事物
事物的基本介绍
总结数据库:
执行不会提交
- 当自动提交关闭时,执行成功SQL语句,不会把数据提交到数据库
-
默认执行就提交
课堂练习
没有事务
//操作转账的业务//1.获得连接Connection connection = null;//2.组织SQ语句String sql = "update account set balance = balance + ? where name = ?";//3.创建PreparedStatement对象PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;try {connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();//默认情况下,connection是默认自动提交preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//给?赋值preparedStatement.setDouble(1,-100);preparedStatement.setString(2,"马云");//执行preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第一条int i = 1 / 0;//抛出异常//马化腾//给?赋值preparedStatement.setDouble(1,100);preparedStatement.setString(2,"马化腾");//执行preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//执行第二条} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//关闭资源
有事务
try {connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();//默认情况下,connection是默认自动提交//将connection 设置为手动提交connection.setAutoCommit(false);//相当于开启了事务preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//给?赋值,//第一条preparedStatement.setDouble(1,-100);preparedStatement.setString(2,"马云");//执行preparedStatement.executeUpdate();//给?赋值, //第二条preparedStatement.setDouble(1,100);preparedStatement.setString(2,"马化腾");//执行preparedStatement.executeUpdate();connection.commit(); //提交事物} catch (SQLException e) {//事务回滚,即撤销执行的SQL//默认回滚事务开始的状态try {connection.rollback();} catch (SQLException throwables) {throwables.printStackTrace();}e.printStackTrace();}//关闭资源
总结事务
try抛出异常之后,catch捕获异常,因此这里进行回滚rollback()
- 事务回滚,即撤销执行的SQL;默认回滚事务开始的状态
commit() 写在java执行sql后面;即catch之前,excuteUpdate之后
2 批处理
2.1基本介绍

2.2批处理总结:
优点:
-
注意:
jdbc配置文件加url后加参数 ?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
