用DriverManager替换Driver进行统一管理public void connect03() throws Exception {//使用反射加载DriverClass<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");Driver driver = (Driver)aClass.newInstance();String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02";String user = "root";String password = "root";DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);//注册Driver驱动Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);System.out.println(conn);}
底层原码分析—注册了Driver:
- 静态代码块,在类加载时,会执行一次
- 注册Driver的registerDriver在静态代码块已经完成
Class.forName()省略原因:
在jdk1.5之后,不需要显示调用Class.forName()注册驱动,因为jar(里面写好了)启动的时候自动调用了
//方式四:使用Class.forName自动完成注册驱动,简化代码public void connect04() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {//使用反射加载Driver类//在加载Driver类时,完成注册/*底层分析:1.静态代码块,在类加载时,会执行一次2.注册Driver的registerDriver在静态代码块中*/Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02";String user = "root";String password = "root";Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);System.out.println(conn);}
配置文件
#properties配置文件user=rootpassword=rooturl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
//方式五:在方式4的基础上改进,增加配置文件,让连接mysql更加灵活public void connect05() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {//通过Properties对象获取配置文件信息Properties properties = new Properties();properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));//获取相关值String user = properties.getProperty("user");String password = properties.getProperty("password");String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");String url = properties.getProperty("url");Class.forName(driver);//建议写上,驱动加载Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);System.out.println(connection);}
7 课堂练习

CREATE TABLE news(id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,title VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',publish_time DATETIME,content TEXT);
public class JdbcTest {public void connect05() throws Exception {Properties pro = new Properties();pro.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));String driver = pro.getProperty("driver");String url = pro.getProperty("url");String user = pro.getProperty("user");String password = pro.getProperty("password");//1.加载驱动Class.forName(driver);//2.获取连接Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);//3.执行SQL// String sql = "insert into news(title,publish_time,content) values('特朗普集团遭刑事调查','2021-05-16 16:50:20','据美国媒体报道,纽约总检察长办公室正与曼哈顿检察院合作,积极调查特朗普集团的刑事犯罪问题,但目前尚未对调查的具体细节透露更多信息。')";// String sql = "update news set title='谷歌正式发布Android' where id=1";String sql = "delete from news where id=3";Statement state = conn.createStatement();int rows = state.executeUpdate(sql);System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功了" : "执行失败了");//4.关闭连接资源conn.close();state.close();}}