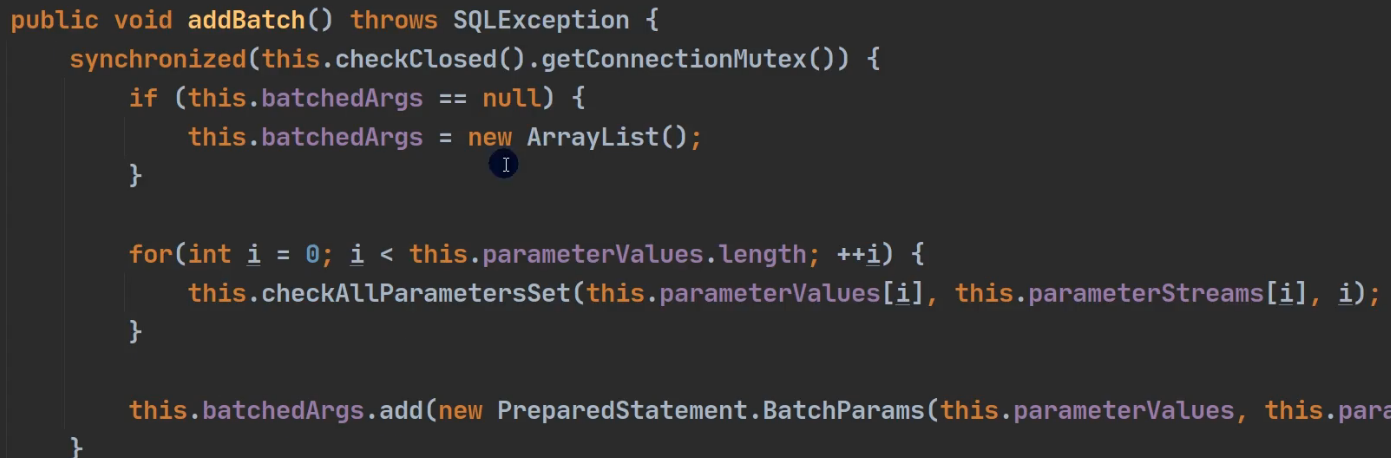
- addBatch()装好之后,然后executeBacth()再执行,最后clearBatch()清空;
发车顺序:(装数据,执行,清空)
就像发车一样,来回拉不同的客人,preparedStatement来回执行不同的数据
2.3 课堂练习
演示向admin表中添加5000条数据
注意:jdbc配置文件加url后加参数 ?rewriteBatchedStatements=true
CREATE TABLE admin3( id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, username VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL, PASSWORD VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL);
a. 传统方式
//连接String sql = "insert into admin2 values(null,?,?)";PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//开始时间for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {preparedStatement.setString(1,"jack" + i);preparedStatement.setString(2,"666");preparedStatement.executeUpdate();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("传统方式耗时=" + (end - start));//传统方式耗时=17939//关闭连接
b. 批处理方式
//连接String sql = "insert into admin3 values(null,?,?)";PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//开始时间for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {preparedStatement.setString(1,"Andy" + i);preparedStatement.setString(2,"123456");//1.将sql语句加入到批处理包中preparedStatement.addBatch();//当有1000条记录时,在批量执行if((i + 1) % 1000 == 0){//满1000条sql//2.批量执行preparedStatement.executeBatch();//3.清空1000条sqlpreparedStatement.clearBatch();}}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("批量处理方式耗时=" + (end -start));//批量处理方式耗时=178//关闭连接
2.4 源码分析
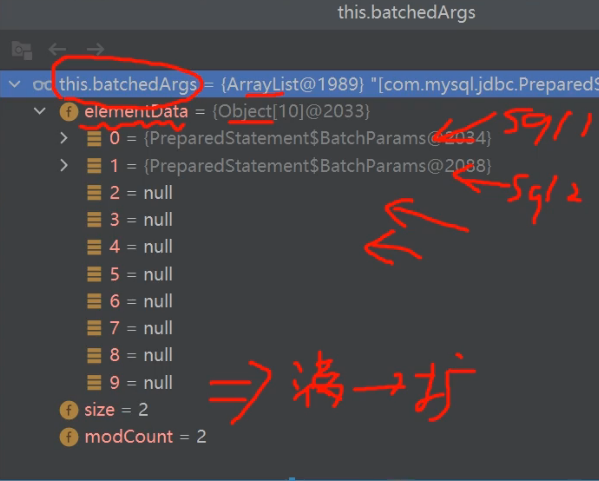
将sql语句放到批处理包中—>源码分析(preparedStatement.addBatch())
- 第一次创建Arraylist - elementDate =>Obejct[]
- elementDate =>Obejct[]就会存放我们预处理的sql语句
- 当 elementDate满后,就按照1.5扩容
- 当添加到指定的值后,就会executeBatch
- 批量处理减少发生sql语句的网络开销,且减少了编译次数,因此效率提高
概括总结:addBatch()会数据放到一个集合里面,等到了指定值之后,就执行executeBatch