8 Result结果集

resultset数据库返回的结果集,通过SQL查询语句生成
resultset对象保持光标指向当前行,最开始光标位于第一行之前,next()将光标移动到下一行
如果resultset没有更多行时返回false,可以通过while循环来遍历结果集
课堂练习
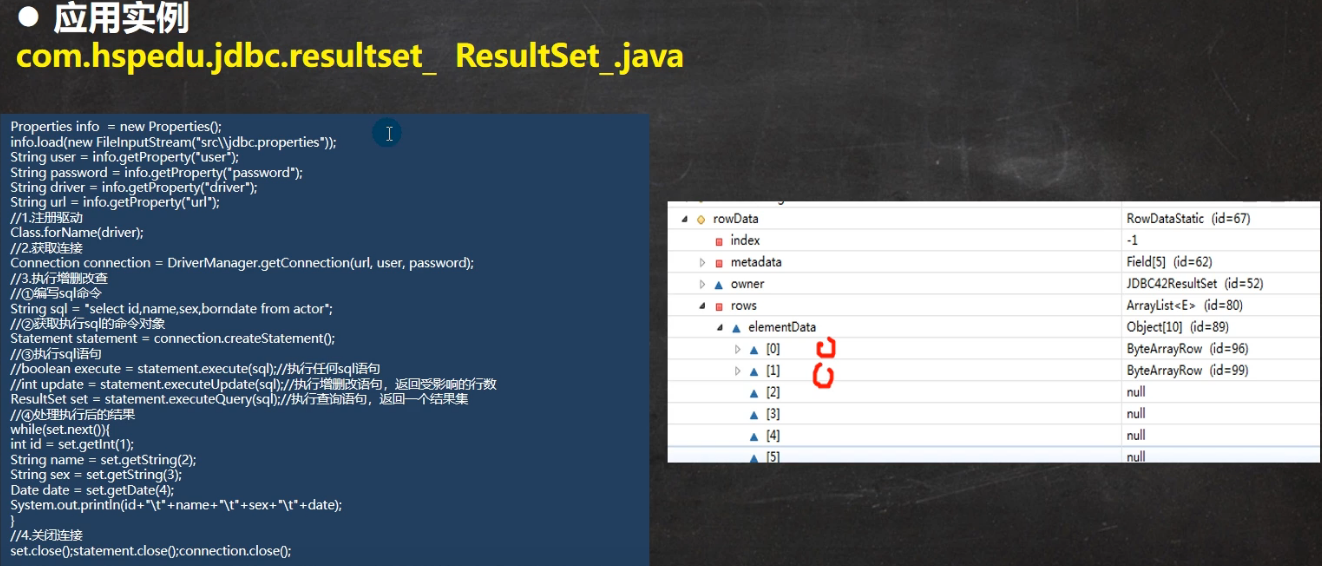
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, IOException {//通过Properties对象获取配置文件的信息//1.加载驱动Class.forName(driver);//2.得到连接Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);//3.得到StatementStatement state = conn.createStatement();//4.组织sqlString sql = "select id,name,gender,birthday from actor";//执行给定的SQL语句,改语句返回单个ResulSet对象ResultSet resultSet = state.executeQuery(sql);//5.循环取出数据while(resultSet.next()){//让光标向后移动,如果没有更多行,返回falseint id = resultSet.getInt(1);//获取该行第一列数据String name = resultSet.getString(2);String gender = resultSet.getString(3);Date birthday = resultSet.getDate(4);System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + gender + "\t" + birthday);}//6.关闭连接resultSet.close();state.close();conn.close();}
Result结果集执行原理
9 SQL注入


-- SQL注入-- 输入用户名为 1' or-- 输入密码为 or '1'='1SELECT * FROM ADMINWHERE NAME = '1' OR' AND pwd = 'OR '1'='1';-- NAME = '1'-- ' AND pwd = '-- '1'='1' 永远成立
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);//让用户输入管理员名和密码System.out.print("请输入管理员的名字:");//next():当接收空格或'就是表示结束String admin_name = scanner.nextLine();//nextLine():如果希望看到SQL注入,需要用nextLine,回车表示结束System.out.print("请输入管理员的密码:");String admin_pwd = scanner.nextLine();//配置Propare省略Class.forName(driver);Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);String sql = "select * from admin where name = '" + admin_name + "'and pwd='" + admin_pwd + "'";Statement state = conn.createStatement();ResultSet resultSet = state.executeQuery(sql);if (resultSet.next()) {//如果查询到一条记录,则说明该管理员存在System.out.println("恭喜登录成功");}else {System.out.println("恭喜登录失败");}state.close();conn.close();resultSet.close();}
10 预处理PrparedStatement
预处理好处


public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//用户输入管理员和密码//Poppareties配置文件//1.注册驱动Class.forName(driver);//2.得到连接Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);//3.得到PreparedStatement//3.1组织sql,sql的?相当于占位符String sql = "select * from admin where name=? and pwd=?";//3.2 PreparedStatement对象实现了PreparedStatement接口实现类的对象PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//3.3给 ? 赋值preparedStatement.setString(1,admin_name);preparedStatement.setString(2,admin_pwd);//4. 执行SQL语句// 如果执行的是dml(update,insert,delete) executeUpdate()// 这里执行excuteQuery,不要在写sqlResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();if(resultSet.next()){System.out.println("恭喜你,登录成功");}else {System.out.println("很遗憾,登录失败");}preparedStatement.close();resultSet.close();connection.close();}
预处理dml
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//用户输入管理员和密码//Poppareties配置文件//3.得到PreparedStatement//3.1组织sql,sql的?相当于占位符//添加记录//String sql = "insert into admin values(?,?)";//String sql = "update admin set pwd=? where name=?";String sql = "delete from admin where name=?";//3.2 PreparedStatement对象实现了PreparedStatement接口实现类的对象PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//3.3给 ? 赋值//4. 执行dml语句使用executeUpdateint rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");//关闭连接资源}
练习
作业
DML
//insertString sql = "insert into admin values(?,?)";PreparedStatement pre = conn.prepareStatement(sql);pre.setString(1,admin_name);pre.setString(2,admin_pwd);int rows = pre.executeUpdate();System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");//delectString sql = "delete from admin where name=?";PreparedStatement pre = conn.prepareStatement(sql);pre.setString(1,admin_name);int rows = pre.executeUpdate();System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");//updateString sql = "update admin set name=? where name=?";PreparedStatement pre = conn.prepareStatement(sql);pre.setString(1,admin_newName);pre.setString(2,admin_name);int rows = pre.executeUpdate();System.out.println(rows > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行失败");
select
String sql = "select * from admin";PreparedStatement pre = conn.prepareStatement(sql);ResultSet resultSet = pre.executeQuery();while(resultSet.next()){String name = resultSet.getString(1);String pwd = resultSet.getString(2);System.out.println(name + "\t" + pwd);}
11 总结方式五操作mysql过程
- DriverManger 驱动管理类
- 操作DriverManger的getConnetion(url,user,password)—>得到connection对象
- Connection接口
- 操作connection对象的crateStatement() —>生成statementd对象
- 操作connection对象的preparedStatement(sql) —>生成preparedstatement对象(预编译对象)
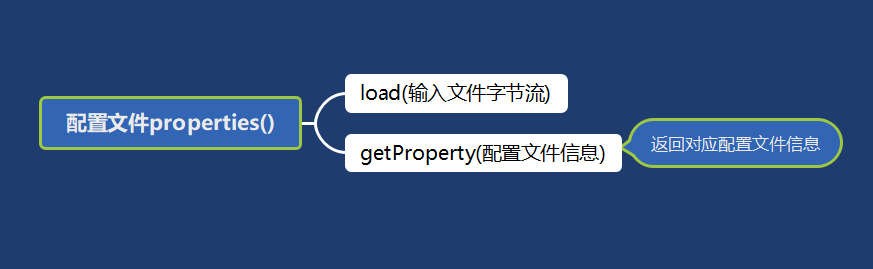
12 获取配置信息
- load()
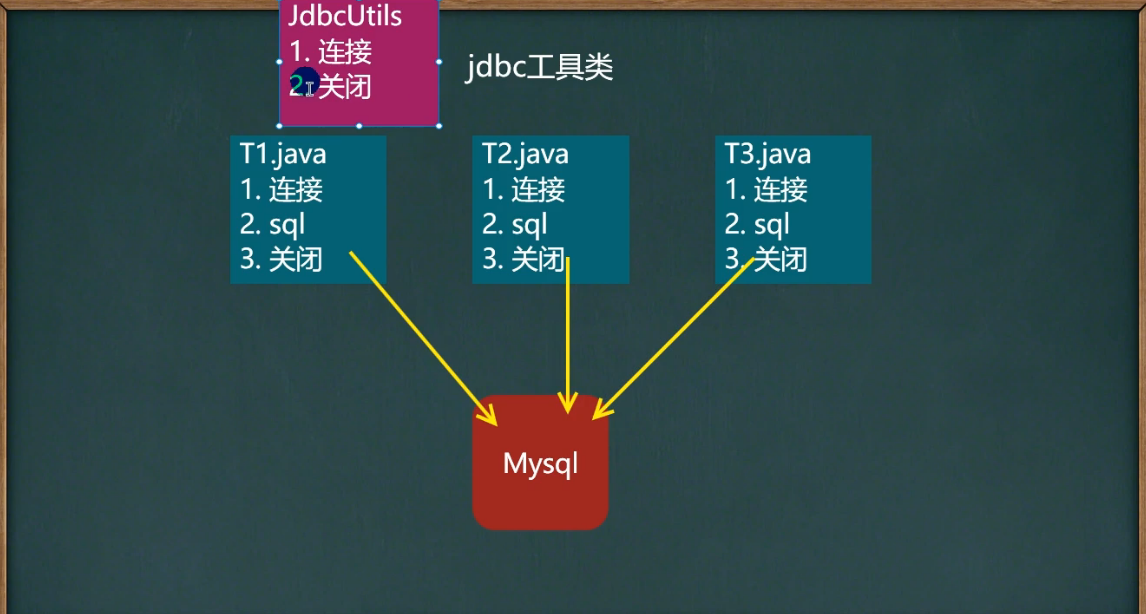
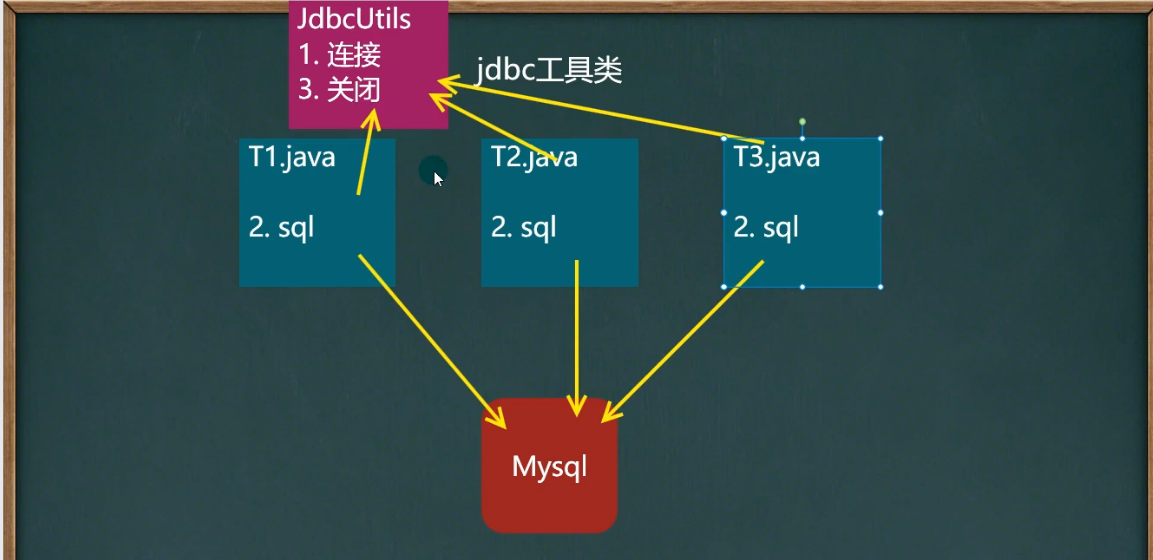
13 封装JDBCUtils(获取连接和关闭连接)
说明:
在jdbc操作种,获取连接和释放资源是经常使用到的操作,可以将其封装为工具类
JDBCUtils
JDBC封装工具类原理
代码实现