3 数据库的连接池-解决连接复用问题
3.1 问题引出
测试
原因分析连接:
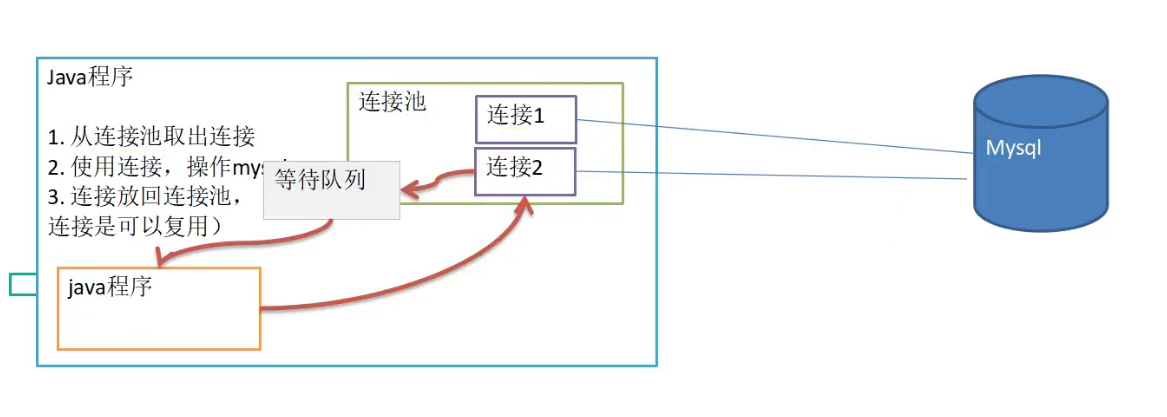
- 连接池放入指定数量的连接,通过网络跟数据库形成了通道
- 程序从连接池取出连接
- 使用完连接之后,放回连接池
-
3.3 连接池原理图:
3.4 数据库连接池种类
 数据库连接池总结
数据库连接池总结
3.5 C3P0 引用实例

连接池代码体现是DataSource(数据源),连接和管理交给数据源了,以后就是数据源帮连接
因此数据源需要知道(user、password、driver以及url)
初始化连接:程序运行创建好的
最大连接:当程序连接超过初始化连接,会创建新的连接,最多所有连接不能超过最大连接
等待队列:当程序连接超过最大连接,会进入等待队列,等待其他连接释放
comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);//程序运行之后连接池放10个连接//方式1:相关参数,在程序中指定user,url,password等public void testC3P0_01() throws Exception {//1.创建一个数据源对象ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();//2.通过配置文件获取相关信息Properties properties = new Properties();properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\mysql.properties"));//读取相关属性值String user = properties.getProperty("user");String password = properties.getProperty("password");String url = properties.getProperty("url");String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");//给数据源comboPooledDataSource设置相关参数//注意:连接管理由comboPooledDataSource来管理的comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driver);//连接数据库的驱动comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(url);comboPooledDataSource.setUser(user);comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(password);//初始化数据源连接数//初始化连接:程序运行创建好的//最大连接:当程序连接超过初始化连接,会创建新的连接,最多所有连接不能超过最大连接//等待队列:当程序连接超过最大连接,会进入等待队列,等待其他连接释放comboPooledDataSource.setInitialPoolSize(10);//程序运行之后连接池放10个连接//最大连接数comboPooledDataSource.setMaxPoolSize(50);//测试连接池的效率,测试连接mysql5000次long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {//这个是实现DataSource接口的方法Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();connection.close();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("C3P0 5000连接,耗时" + (end - start));//C3P0 5000连接,耗时2300}
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource("hsp_edu");//测试连接池的效率,测试连接mysql5000次long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 5000; i++) {Connection connection = comboPooledDataSource.getConnection();connection.close();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("C3P0的第二种方式:5000连接,耗时" + (end - start));//C3P0的第二种方式:5000连接,耗时2157
修改配置文件c3p0-config.xml
url、driver、user、password
最大连接,最小连接,初始化连接、每次增长连接、每个连接最多执行的语句
3.5 DRUID 引用实例
数据源是帮忙管理的数据库的连接,因此需要驱动,仅仅在上面做了包装做了缓冲池而已
配置文件
#key=valuedriverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hsp_db02?rewriteBatchedStatements=trueusername=rootpassword=root#initial connection SizeinitialSize=10#min idle connecton sizeminIdle=5#max active connection sizemaxActive=50#max wait time (5000 mil seconds)maxWait=5000
maxWait=5000
等待队列:超过5秒还没有取到连接,放弃等待
解决方案:调整initialSize和MaxActive
//1.加入Druid jar包//2.加入配置文件,将文件拷贝项目的src目录//3.创建properties对象,读取配置文件Properties properties = new Properties();properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));//4.创建一个指定参数的数据库连接池,Druid的连接池//连接池创建根据配置文件properties的参数作为依据DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);long start = System.currentTimeMillis();for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();connection.close();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("druid连接池 操作500000次,耗时=" + (end - start));//druid连接池 操作500000次,耗时=3517
mysql数据库厂商原生和Druid是Alibaba第三方实现
- 前后者实现java接口的方式不同,因此两者实现类是不同的(动态绑定)
- 前者的connection是创建连接,而后者是取到连接
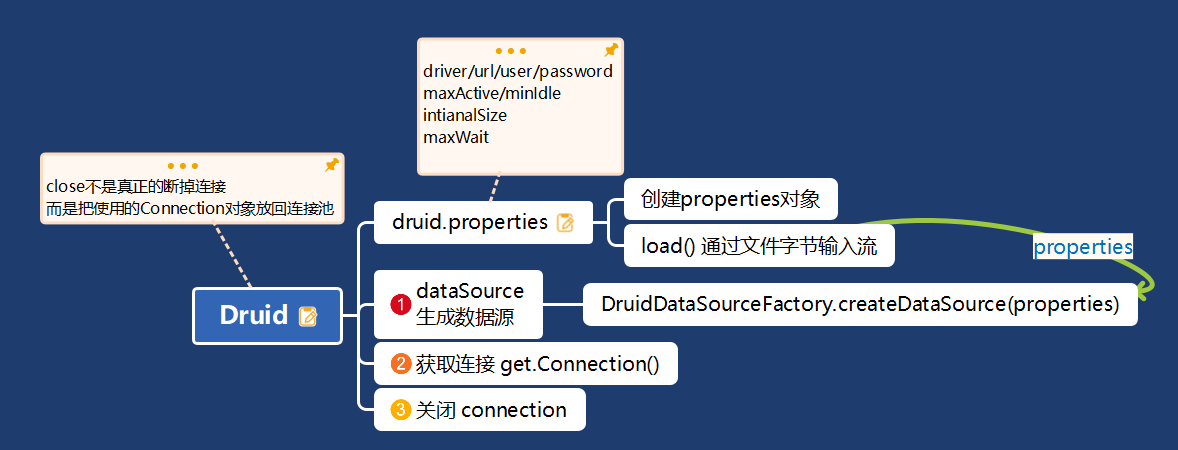
前者close是真正关闭连接,后者是把连接引用断掉,连接放到数据源中
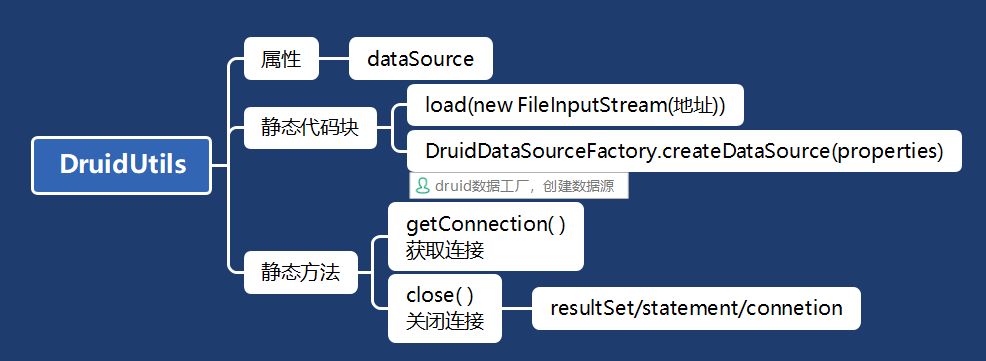
把Druid的配置文件和连接、关闭改为工具类
工具类