public class JDBCUtils {//定义相关属性(4个)private static String user; //用户名private static String password; //密码private static String url; //连接数据库标准private static String driver; //驱动名//在static代码块去初始化,随类加载static {try {Properties properties = new Properties();properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));//读取相关属性值user = properties.getProperty("user");password = properties.getProperty("password");url = properties.getProperty("url");driver = properties.getProperty("driver");} catch (IOException e) {//在实际开发中,这样处理的优点://1.将编译时异常转成运行时异常抛出去//2.调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以默认处理该异常,比较方便throw new RuntimeException(e);}}//连接数据库,返回Connectionpublic static Connection getConnection(){try {return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);} catch (SQLException e) {//1.将编译时异常转成运行时异常抛出去//2.调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以默认处理该异常,比较方便throw new RuntimeException(e);}}//关闭相关资源//1.ResultSet 结果集//2.Statement或者PreparedStatement//3.Connection//4.如果需要关闭资源,就传入对象,否则传入nullpublic static void close(ResultSet set, Statement statement, Connection connection){//Statement是PreparedStatement的父接口,因此可以接收2个实现类//判断是否为nulltry {if(set != null){set.close();}if(statement != null){statement.close();}if(connection != null){connection.close();}} catch (SQLException e) {//1.将编译时异常转成运行时异常抛出去//2.调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以默认处理该异常,比较方便throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
总结代码:
编译异常变运行时异常的优点:
- 将编译时异常转成运行时异常抛出去
调用者,可以选择捕获该异常,也可以默认处理该异常,比较方便
throw new RuntimeException(e);
调用父类就可以调用子类:
关闭Statement或者PreparedStatement,只用父类Statement
因为Statement是PreparedStatement的父接口,因此可以接收2个实现类工具类属性和方法都是静态
- 因为是工具类要求方便,节省了创建对象
- 方法和属性都是静态的,直接调用
如果有些功能是必须项,可以写在静态代码块中,随类加载(调用者无需调用)
调用工具类代码:
public void testDML(){//insert,update,delete//1.得到连接Connection connection = null;//2.组织一个sqlString sql = "update actor set name = ? where id = ?";//测试delete 测试insertPreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;//3.创建PreparedStatement对象try {//因为连接有异常,捕获起来,如果出现异常下面可以看到出错信息connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//给占位符赋值preparedStatement.setString(1,"曹德旺");preparedStatement.setInt(2,4);//执行preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//结果不一定要接收} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {//关闭资源JDBCUtils.close(null,preparedStatement,connection);}}
finnaly
无论是否出现异常还是正常执行,finnaly一定会执行 ```java //执行sql,得到结果集 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //遍历该结果集 while(resultSet.next()){ int id = resultSet.getInt(“id”); String name = resultSet.getString(“name”); String gender = resultSet.getString(“gender”); String birthday = resultSet.getString(“birthday”); String cellphone = resultSet.getString(“cellphone”); System.out.println(id + “\t” +name + “\t” +gender + “\t”
+ birthday + "\t" + cellphone);
}
疑问总结???????????
- import java.sql.Date 只有日期,没有时间