public class JDBCUtilsByDruid {private static DataSource ds;//在静态代码块完成ds初始化static {Properties properties = new Properties();try {properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\druid.properties"));ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//编写getConnection方法public static Connection getConnection(){try {return ds.getConnection();} catch (SQLException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}//关闭连接,强调:在数据库连接池技术中,close不是真正的断掉连接//而是把使用的Connection对象放回连接池public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement,Connection connection){//判断是否为nulltry {if(resultSet != null){resultSet.close();}if(statement != null){statement.close();}if(connection != null){connection.close();}} catch (SQLException e) {//将编译异常转成运行异常抛出throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
工具类总结:
工具类必要项——静态代码块:配置文件读取和创建数据源
多处使用的部分——静态属性:数据源(传入配置文件参数到druid的数据工厂获得一个数据源)
分离的部分——静态方法:connection( )和close( )使用工具类
//1.得到连接Connection connection = null;//2.组织sqlString sql = "select * from actor where id >= ?";//3.创建PreparedStatement对象PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;ResultSet resultSet = null;try {connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);preparedStatement.setInt(1,4);//执行,得到结果集resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();//遍历结果集while(resultSet.next()){int id = resultSet.getInt("id");String name = resultSet.getString("name");String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");Date birthday = resultSet.getDate("birthday");String cellphone = resultSet.getString("cellphone");System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + gender + "\t" + birthday + "\t" + cellphone);}} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);}
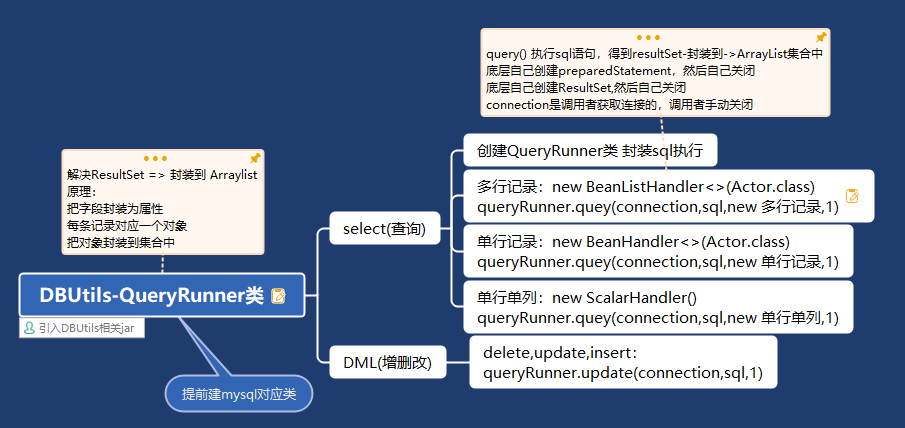
4.Apache-DBUtils-解决结果集复用和增删改查问题
4.1 分析一个问题
分析问题:
- resultSet要connectin一直处于连接状态
- 其他处不能调用ressultSet
4.2 原理图
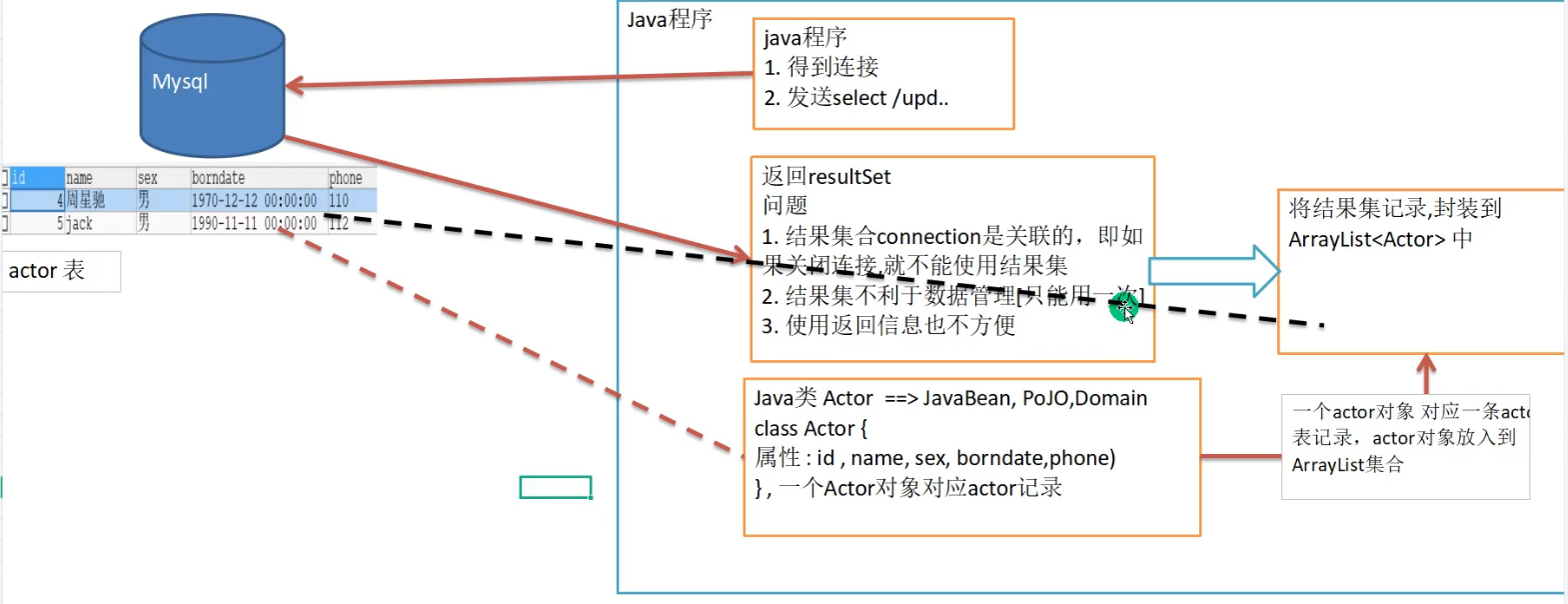
Actor类把mysql的字段封装到属性中 ```java //核心代码 //创建ArrayList对象,存放Actor ArrayListlist = new ArrayList<>();
//把得到的resultSet的记录,封装到Actor对象,放入到list集合 list.add(new Actor(id,name,gender,birthday,cellphone));
//调用者直接调用方法得mysql集合复用
public ArrayList
}
<a name="DQZUF"></a>### 封装到集合优势:1. 可复用:把字段存放=>Actor类中,然后把Actor对象=>存放到集合中 可复用1. 方法返回集合:可以把方法void改为返回集合,这样调用者可直接得到数据集合1. 依赖性变得更差:断掉connection,resultSet不影响,已经把数据封装到集合中了,集合跟连接是没有关系的<a name="wKPzd"></a>## 4.3 Apache-DBUtils<a name="I0S2d"></a>## <a name="NrRx6"></a>#### jar包[commons-dbutils-1.3.jar](https://www.yuque.com/attachments/yuque/0/2021/jar/12555714/1621837842778-2fd7d256-83c1-458f-8576-f42880595b11.jar?_lake_card=%7B%22src%22%3A%22https%3A%2F%2Fwww.yuque.com%2Fattachments%2Fyuque%2F0%2F2021%2Fjar%2F12555714%2F1621837842778-2fd7d256-83c1-458f-8576-f42880595b11.jar%22%2C%22name%22%3A%22commons-dbutils-1.3.jar%22%2C%22size%22%3A41376%2C%22type%22%3A%22%22%2C%22ext%22%3A%22jar%22%2C%22status%22%3A%22done%22%2C%22taskId%22%3A%22ud339c9ce-515a-4680-92e2-6d19946b9c8%22%2C%22taskType%22%3A%22upload%22%2C%22id%22%3A%22u7f42bd5c%22%2C%22card%22%3A%22file%22%7D)<a name="ktiD3"></a>## 4.4 课堂练习<a name="YXUCq"></a>### 代码实现:<a name="fDvNv"></a>#### 多行实现```java//演示apache-dbutils + druid完成返回结果是多行记录public void testQueryMany() throws SQLException {//返回结果是多行的情况//1.得到连接(druid)Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();//2.使用DBUtils类和接口,先引入DBUtils相关jar//3.创建QueryRunnerQueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();//4.可以执行相关的方法,返回Arraylist结果集String sql = "select * from actor where id >= ?";//说明:query()List<Actor> list =queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class), 1);for(Actor actor : list){System.out.println(actor);}JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null,null,connection);}
单行实现
//演示apache-dbutils + druid完成返回结果是单行记录(单个记录)核心代码//因为返回单个记录--->单个记录,使用Handler是BeanHandlerActor actor = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<>(Actor.class),4);//释放连接
单行单列
//演示 apache-dbutils + druid 完成查询结果是单行单列-返回就是object//核心代码//因为返回的是一个对象,使用handler就是ScalarHandlerObject obj = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler(), 4);
dml
//演示 apache-dbutils + druid 完成dml//执行相关方法,返回单个对象String sql = "update actor set name = ? where id = ?";//1.执行dml操作是queryRunner.update()//2.返回值是受影响的行数int affectRow = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, "刘德华", 8);System.out.println(affectRow > 0 ? "执行成功" : "执行没有影响到表");String sql = "insert into actor values(null,?,?,?,?)";int affectRow = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, "赵敏","女","2000-10-10","17984559847");String sql = "delete from actor where id = ?";int affectRow = queryRunner.update(connection, sql, 4);
4.5 总结说明:
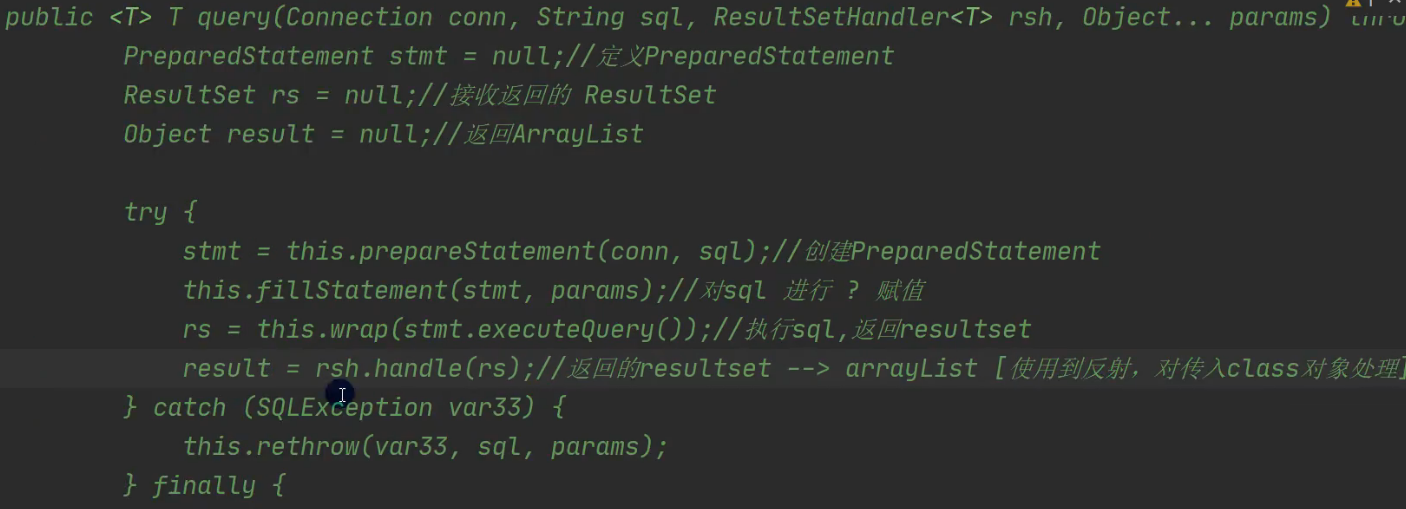
- query() 执行sql语句,得到resultSet—-封装到—->ArrayList集合中
- 返回集合
- connection:连接
- sql:执行sql语句
- new BeanListHandler<>(Actor.class):在resultSet—>Actor对象—>封装到ArrayList
底层使用反射机制去获取Actor类的属性,然后进行封装
- 1就是给sql语句中的?赋值,可以有多个值,因为是可变餐宿Object…params
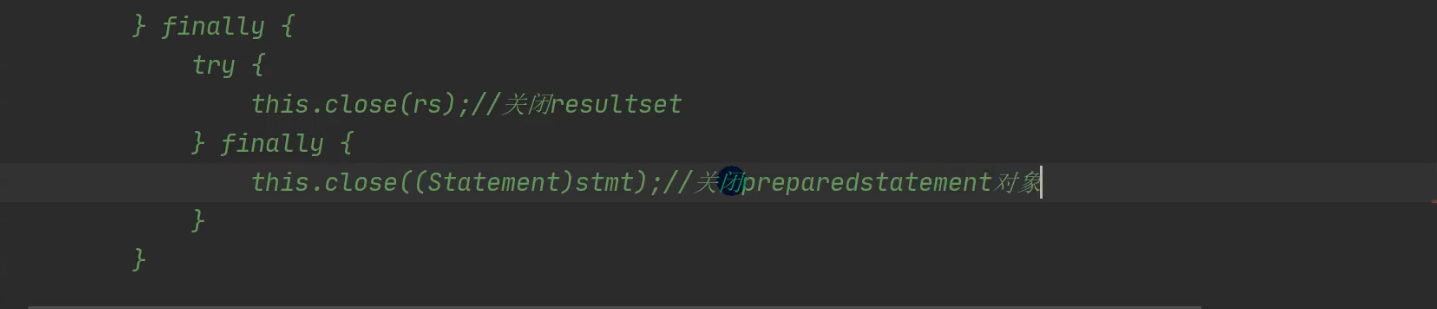
- 底层得到resultSet,会在query() 关闭,还会关闭PreparedStatement
4.6 源码分析:
4.7 表和JavaBean的类型映射关系
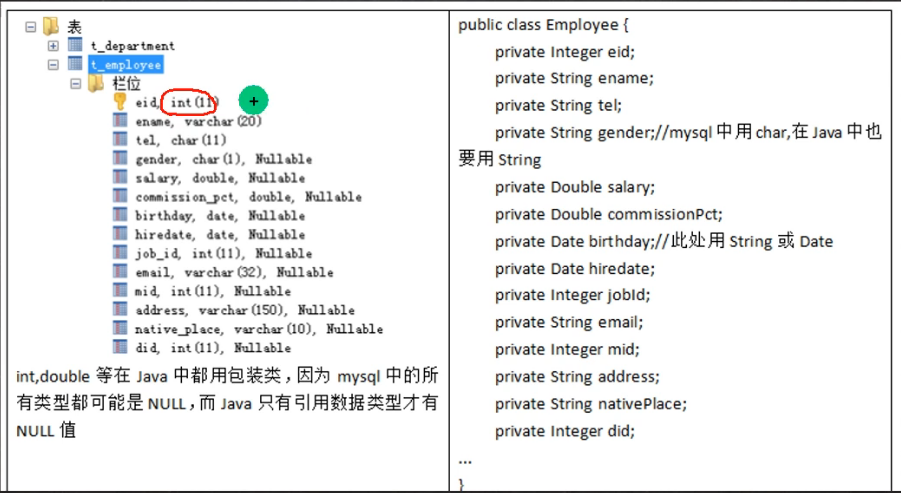
mysql列类型和java数据类型总结:
- 数值型:基本类型用包装类,因为msql的所有类型都有可能是null
- 字符串:mysql中的char,java要用String
日期型:mysql中的date,java可以用date或String
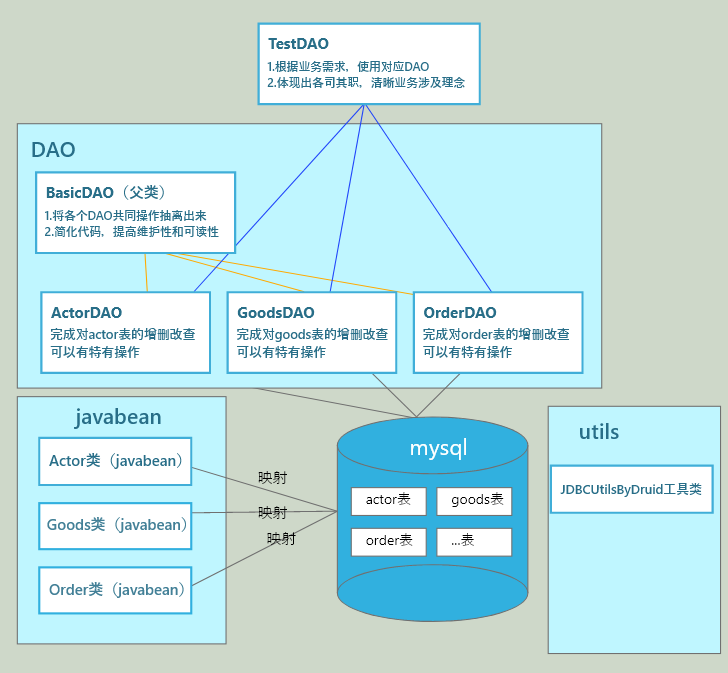
5.Dao-解决灵活使用sql
5.1 先分析一个问题
 5.2 原理图
5.2 原理图5.3 基本说明
5.4 应用实例

代码实现
utils====>JDBCUtilsByDruid apach-dbutils
javabean====>Actor
DAO====>ActorDAO继承BasicDAO,BasicDAO是其他DAO的父类,ActorDAO根据业务需求写特有的功能(演示为空)
test====>创建ActorDAO对象,因为ActorDAO继承BasicDAO,所以可以直接使用BasicDAO的增删改查BasicDAO
// apach-dbutilspublic class BasicDAO<T> {//泛型指定具体类型private QueryRunner qr = new QueryRunner();//开发通用dml方法,针对任意的表public int update(String sql,Object... params) throws Exception {Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();int rows = qr.update(connection, sql, params);return rows;JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);}//查询多行记录public List<T> queryMultiple(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object... params){Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();return qr.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<T>(clazz), params);JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);}//查询单行结果的通用方法public T querySingle(String sql,Class<T> clazz,Object... params) {Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();return qr.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<T>(clazz), params);JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);}//查询单行单列结果的通用方法public Object queryScalar(String sql,Object... params){Connection connection = JDBCUtilsByDruid.getConnection();return qr.query(connection, sql,new ScalarHandler(), params);JDBCUtilsByDruid.close(null, null, connection);}}
5.4 课后练习
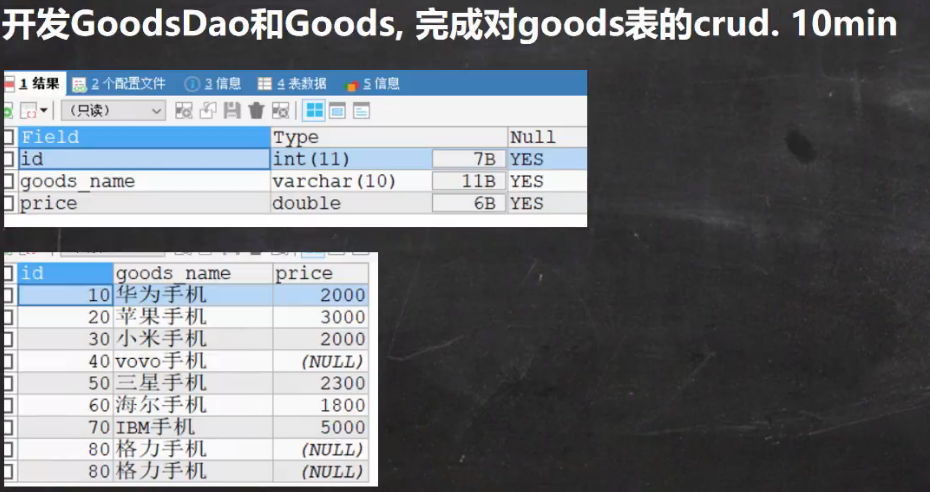
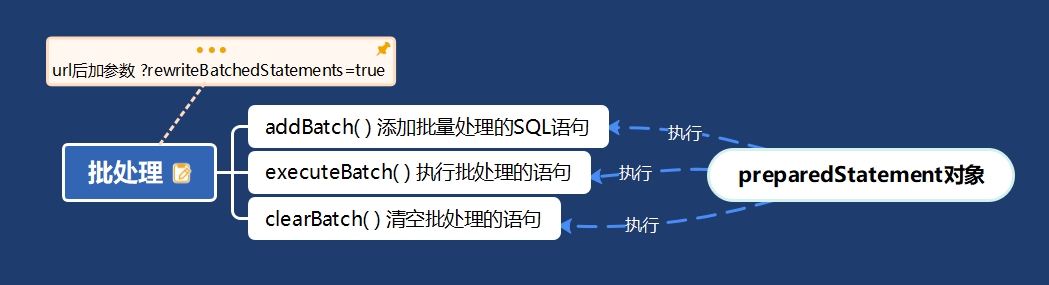
 总结两个问题:
总结两个问题: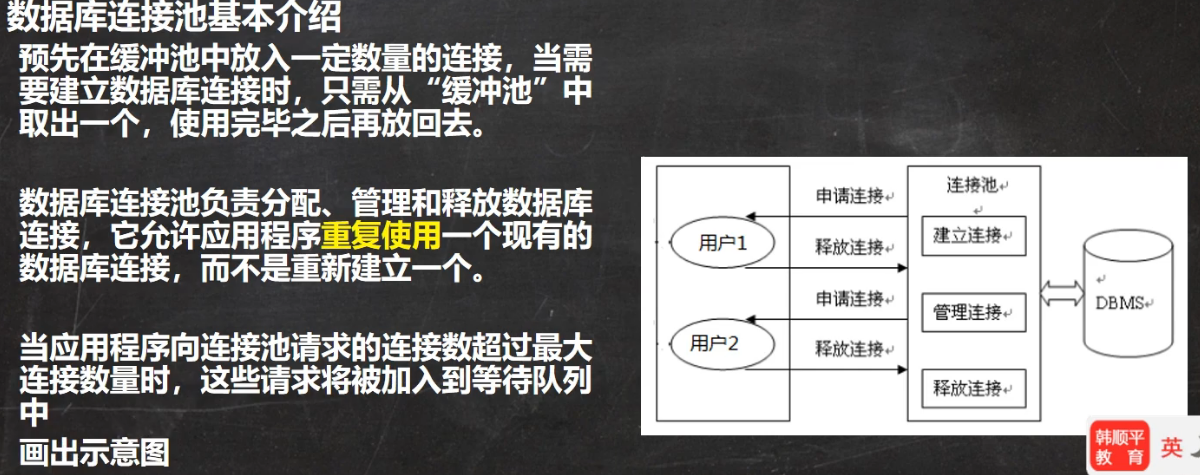 连接池总结:
连接池总结: